- Dimethyl disulfide
-
Dimethyl disulfide 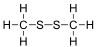
 (Methyldisulfanyl)methaneOther namesDimethyl disulphide; Methyl disulfide; Methyldisulfide; Dimethyldisulfide; Methyldithiomethane; 2,3-Dithiabutane
(Methyldisulfanyl)methaneOther namesDimethyl disulphide; Methyl disulfide; Methyldisulfide; Dimethyldisulfide; Methyldithiomethane; 2,3-DithiabutaneIdentifiers Abbreviations DMDS CAS number 624-92-0 
PubChem 12232 ChemSpider 11731 
ChEBI CHEBI:4608 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - S(SC)C
Properties Molecular formula C2H6S2 Molar mass 94.2 g mol−1 Appearance Colorless to yellowish liquid[1] Density 1.06 g/cm3[1] Melting point -85 °C, 188 K, -121 °F ([1])
Boiling point 110 °C, 383 K, 230 °F ([1])
Solubility in water 2.5 g/L (20 °C)[1] Hazards Flash point 15 °C (59 °F)[1] Autoignition
temperature370 °C (698 °F)[1] LD50 190 mg/kg (oral, rat)[2]  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dimethyl disulfide (DMDS) is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula CH3SSCH3 which is the simplest disulfide. It is a flammable liquid with an unpleasant odor.
DMDS can be produced by the reaction of methanethiol with sulfur:
- 2 CH3SH + S → CH3SSCH3 + H2S
Uses
DMDS is used as a food additive in onion, garlic, cheese, meats, soups, savory flavors, and fruit flavors.[2]
Industrially, DMDS is used in oil refineries as a sulfiding agent.[3]
References
Categories:- Organic disulfides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
