- Morocco–Portugal relations
-
Portugal - Morocco relations 

Portugal
MoroccoMorocco-Portugal relations cover a period of several centuries to the present. Initial contacts started in the 8th century, when Muslim forces invaded most of the territory of the Iberian peninsula. After the Reconquista, Portugal would then expand into Africa, starting with the territory of Morocco, by occupying cities and establishing fortified outposts along the Moroccan coast.
Contents
Islamic invasions
Battles in Iberia
Ourique – 1st Santarém – Lisbon – 2nd Santarém Las Navas de Tolosa – Salado
Battles in Morocco
Ceuta –1st Tangier – Asilah – Azemmour – Agadir – Ksar El KebirFirst contacts (8th century)
Following the invasion of southern Spain from the coast of Morocco by the Berber Commander Tariq ibn Ziyad in 711, during the 8th century Arab and Berber armies invaded Iberia, and even went beyond to Southern France, and as far as Poitiers and the Rhône valley until the turning point of the Battle of Tours in 732.[1]
Portugal would again become affected by the expansion of the Moroccan Almoravid Empire in the 11th and 12th centuries.[2]
The Portuguese managed to recapture Lisbon in the 1147 Siege of Lisbon.
Portuguese expansion (1415-1769)
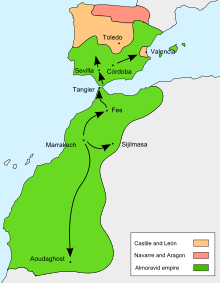
Portugal started to occupy parts of coastal Morocco from 1415 with the occupation of Ceuta. Then under Afonso V of Portugal, Portugal conquered Alcácer Ceguer (1458), Tangiers (won and lost several times between 1460 and 1464) and Arzila (1471). This achievements granted the king the nickname of the African.
Portugal and Spain had passed an agreement in 1496 in which they effectively established their zones on influence on the North African coast: Spain could only occupy territory east of Peñon de Velez. This restriction would only end with the absorption of Portugal into the Spanish crown of Philip II after the 1578 Battle of Ksar El Kebir, when Spain started to take direct actions in Morocco, as in the occupation of Larache.[3]
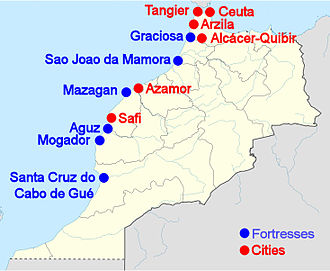
Altogether, the Portuguese are documented to have seized 6 Moroccan cities and built 6 stand-alone fortresses on the Moroccan Atlantic coast, between the river Loukos in the north and the river of Sous in the south.
The 6 cities were: Ceuta (1415-1668), Tangier (1471-1661), Arzila (1471-1549), Alcácer-Ceguer (1458–1550), Azamor (1513-1541) and Safi (1488-1541).
Moroccan reconquest
Of the 6 stand-alone fortresses, four of them only had a short duration: Graciosa (1489), São João da Mamora (1515), Castelo Real of Mogador (1506-10) and Aguz (1520-25). Two of them were to become permanent urban settlements: Santa Cruz do Cabo de Gué (Agadir, founded in 1505-06), and Mazagan founded in 1514-17.[4]
The Portuguese had to abandon most of their settlements between 1541 and 1550 following the offensives of Mohammed ash-Sheikh, particularly the Fall of Agadir in 1541 and the Conquest of Fez in 1550. Nevertheless, they were able to keep a few bases: Ceuta (1415-1668), Tangier (1471-1661) and Mazagan (1502-1769).[4]
The Battle of Ksar El Kebir in 1578 was a landslide event, as the Portuguese king Sebastian of Portugal was killed in the encounter and his army eliminated by Moroccan forces in alliance with the Ottoman Empire. This ultimately led to the loss of independence of Portugal, and its absorption by Spain.
Tangier was ceeded to England in 1661 in order to encourage England to support Portugal's independence, and Ceuta was finally handed over to Spain in 1668 through the Treaty of Lisbon, which finally recognized the independence of Portugal and confirmed the repossession of Portugal's remaining overseas colonies. These events essentially ended Portugal's direct involvement in Morocco, until they abandoned Mazagan under the pressure of Mohammed ben Abdallah in 1769.
Notes
- ^ Tricolor and crescent: France and the Islamic world by William E. Watson p.1
- ^ Reconquest and crusade in medieval Spain by Joseph F. O'Callaghan p.31
- ^ The last great Muslim empires: history of the Muslim world by Frank Ronald Charles Bagley, Hans Joachim Kissling p.103ff
- ^ a b City walls: the urban enceinte in global perspective James D. Tracy p.352
 Foreign relations of Portugal
Foreign relations of PortugalEurope 
Elsewhere Angola · Armenia · Brazil · China · East Timor · India · Morocco · Mozambique · São Tomé and Príncipe · United StatesMissions  Foreign relations of Morocco
Foreign relations of MoroccoAfrica 
Americas Asia Europe Bulgaria · European Union · France · Greece · Netherlands · Norway · Portugal · Russia · Spain · Turkey · United KingdomWestern Sahara conflict Related topics Moroccan Ministry of Foreign Affairs Categories:- Bilateral relations of Morocco
- Bilateral relations of Portugal
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.