- Arachidonoyl serotonin
-
Arachidonoyl serotonin 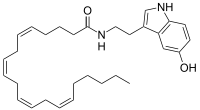 (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-N-(2-(5-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenamideOther namesN-arachidonoyl-serotonin
(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-N-(2-(5-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenamideOther namesN-arachidonoyl-serotoninIdentifiers CAS number 187947-37-1 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(CCC/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\CCCCC)NCCC1=CNC2=C1C=C(O)C=C2
Properties Molecular formula C30H42N2O2 Molar mass 462.67 g mol−1 Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Arachidonoyl serotonin (N-arachidonoyl-serotonin, AA-5-HT) is an endogenous lipid signaling molecule. It was first described in 1998 as being an inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).[1] In 2007, it was shown to have analgesic properties and to act as an antagonist of the TRPV1 receptor.[2] In 2011, it was shown to be present in the ileum and jejunum of the gastrointestinal tract and modulate glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion.[3]
References
- ^ Bisogno, T.; Melck, D.; De Petrocellis, L.; Bobrov, M. U.; Gretskaya, N. M.; Bezuglov, V. V.; Sitachitta, N.; Gerwick, W. H. et al. (1998). "Arachidonoylserotonin and other novel inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase". Biochemical and biophysical research communications 248 (3): 515–522. PMID 9703957.
- ^ Maione, S.; Petrocellis, L.; Novellis, V.; Moriello, A. S.; Petrosino, S.; Palazzo, E.; Rossi, F. S.; Woodward, D. F. et al. (2007). "Analgesic actions of N-arachidonoyl-serotonin, a fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor with antagonistic activity at vanilloid TRPV1 receptors". British Journal of Pharmacology 150 (6): 766–781. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707145. PMC 2013858. PMID 17279090. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2013858.
- ^ Verhoeckx, K. C. M.; Voortman, T.; Balvers, M. G. J.; Hendriks, H. F. J.; m.Wortelboer, H.; Witkamp, R. F. (2011). "Presence, formation and putative biological activities of N-acyl serotonins, a novel class of fatty-acid derived mediators, in the intestinal tract". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 1811 (10): 578–586. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.07.008. PMID 21798367.
Categories:- Serotonin
- Fatty acid amides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
