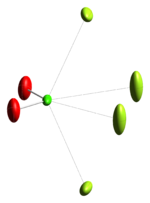- Chloryl
-
Chloryl 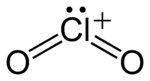
 ChlorylSystematic nameDioxo-λ5-chloranylium
ChlorylSystematic nameDioxo-λ5-chloranyliumIdentifiers CAS number 25052-55-5 ChemSpider 19127824 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=[Cl+]=O
- InChI=1S/ClO2/c2-1-3/q+1
Key: UVQYMEMTCMFUIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references In chemistry, chloryl refers to the red-colored cation having the chemical formula ClO+
2. It is polyatomic ion, structurally identical to chlorite and having the same chemical formula but with chlorine in the +5 oxidation state rather than +3. In chloryl, the two oxygen atoms oxidize the central chlorine atom, forming one double covalent bond each, and another elmement or ion oxidizes the chlorine further, leaving the chlorine with one electron pair. (In chlorite, one oxygen atom forms a double covalent bond with the central chlorine atom, and another oxygen atom forms a single bond with the chlorine atom and an ionic bond, or, more rarely, another single covalent bond). Chloryl is isoelectronic with sulfur dioxide.[1]. Chloryl compounds, such as FClO2 and [ClO2][RuF6] are all highly reactive, and react violently with water and most organic compounds.[2][3]Structure
The ClO+
2 cation is isoelectronic with SO2,[1] and has a bent structure with a bond angle close to 120°. The bond-stretching force constant for its bonds indicate that the Cl–O bond has double bond character.[4]The red color of ClO+
2 is caused by electron transitions into an antibonding orbital. The analogous transition in SO2 is not in the visible spectrum, so SO2 is colorless. The strength of interaction with the counterion affects the energy of this antibonding orbital; thus, in colorless chloryl compounds, strong interactions with the counterion, corresponding with the higher covalent character of the bonding, shift the transition energy out of the visible spectrum.[1]Compounds
There are two categories of chloryl compounds. The first category is colorless, and includes chloryl fluoride (FClO2). These are moderately reactive. Although named as an ionic "chloryl" compound, chloryl fluoride is more a covalent compound than an ionic compound of fluoride and cloryl cation.
The second category features red-colored compounds that are highly reactive. These include chloryl fluorosulfate, ClO2SO3F, and dichloryl trisulfate, (ClO2)2(S3O10). These chloryl compounds form red solutions in fluorosulfuric acid, and do contain a red-colored ClO+
2 cation which dissociates in solution. In the solid state, the Raman and infrared spectra indicate strong interactions with the counterion.[1][2] Not all chloryl compounds in the solid state are necessarily ionic. The reaction products of FClO2 with BF3 and PF5 are assumed to be molecular adducts rather than true salts.[1][4]One notable chloryl compound is dichlorine hexoxide, which exists as an ionic compound more accurately described as chloryl perchlorate, [ClO2]+[ClO4]−.[5] It is a red fuming liquid under standard conditions.
Chloryl compounds are best prepared by the reaction of FClO2 with a strong Lewis acid. For example:[4]
- FClO2 + AsF5 → [ClO2][AsF6]
Other synthesis routes are also possible, including:[4]
- 5 ClO2 + 3 AsF5 → 2 [ClO2][AsF6] + AsF3O + 4 Cl2
- Cl2O4 + 2 SbF5 → [ClO2][SbF6] + SbF3O + FClO3
Metathesis reactions may be carried out with strong Lewis bases. For example, the reaction of the hexafluoroplatinate salt with nitryl fluoride yields the nitronium salt:[4]
- [ClO2][PtF6] + FNO2 → [NO2][PtF6] + FClO2
References
- ^ a b c d e H. A. Carter; W. M. Johnson; F. Aubke (1969). "Chloryl compounds. Part II. Chloryl hexafluoroarsenate and chloryl fluoride". Canadian Journal of Chemistry 47 (24): 4619–4625. http://article.pubs.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/ppv/RPViewDoc?issn=1480-3291&volume=47&issue=24&startPage=4619.
- ^ a b Christe, K. O.; Schack, C. J.; Pilipovich, D.; Sawodny, W. (1969). "Chloryl cation, ClO+
2". Inorganic Chemistry 8 (11): 2489–2494. doi:10.1021/ic50081a050. - ^ Bougon, R.; Cicha, W. V.; Lance, M.; Meublat, L.; Nierlich, M.; Vigner, J. (1991). "Preparation characterization and crystal structure of chloryl hexafluororuthenate(1-). Crystal structure of [ClF2]+[RuF6]−". Inorganic Chemistry 30 (1): 102–109. doi:10.1021/ic00001a019.
- ^ a b c d e K. O. Christe; C. J. Schack (1976). Harry Julius Emeléus, A. G. Sharpe. ed. Chlorine Oxyfluorides. Advances in inorganic chemistry and radiochemistry, Volume 18. Academic Press. pp. 356–358. ISBN 0120236184. http://books.google.ca/books?hl=en&lr=&id=EWlBFTxYth4C&oi=fnd&pg=PA319&dq=chloryl+cation&ots=-jlVcXkz7a&sig=k5zbfE5SYGnLnSO1TXz40f7MJ1U#v=onepage&q=chloryl%20cation&f=false.
- ^ Tobias, K. M.; Jansen, M. (1986). "Crystal Structure of Cl2O6". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English 25 (11): 993–994. doi:10.1002/anie.198609931.
Categories:- Chloryl compounds
- Cations
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.