- 1926 Nassau hurricane
-
Nassau Hurricane of 1926 Category 4 hurricane (SSHS) Formed July 22, 1926 Dissipated August 2, 1926 Highest winds 1-minute sustained:
140 mph (220 km/h)Lowest pressure ≤ 975 mbar (hPa; 28.79 inHg) Fatalities 287 direct Damage $7.85 million (1926 USD) Areas affected Lesser Antilles, Puerto Rico, Hispaniola, Bahamas, Florida, Southeastern United States Part of the 1926 Atlantic hurricane season The Nassau Hurricane of 1926,[1] also known as the Bahamas-Florida Hurricane of July 1926 and Hurricane San Liborio, was a destructive Category 4 hurricane that affected the Bahamas at peak intensity. Although it weakened considerably before its Florida landfall, it was reported as one of the most severe storms to affect Nassau in the Bahamas in several years until the 1928 Okeechobee Hurricane, which occurred just two years later. The storm also delivered flooding rains and loss of crops to the southeastern United States and Florida.
Contents
Meteorological history
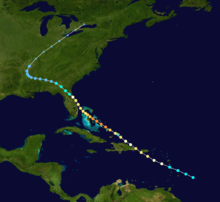
The system was first spotted east of the Lesser Antilles as a tropical disturbance on July 22. Moving northwest, the tropical storm passed near Dominica with moderate intensity, then passed just south of Puerto Rico on July 23 with a gradual increase in intensity. San Juan, Puerto Rico, recorded maximum winds of around 66 mph (105 km/h) and a low barometric pressure of 1005 mbar as the storm's center passed near the extreme southwest corner of Puerto Rico.[2] The storm continued northwest and tracked over Hispaniola while strengthening to hurricane status. The storm continued strengthening, and by the time it reached the central Bahamas, it was at full Category 4 intensity with 140 mph (225 km/h) winds. On July 26, while still moving northwest, the storm's eye passed directly over Nassau,[3] where winds were unofficially estimated at 135 mph (220 km/h) and heavy damage was reported.[1] Moving slowly, the storm weakened while sliding up the Florida coast, making final landfall near Melbourne, Florida, on July 27 as a Category 2 hurricane.[4] In Florida, the storm's lowest barometric pressure of 975 mbar was observed.
The storm weakened rapidly as it moved inland, weakening to a tropical storm and eventually a depression as it moved across Georgia and Alabama while dumping heavy rains, resulting in serious flooding. It continued across the southeastern United States while losing tropical characteristics, gradually beginning to curve northeastward over Arkansas, Missouri, and the Ohio Valley, becoming extratropical on August 1.[5] It finally dissipated the following day as it moved northeastward over Lake Ontario.[6]
Impact
More than 287 people were killed in Puerto Rico, the Dominican Republic, Bahamas, and Florida by the storm.[5]
Puerto Rico
The storm initially caused little damage until it passed near Puerto Rico, where heavy crop damage, most notably to coffee plantations in the west-central region of the island, occurred. Heavy rainfall of around 6.18 inches occurred on the island, while the average rainfall reported for July was 6.50 inches. Around 25 lives were lost when heavy floods resulted from rapid rise of rivers. Total losses in Puerto Rico were estimated at $2.350 million dollars.[2]
Hispaniola
Estimated damage amounted to around $3 million in eastern Santo Domingo as the storm center passed over the eastern half of the island.[2]
Bahamas
Although damage reports are not clear, the storm was reported to be destructive around Nassau, where "some roofs were torn off entirely" and that the storm was "more fearful and devastating than any most people can remember", according to an eyewitness account posted in the July issue of the Monthly Weather Review. Trees, power poles, and various debris littered streets, and many people were left homeless. Automobiles at Nassau were also reported damaged by the storm, and flooding was reported.[1] The hurricane also caused heavy damage nearby on Eleuthera and Andros, as well as in the Exumas.
Florida
The storm was also reported to have caused damage around the point of landfall in Melbourne, Florida, where uprooted citrus trees and roofs blown off were reported. An observer on Merritt Island reported a heavy storm surge along the Indian River which damaged or destroyed homes, docks, and boats.
Points further south along the Florida coast, such as Miami, received only a brush from the storm, resulting in rains and some light wind damage.[7] Flooding was also experienced at points such as Palm Beach.[8] Damage estimates in Florida exceeded $2.5 million.
Records
Prior to the record-breaking 2005 Atlantic hurricane season, this was the most intense hurricane ever recorded in July (with 140 mph winds) until Hurricane Emily of 2005, a Category 5 hurricane which had top sustained winds of 160 mph (260 km/h) and a pressure of 929 millibars,[9] surpassed the intensity of the July 1926 hurricane. Hurricane Dennis, also from 2005, was also still more intense in barometric pressure and wind strength than the hurricane of July 1926.[10] Note that Hurricane Audrey was also more intense and occurred even earlier in the season in June.
See also
References
- ^ a b c Nassau Guardian (1926). "The Nassau Hurricane, July 25–26, 1926". U.S. Weather Bureau. http://docs.lib.noaa.gov/rescue/mwr/054/mwr-054-07-0296.pdf. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ^ a b c Charles L. Mitchell (1926). "Storms and Weather Warnings". U.S. Weather Bureau. http://docs.lib.noaa.gov/rescue/mwr/054/mwr-054-07-0312.pdf. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ^ Nassau Bahamas Hurricanes
- ^ Blake, Rappaport, and Landsea (2006). "The Deadliest, Costliest, and Most Intense United States Tropical Cyclones (1851 to 2006)". NOAA. http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/pdf/NWS-TPC-5.pdf. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ^ a b Jay Barnes on Hurricanes | Florida's Hurricane History
- ^ http://weather.unisys.com/hurricane/atlantic/1926/1/track.gif
- ^ The American Experience | Mr. Miami Beach | People & Events | The Hurricane of 1926
- ^ http://www.co.palm-beach.fl.us/pubsafety/eoc/floodawareness/main/primary_flood_events.htm
- ^ http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/pdf/TCR-AL052005_Emily.pdf
- ^ Hurricane Emily Becomes Most Powerful July Hurricane Ever-8/10/05
External links
Categories:- 1926 Atlantic hurricane season
- Category 4 Atlantic hurricanes
- Hurricanes in the Bahamas
- Hurricane articles needing attention
- 1926 in the Bahamas
- Nassau, Bahamas
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.