- 4-Aminophenol
-
4-Aminophenol 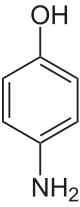
 4-Aminophenol
4-AminophenolIdentifiers CAS number 123-30-8 
PubChem 403 ChemSpider 392 
UNII R7P8FRP05V 
KEGG C02372 
MeSH Aminophenols ChEBI CHEBI:17602 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1142 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- Oc1ccc(N)cc1
c1cc(ccc1N)O
Properties Molecular formula C6H7NO Molar mass 109.13 g/mol Density 1.13 g/cm3 Melting point 188–190 °C
Boiling point 284 °C
Solubility in water 1.5 g/100 ml (25 °C) Hazards EU Index 616-003-00-0 EU classification Carc. Cat. 2
Muta. Cat. 2
Repr. Cat. 3
Toxic (T)R-phrases R20/21, R22, R40
R52, R54, R68S-phrases S28, S36, S37
S60, S61NFPA 704 Flash point 195 °C Related compounds Related aminophenols 2-Aminophenol
3-AminophenolRelated compounds Aniline
Phenol (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 4-Aminophenol is the organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4OH. Typically available as a white powder,[1] it is commonly used as a developer in black-and-white film, marketed under the name Rodinal.
Reflecting its slight hydrophilic character, the white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallised from hot water. In the presence of base, it oxidizes readily. The N-methyl and N,N-dimethyl derivatives are of commercial value.
The compound is one of three isomeric aminophenols, the other two being 2-aminophenol and 3-aminophenol.
Contents
Preparation
It is produced from phenol by nitration followed by reduction with iron. Alternatively, the partial hydrogenation of nitrobenzene affords phenylhydroxylamine, which rearranges primarily to 4-aminophenol:[2]
- C6H5NO2 + 2 H2 → C6H5NHOH + H2O
- C6H5NHOH → HOC6H4NH2
Uses
p-Aminophenol is a building block compound. Prominently, it is the final intermediate in the industrial synthesis of paracetamol. Treating p-aminophenol with acetic anhydride gives paracetamol:[3][4][5]
References
- ^ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 65th Ed.
- ^ Mitchell, S.C. & Waring, R.H. “Aminophenols.” In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; 2002 Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_099
- ^ Ellis, Frank (2002). Paracetamol: a curriculum resource. Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 0-85404-375-6.
- ^ Anthony S. Travis (2007). "Manufacture and uses of the anilines: A vast array of processes and products". In Zvi Rappoport. The chemistry of Anilines Part 1. Wiley. p. 764. ISBN 978-0-470-87171-3.
- ^ Elmar Friderichs, Thomas Christoph, Helmut Buschmann (2005), "Analgesics and Antipyretics", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_269.pub2
Categories:- Phenols
- Anilines
- Oc1ccc(N)cc1
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


