- dBm
-
For other uses, see DBM (disambiguation).
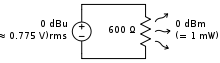 A schematic showing the relationship between dBu (the voltage source) and dBm (the power dissipated as heat by the 600 Ω resistor)
A schematic showing the relationship between dBu (the voltage source) and dBm (the power dissipated as heat by the 600 Ω resistor)
dBm (sometimes dBmW) is an abbreviation for the power ratio in decibels (dB) of the measured power referenced to one milliwatt (mW). It is used in radio, microwave and fiber optic networks as a convenient measure of absolute power because of its capability to express both very large and very small values in a short form. Compare dBW, which is referenced to one watt (1000 mW).
Since it is referenced to the watt, it is an absolute unit, used when measuring absolute power. By comparison, the decibel (dB) is a dimensionless unit, used for quantifying the ratio between two values, such as signal-to-noise ratio.
Contents
Unit conversions
Zero dBm equals one milliwatt. A 3 dB increase represents roughly doubling the power, which means that 3 dBm equals roughly 2 mW. For a 3 dB decrease, the power is reduced by about one half, making −3 dBm equal to about 0.5 milliwatt. To express an arbitrary power P as x dBm, or vice versa, the following equations may be used:
 or,
or, 
and
 or,
or, 
where P is the power in W and x is the power ratio in dBm. Below is a table summarizing useful cases:
dBm level Power Notes 80 dBm 100 kW Typical transmission power of FM radio station with 50-kilometre (31 mi) range 60 dBm 1 kW = 1000 W Typical combined radiated RF power of microwave oven elements Maximum RF output power from a ham radio transceiver allowed without special permission
50 dBm 100 W Typical thermal radiation emitted by a human body Typical maximum output RF power from a ham radio HF transceiver
40 dBm 10 W Typical PLC (Power Line Carrier) Transmit Power 37 dBm 5 W Typical maximum output RF power from a handheld ham radio VHF/UHF transceiver 36 dBm 4 W Typical maximum output power for a Citizens' band radio station (27 MHz) in many countries 33 dBm 2 W Maximum output from a UMTS/3G mobile phone (Power class 1 mobiles) Maximum output from a GSM850/900 mobile phone
30 dBm 1 W = 1000 mW Typical RF leakage from a microwave oven - Maximum output power for DCS 1800 MHz mobile phone Maximum output from a GSM1800/1900 mobile phone
27 dBm 500 mW Typical cellular phone transmission power Maximum output from a UMTS/3G mobile phone (Power class 2 mobiles)
26 dBm 400 mW Access point for Wireless networking 25 dBm 316 mW 24 dBm 250 mW Maximum output from a UMTS/3G mobile phone (Power class 3 mobiles) 23 dBm 200 mW Maximum output in interior environment from a WiFi 2.4Ghz antenna (802.11b/g/n). 22 dBm 160 mW 21 dBm 125 mW Maximum output from a UMTS/3G mobile phone (Power class 4 mobiles) 20 dBm 100 mW Bluetooth Class 1 radio, 100 m range Maximum output power from unlicensed AM transmitter per U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) rules 15.219.[1] Typical wireless router transmission power.
15 dBm 32 mW Typical WiFi transmission power in laptops. 10 dBm 10 mW 6 dBm 4.0 mW 5 dBm 3.2 mW 4 dBm 2.5 mW Bluetooth Class 2 radio, 10 m range 3 dBm 2.0 mW More precisely (to 8 decimal places) 1.9952623 mW 2 dBm 1.6 mW 1 dBm 1.3 mW 0 dBm 1.0 mW = 1000 µW Bluetooth standard (Class 3) radio, 1 m range −1 dBm 794 µW −3 dBm 501 µW −5 dBm 316 µW −10 dBm 100 µW Typical maximum received signal power (−10 to −30 dBm) of wireless network −20 dBm 10 µW −30 dBm 1.0 µW = 1000 nW −40 dBm 100 nW −50 dBm 10 nW −60 dBm 1.0 nW = 1000 pW The Earth receives one nanowatt per square metre from a magnitude +3.5 star[2] −70 dBm 100 pW Typical range (−60 to −80 dBm) of wireless received signal power over a network (802.11 variants) −73 dBm 50.12 pW "S9" signal strength, a strong signal, on the S-meter of a typical ham or shortwave radio receiver −80 dBm 10 pW −100 dBm 0.1 pW −111 dBm 0.008 pW = 8 fW Thermal noise floor for commercial GPS single channel signal bandwidth (2 MHz) −127.5 dBm 0.178 fW = 178 aW Typical received signal power from a GPS satellite −174 dBm 0.004 aW = 4 zW Thermal noise floor for 1 Hz bandwidth at room temperature (20 °C) −192.5 dBm 0.056 zW = 56 yW Thermal noise floor for 1 Hz bandwidth in outer space (4 kelvins) −∞ dBm 0 W Zero power is not well-expressed in dBm (value is negative infinity) The signal intensity (power per unit area) can be converted to received signal power by multiplying by the square of the wavelength and dividing by 4π (see Free-space path loss).
In United States Department of Defense practice, unweighted measurement is normally understood, applicable to a certain bandwidth, which must be stated or implied.
In European practice, psophometric weighting may be, as indicated by context, equivalent to dBm0p, which is preferred.
The dBm is not a part of the International System of Units and therefore is discouraged from use in documents or systems that adhere to SI units (the corresponding SI unit is the watt). However the straight decibel (dB), being a unitless ratio of two numbers, is perfectly acceptable.[3]
Expression in dBm is typically used for optical and electrical power measurements, not for other types of power (such as thermal). A listing by power levels in watts is available that includes a variety of examples not necessarily related to electrical or optical power.
See also
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C" (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C" (in support of MIL-STD-188).External links
decibel units (dB) Categories:- Units of measure
- Radio frequency propagation
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
