- Chesapeake (Amtrak)
-
Chesapeake Overview Service type Inter-city rail Status Transferred to SEPTA and MTA Locale Mid-Atlantic states First service 1973(First version)
1978(Second and third versions)Last service 1977(First version)
1995(Second and third versions)Successor SEPTA
MARC TrainFormer operator(s) Amtrak Route Start Washington, DC End Philadelphia Distance travelled 134 miles (216 km) Average journey time 2 hour 18 minutes Service frequency Monday through Friday Train number(s) 182 & 187 (1973-1977)
420 & 421 (1978-1995)On-board services Class(es) Unreserved coach Technical Rolling stock Amfleet coaches Gauge 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) Electrification Overhead caternary Track owner(s) Amtrak Route map Legend
Station 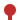
Philadelphia (SEPTA) 
Chester 
Wilmington 
Newark, DE 
Elkton 
Perryville 
Aberdeen 
Edgewood 
Baltimore Penn Station 
Edmonson Avenue (Baltimore) 
Baltimore Airport 
Odenton 
Bowie 
Beltway-Lanham 
Washington, D.C. (METRO) Chesapeake was a daily passenger train operated by Amtrak along the Northeast Corridor between Washington, D.C. and Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
The Chesapeake was originally established on April 29, 1973 as a train that ran between Washington, D.C. and New York City. This service ended on June 11, 1977, however on April 30, 1978, the name was revived for a commuter service that was financed through funding from the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the State of Maryland. Chester Transportation Center, which was closed by the Pennsylvania Railroad in either 1966 or 1967, was added to service in 1978[1] and the Baltimore-Washington International Airport railroad station was added to the service in 1980.[2]
On October 29, 1983, Maryland and Pennsylvania, along with a number of other Northeastern states, took control of its commuter railroads. SEPTA expanded to commuter railroads previously used by the Pennsylvania Railroad and Reading Railroad, and the "MARC" (Maryland Area Regional Commuter) service name was established.[3] The SEPTA R2 (now the Wilmington/Newark Line) and MARC Penn Line became the replacements for Amtrak's Chesapeake, although no service existed between Perryville and Newark. The name remained and service was extended not only back to New York City, but south into Richmond, Virginia until October 28, 1995 when it was replaced by the NortheastDirect.
Station stops (1978–1983)
The following station stops were made by Chesapeake trains; not all trains made all stops.
State City Station Notes and Connections Pennsylvania Philadelphia 30th Street Station SEPTA subway service; SEPTA Regional Rail Chester Chester Transportation Center SEPTA Wilmington/Newark Line Delaware Wilmington French Street Station SEPTA Wilmington/Newark Line Newark Newark Rail Station SEPTA Wilmington/Newark Line Maryland Elkton Elkton Perryville Perryville Now stop on Penn Line Aberdeen Aberdeen Now stop on Penn Line Edgewood Edgewood Now stop on Penn Line Baltimore Pennsylvania Station Now stop on Penn Line and Baltimore Light Rail Edmonson Avenue Station Linthicum Baltimore Airport Now stop on Penn Line Odenton Odenton Now stop on Penn Line Bowie Bowie New Carrollton Beltway-Lanham Station Metro Orange Line; now stop on Penn Line Washington, D.C Union Station Metro Red Line; MARC; various Amtrak trains References
External links
- October 1, 1979 Amtrak Chesapeake Timetable (Railroad Picture Archives)
- Inaugural Run of Amtrak's Chesapeake (Window on Cecil County's Past)
Categories:- Former Amtrak routes
- Passenger rail transportation in Washington, D.C.
- Passenger rail transportation in Maryland
- Passenger rail transportation in Delaware
- Passenger rail transportation in Pennsylvania
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
