- cis-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride
-
cis-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride 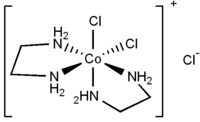
Identifiers CAS number 14040-32-5 PubChem 407212 ChemSpider 360279 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - Cl[Co]Cl.[NH-]CC[NH-].[NH-]CC[NH-]
Properties Molecular formula C4H16Cl3CoN4 Appearance violet solid Melting point dec.
Solubility in water good Hazards R-phrases R36/37/38 S-phrases S26 S36  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references cis-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is an organic compound with formula [CoCl2(en)2]Cl (en = ethylenediamine). It is a violet diamagnetic solid that is soluble in water. One chloride ion in this salt readily undergoes ion exchange but the two other chlorides are less reactive, being bound to the metal center.
Contents
Synthesis
Cis-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is obtained by heating trans-[CoCl2(en)2]Cl e.g. using a steam bath. The trans isomer is in turn synthesized by the reaction of cobalt chloride and ethylenediamine in hydrochloric acid in the presence of oxygen:
- 4 CoCl2 + 8 en + 4 HCl + O2 → 4 trans-[CoCl2(en)2]Cl + 2 H2O
The initial product contains HCl, which is removed by heating. Alternatively, (carbonato)bis(ethylenediamine)cobalt (III) chloride reacts with hydrochloric acid at 10 °C to give the same species.[1]
- [Co(CO3)en2)]Cl + 2 HCl → trans-[CoCl2(en)2]Cl + CO2 + H2O
Optical resolution
The cis isomer is formed as a racemate, which can be resolved into two enantiomers (Λ and Δ) by the formation of the d-α-bromocamphor-π-sulfonate salt. The diastereomeric salts are separated by recrystallization. After their purification, the individual diastereomers are converted back to the chloride salt by reaction with ice cold hydrochloric acid.[2]
Comparison of cis and trans isomers
This salt is less soluble than the dull-green isomeric trans-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride (CAS#14040-33-6). This pair of isomers were significant in the development of the area of coordination chemistry.[3] The chiral cis isomer can be obtained by heating the trans isomer. Both isomers of dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride have often used in stereochemical studies and as intermediates (like Tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride) for the preparation of other cobalt salt complexes.
Properties of the trans isomer
Crystallographic analysis shows that the trans isomer has the following bond distances: Co-N: 1.99, Co-Cl: 2.22, C-N: 1.47, C-C 1.54 Å.[4] The trans isomer cation has idealized D2h point group symmetry, whereas the cis isomer cation has C2 symmetry.
References
- ^ Springbørg, J.; Schaffer, C.E. “Dianionobis(Ethylenediamine)Cobalt (III) Complexes” Inorganic Synthesis, 1973; volume 14, pages 63-77. doi:10.1002/9780470132456.ch14
- ^ Bailar, J.C. “Cis- and Trans-Dichlorobis-(Ethylenediamine) Cobalt (III) Chloride and the Resolution of the Cis Form”. Inorganic Synthesis, 1946, volume 2, pages 222-225. doi:10.1002/9780470132333.ch71
- ^ Jörgensen, S.M. “Ueber Metalldiaminverbindungen“ J. prakt. Chem., 1889, volume 39, page 8. doi:10.1002/prac.18890390101
- ^ Sharma, R. J.; Sharma, R.; Bala, R; Salas, J. M.; Quiros, M. “Second sphere coordination complexes via hydrogen bonding: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterisation of [trans-Co(en)2Cl2]CdX4 (X=Br or I) and single crystal X-ray structure determination of [trans-Co(en)2Cl2]CdBr4” Journal of Molecular Structure, 2006, volume 794, pages 342-344. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2006.02.053
Categories:- Cobalt compounds
- Chlorides
- Metal halides
- Coordination compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.