- Nitramide
-
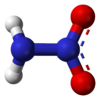
Nitramide 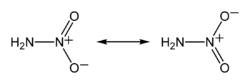
 Other namesnitramine
Other namesnitramineIdentifiers CAS number 7782-94-7 PubChem 24534 ChemSpider 22941 
ChEBI CHEBI:29273 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - N[N+](=O)[O-]
Properties Molecular formula H2N2O2 Molar mass 62.03 g mol−1 Appearance colourless solid[1] Melting point 72-75 °C[1]
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Nitramide, H2NNO2, is a chemical compound. Organyl derivatives of nitramide, RNHNO2 are termed nitroamines, and are widely used as explosives: examples include RDX and HMX.
Structure
The nitramide molecule is reported to be non-planar in the gas phase[2], but planar in the crystal phase[1].
Synthesis
Thiele and Lachman's original synthesis of nitramide involved the hydrolysis of potassium nitrocarbamate[1]:
- K2(O2NNCO2) + 2H2SO4 → O2NNH2 + CO2 + 2KHSO4
Other routes to nitramide include hydrolysis of nitrocarbamic acid,
- O2NNHCO2H → O2NNH2 + CO2
reaction of sodium sulfamate with nitric acid,
- Na(SO3NH2) + HNO3 → O2NNH2 + NaHSO4
and reaction of dinitrogen pentoxide with two equivalents of ammonia.
- N2O5 + 2NH3 → O2NNH2 + NH4NO3
References
- ^ a b c d Angelika Häußler, Thomas M. Klapötke, and Holger Piotrowski (2002). "Experimental and Theoretical Study on the Structure of Nitramide H2NNO2". Z. Naturforsch. 57 b: 151–156. http://www.znaturforsch.com/ab/v57b/s57b0151.pdf.
- ^ J. K. Tyler (1963). "Microwave spectrum of nitramide". Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy 11 (1-6): 39–46. doi:10.1016/0022-2852(63)90004-3.
Categories:- Nitroamines
- Inorganic compound stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
