- Cynaroside
-
Cynaroside 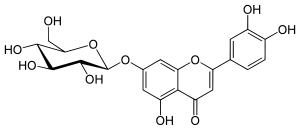 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-oneOther namesGlucoluteolin
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-oneOther namesGlucoluteolin
Luteoloside
Cinaroside
7-Glucoluteolin
7-Glucosylluteolin
Luteolin 7-glucoside
Luteolin-7-glucoside
Luteolin 7-O-glucoside
Luteolin-7-O-glucosideIdentifiers CAS number 68321-11-9 PubChem 5280637 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C1=CC(=C(C=C1C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O)O)O)O
Properties Molecular formula C21H20O11 Molar mass 448.37 g/mol Exact mass 448.100561 Appearance Yellow amorphous powder Melting point 266–268ºC
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cynaroside is a flavone, a flavonoid-like chemical compound. It is a 7-O-glucoside of luteolin and can be found in dandelion coffee, in Ferula varia and F. foetida[1] in Campanula persicifolia and C. rotundifolia[2], in the bamboo Phyllostachys nigra[3] and in Cynara scolymus (artichoke)[4].
Metabolism
Flavone 7-O-beta-glucosyltransferase adds a glucose to luteolin.
A cynaroside 7-O-glucosidase has been identified in the artichoke[4].
Spectral datas
UV-Vis Lambda-max UV : 348, 260 nm Extinction coefficient (log ε): 4.11, 4.23 IR Major absorption bands ? cm−1 NMR Proton NMR 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CD3COCD3 + D2O):
δ 3.42 (1H, t, J = 9.0 Hz, H-4′), 3.49
(1H, t, J = 9.0 Hz, H-2″), 3.56
(1H, t, J = 9.0 Hz, H-3″), 3.60 (1H, m, H-5″)
, 3.68 (1H, dd, J = 12.2, 5.6 Hz, H-6a″),
3.85 (1H, dd, J = 12.2, 1.8 Hz, H-6b″),
5.10 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1″), 6.44
(1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz, H-6), 6.63 (1H, s, H-3),
6.83 (1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz, H-8), 6.95
(1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-5′), 7.41
(1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-6′), 7.43 (1H, bs, H-2′)Carbon-13 NMR 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CD3COCD3 + D2O):
δ 61.7 (C-6″), 70.3 (C-4″), 73.8 (C-2″),
76.8 (C-3″), 77.4 (C-5″), 95.8 (C-8), 100.5
(C-6), 100.7 (C-1″), 103.7 (C-3), 106.3 (C-10),
113.8 (C-2″), 116.5 (C-5′), 120.3 (C-6′),
122.6 (C-1′), 146.3(C-3′), 150.4 (C-4′),
158.0 (C-9), 161.8 (C-5), 163.9 (C-7),
165.8(C-2), 183.1 (C-4)Other NMR data MS Masses of
main fragmentsESI-MS [M+H]+ m/z 449.1 Reference[5]
References
- ^ Cynaroside content of the plants Ferula varia and F. foetida, M. P. Yuldashev, 1997
- ^ Cynaroside and luteolin from Campanula persicifolia and C. rotundifolia, L. S. Teslov and S. V. Teslov, 1971
- ^ Evaluation of antioxidant and prooxidant activities of bamboo Phyllostachys nigra var. Henonis leaf extract in vitro. Hu C, Zhang Y, Kitts DD. J Agric Food Chem. 2000 Aug;48(8):3170-6.
- ^ a b Purification and characterization of a cynaroside 7-O-β-D-Glucosidase from Cynarae scolymi folium, B. Nüβlein, W. Kreis
- ^ Neural cell protective compounds isolated from Phoenix hanceana var. formosana. Yi-Pei Lin, Tai-Yuan Chen, Hsiang-Wen Tseng, Mei-Hsien Lee and Shui-Tein Chen, Phytochemistry, Volume 70, Issue 9, June 2009, Pages 1173-1181
Flavones O-methylated flavones Acacetin | Diosmetin | Eupatilin | Genkwanin | Nepetin | Nobiletin | Oroxylin A | Sinensetin | Tangeritin | Techtochrysin | Tricin | WogoninGlycosides acetylated Artoindonesianin PSynthetic This article about a natural phenol is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
