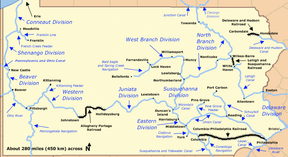
- Main Line of Public Works
-
Main Line of Public Works Map of historic Pennsylvania canals and connecting railroads Original owner Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Construction began 1826 Date completed 1834 Date closed Sold to Pennsylvania Railroad in 1857; last segment, near Harrisburg, closed in 1901 Start point Philadelphia End point Pittsburgh Branch(es) Wiconisco Canal, Kittanning Feeder, Allegheny Outlet Branch of Pennsylvania Canal Connects to Delaware River, Schuylkill Canal, Conestoga Navigation, Susquehanna and Tidewater Canal, Codorus Navigation, Union Canal, Susquehanna Division, Allegheny River, Monongahela River, Ohio River Locks 168
(The Eastern Division Canal had 14 locks, the Juniata Division 86, and the Western Division 68.)Maximum height above sea level 2,322 ft (708 m)
(Summit of the Allegheny Portage Railroad)Status Abandoned except for historic and recreational segments The Main Line of Public Works was a railroad and canal system built by the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania in the 19th century. It ran from Philadelphia west through Harrisburg and across the state to Pittsburgh and connected with other divisions of the Pennsylvania Canal. It consisted of the following principal sections, moving from east to west:[1][2]
Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad: 82 miles (132 km) from Philadelphia to Columbia in Lancaster County; Eastern Division Canal: 43 miles (69 km) from Columbia to Duncan's Island at the mouth of the Juniata River; Juniata Division Canal: 127 miles (204 km) from Duncan's Island to Hollidaysburg; Allegheny Portage Railroad: 36 miles (58 km) from Hollidaysburg to Johnstown; Western Division Canal: 103 miles (166 km) from Johnstown to the terminus in Pittsburgh. The system opened in 1834 and was sold to the Pennsylvania Railroad in 1857.
Contents
Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad
The Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad began in Philadelphia at Broad and Vine Streets, running north on Broad and west on Pennsylvania Avenue (later taken over and submerged/tunneled over by the Reading Railroad) before heading northwest across the Columbia Bridge over the Schuylkill River. Just after crossing the river, it traveled up the Belmont Plane, an inclined plane in the current location of West Fairmount Park, and continued west across the eastern part of the state to Columbia, where the Columbia Plane headed down to the Susquehanna River. At that point, the eastern division of the canal continued north along the river and then west.
The Northern Liberties and Penn Township Railroad was incorporated in 1829 to build a branch continuing east on Noble Street and Willow Street to the Delaware River. This opened in 1834.[3]
Belmont Plane
The Belmont Plane ran from the Schuylkill River for 2,805 feet (855 m), rising 1 foot (0.3 m) in 15 feet (4.6 m) for a total of 187 feet (57 m). Steam-driven cables dragged the railway cars to the top of Belmont Hill.
A very important event in railroad history occurred on this inclined plane. On July 10, 1836, the Norris Locomotive Works, a Philadelphia firm, ran a test of a 4-2-0 locomotive named George Washington. The engine of 14,400 pounds (6,532 kg) hauled a load of 19,200 pounds (8,709 kg) (including 24 people riding on tender and one freight car) up the grade at 15 miles (24 km) per hour. This engine, the first to ascend a hill by its own power, proved that steam locomotives could climb an ascending grade while pulling a load. So remarkable was this accomplishment that reports in engineering journals emphatically doubted its occurrence[citation needed]. A second, more formal trial with an even greater load proved the engine's capabilities on July 19, 1836.
In 1850 the state bought the West Philadelphia Railroad, which had been incorporated in 1835 to bypass the Belmont Plane and failed after completing only the section from 52nd Street west to the main line at Rosemont. The state built the rest from 52nd Street east to downtown, but on a different alignment than the one originally planned; the new line, put into operation October 15, 1850,[4] ended at the west end of the Market Street Bridge, from which the City Railroad continued east. The old line, which ran from the Schuylkill River up the Belmont Plane to Ardmore along the route of present-day Montgomery Avenue in Lower Merion Township, was abandoned.
The Columbia Bridge and line east to Broad and Vine Streets were sold to the Philadelphia and Reading Railroad as part of its main line. The Reading acquired the Northern Liberties and Penn Township Railroad in 1870, giving it access to the Delaware River.
The section of the old Pennsylvania Railroad running from Philadelphia west through Chester County and, by extension, the western suburbs of Philadelphia, is still known as the Main Line.
The Columbia Plane, which lowered railway cars down to the Eastern Division Canal along the Susquehanna River, was bypassed in 1840 by a new track alignment.[5]
Eastern Division Canal
The Pennsylvania Canal's Eastern Division, which opened in 1833, ran 43 miles (69 km) along the east side of the Susquehanna River between Columbia and Duncan's Island at the mouth of the Juniata River. The canal included 14 locks with an average lift of 7.5 feet (2.3 m). The state originally planned a canal of 24 miles (39 km) running between the Union Canal at Middletown to the Juniata. However, the plan changed in 1828, when the state opted to extend the Eastern Division 19 miles (31 km) further south to connect with the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad at Columbia.[6]
Engineers faced complications at the northern end of the Eastern Division Canal, where it met the Juniata Division Canal and the Susquehanna Division Canal at Duncan's Island. Boats had to cross from one side of the Susquehanna River to the other between either the Susquehanna Division or the Juniata Division on the west side and the Eastern Division on the east side. They solved the problem by building a dam 1,998 feet (609 m) long and 8.5 feet (2.6 m) high between the lower end of Duncan's Island and the east bank of the Susquehanna. This formed a pool across which boats could be pulled from a wooden, two-tier towpath bridge at Clark's Ferry. Two Duncan's Island lift locks raised or lowered the boats traveling between the dam pool and the other canals.[6]
Juniata Division Canal
The Juniata Division Canal was approved in segments starting in 1827 with a canal from near Duncan's Island in the Susquehanna River to Lewistown, 40 miles (64 km) upstream. Subsequently the state agreed to extend the canal to Hollidaysburg and the eastern end of the Allegheny Portage Railroad, 127 miles (204 km) from the Susquehanna. A total of 86 locks were required to overcome a change in elevation of 584 feet (178 m) over the full length of the canal, which opened in 1832.[6]
From the canal basin, westbound boats began their journey by being elevated about 10 feet (3 m) by a lock that brought them to the level of a wooden aqueduct on which they were towed 600 feet (183 m) to the south side of the Juniata. At North's Island, 18 miles (29 km) from the Susquehanna, they were towed to the north side of the river across a slack water pool formed by a dam. From North's Island to Huntingdon, the river was dammed in three more places to feed water to the canal, and above Huntingdon, 14 more dams were needed to create 16 miles (26 km) of slack water navigation in the river to supplement 22 miles (35 km) miles of travel in segments of canal. In addition, the state built three reservoirs on Juniata tributaries to keep the upper parts of the canal filled with water.[6]
Remnants
A canal section of 1.5 miles (2.4 km) has been restored near Locust Campground, 3 miles (4.8 km) west of Lewistown. At the western end of the canal, the Hollidaysburg Canal Basin Park has preserved two canal basins and a connecting lock; a museum at the park illustrates how canal boats transferred between the canal and the Allegheny Portage Railroad.[7]
Allegheny Portage Railroad
Main article: Allegheny Portage Railroad Lilly Culvert under the railroad
Lilly Culvert under the railroad
From 1834 until 1854, when the Pennsylvania Railroad Company finished a competing line, the Allegheny Portage Railroad made continuous boat traffic possible over the Allegheny Mountains between the Juniata and Western Division Canals. It followed a 36-mile (58 km) route that included 11 levels, 10 inclined planes fitted with stationary engines that could raise and lower boats and cargo, a 900-foot (270 m), viaduct over the Little Conemaugh River, and many bridges.[8] Infrastructure included 153 drains and culverts.[9] The railroad climbed 1,398 feet (426 m) from the eastern canal basin at Hollidaysburg and 1,171 feet (357 m) from the western basin at Johnstown.[8] At its summit, the railroad reached an elevation of 2,322 feet (708 m) above sea level.[9]
Western Division Canal
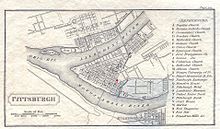 A map of downtown Pittsburgh in 1828 shows the routes of the Pennsylvania Canal in and near the city and the canal connections to the city's three rivers.
A map of downtown Pittsburgh in 1828 shows the routes of the Pennsylvania Canal in and near the city and the canal connections to the city's three rivers.
In 1826, the state legislature authorized the first segment of the Western Division Canal, from Pittsburgh up the Allegheny River to its confluence with the Kiskiminetas River at Freeport. Pittsburgh residents favored a route that would follow the south bank of the Allegheny River and terminate in Pittsburgh, while residents of the borough of Allegheny favored a north bank canal ending in the borough, across the river from Pittsburgh. Eventually, the canal was run along the physically more favorable north bank, but the state agreed to build the main terminal and turning basin in Pittsburgh and a secondary terminal and connecting canal, the Allegheny Outlet, in the borough. Getting the main canal across the Allegheny River into Pittsburgh required an aqueduct of 1,140 feet (347 m), the longest on the Pennsylvania Main Line route. Linking to the Ohio River at Pittsburgh, the Western Division Canal also linked, through a tunnel of 810 feet (250 m) under Grant's Hill in Pittsburgh, with the Monongahela River.[6]
Subsequent Western Division Canal extensions went from Freeport up the Kiskiminetas and Conemaugh Rivers to Blairsville and then to the western end of the Allegheny Portage Railroad at Johnstown. East of Tunnelton, the route went through a canal tunnel of 817 feet (249 m) built to avoid a long loop of the Conemaugh River. The first fully loaded freight boat traveled from Johnstown to Pittsburgh in 1831; the route through Grant's Hill opened in 1832. Over its length of 104 miles (167 km), the canal employed 68 locks, 16 river dams, and 16 aqueducts. From Freeport, a separate extension, the Kittanning Feeder, ran 14 miles (23 km) up the Allegheny River to Kittanning.[6]
Johnstown Flood
The 1889 Johnstown Flood was caused by the failure of the South Fork Dam, which dammed the waters of the Little Conemaugh River creating a reservoir, Lake Conemaugh, in the hills above Johnstown, Pennsylvania. Part of the Main Line of Public Works, the man-made, two-square-mile (5.2 km2) lake supplied water to the Western Division Canal. With the decline of the canal, the lake and dam were abandoned, sold to the Pennsylvania Railroad in 1857, which then sold them to private interests. They were purchased by the South Fork Fishing and Hunting Club in 1879, and a private resort was built surrounding the lake. On May 31, 1889, following heavy rains, the South Fork Dam failed, sending 20 million tons (18.2 million cubic meters) of water down the gorge toward Johnstown. More than 2,200 people were killed.[10]
Remnants
The Tunnelview Historical Site shows where in 1830 a canal tunnel of 817 feet (249 m) was built through Bow Ridge to avoid a long bend on the Conemaugh River, 10 miles (16 km) west of Blairsville. Saltsburg Canal Park, where Loyalhanna Creek joins the Conemaugh River to form the Kiskiminetas River, recognizes the canal's economic contribution to Saltsburg.[7]
Points of interest
Feature Coordinates Description Philadelphia 39°57′08″N 75°09′50″W / 39.95222°N 75.16389°W[11] City at the eastern terminus of the Main Line of Public Works and the Columbia–Philadelphia Railroad Columbia 40°02′01″N 76°30′16″W / 40.03361°N 76.50444°W[12] Borough at the western terminus of the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad and the southern terminus of the Eastern Division Canal Duncan's Island 40°25′02″N 77°00′33″W / 40.41722°N 77.00917°W.[13] Island at the northern terminus of the Eastern Division Canal and the eastern terminus of the Juniata Division Canal Lewistown 40°35′57″N 77°34′17″W / 40.59917°N 77.57139°WCoordinates: 40°35′57″N 77°34′17″W / 40.59917°N 77.57139°W[14] Borough at the western terminus of the Juniata Division Canal and the eastern terminus of the Allegheny Portage Railroad Hollidaysburg 40°25′38″N 78°23′20″W / 40.42722°N 78.38889°W[15] Borough at the western terminus of the Juniata Division Canal and the eastern terminus of the Allegheny Portage Railroad Johnstown 40°19′36″N 78°55′19″W / 40.32667°N 78.92194°W[16] City at the western terminus of the Allegheny Portage Railroad and the eastern terminus of the Western Division Canal Pittsburgh 40°26′26″N 79°59′45″W / 40.44056°N 79.99583°W[17] City at the western terminus of the Main Line of Public Works and the Western Division Canal Kittanning 40°48′59″N 79°31′19″W / 40.81639°N 79.52194°W[18] Borough at the northern terminus of the Kittanning Feeder Canal See also
References
- ^ "Pennsylvania Canals". Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission. Archived from the original on August 18, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070818161137/http://www.phmc.state.pa.us/ppet/canals/page1.asp?secid=31. Retrieved August 7, 2007.
- ^ Roberts, Charles S. (1997). Triumph I. Baltimore: Barnard, Roberts, and Company. p. 34. ISBN 0-934118-23-X.
- ^ PRR Chronology, 1834
- ^ Burgess, George H. and Kennedy, Miles C. (1949), Centennial History of the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, Philadelphia: The Pennsylvania Railroad Company
- ^ PRR Chronology, 1836
- ^ a b c d e f Shank, William H. (1986). The Amazing Pennsylvania Canals, 150th Anniversary Edition. York, Pennsylvania: American Canal and Transportation Center. ISBN 0-933788-37-1.
- ^ a b "Introduction to Pennsylvania's Historic Canals". Pennsylvania Canal Society. http://pacanalsociety.org/sites.htm. Retrieved November 26, 2009.
- ^ a b "The Allegheny Portage Railroad". Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission. http://www.portal.state.pa.us/portal/server.pt/community/things/4280/allegheny_portage_railroad/478191. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^ a b Bianculli, Anthony J. (2003). Trains and Technology: The American Railroad in the 19th Century, Vol. 3, Tracks and Structures. Newark, Del.: University of Delaware Press. p. 48. ISBN 0-87413-802-7. http://books.google.com/?id=7T3qECx0CLUC&pg=PA45&lpg=PA45&dq=allegheny+portage+railroad+high+point. Retrieved March 22, 2009.
- ^ Frank, Walter Smoter (2004). "The Cause of the Johnstown Flood". Walter Smoter Frank. http://smoter.com/flooddam/johnstow.htm. According to the source, the article is a version of a May 1988 article in Civil Engineering, pp. 63–66
- ^ "Philadelphia". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. August 30, 1990. http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gnispublic/f?p=gnispq:3:::NO::P3_FID:1215531. Retrieved March 22, 2009.
- ^ "Columbia". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. August 2, 1979. http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gnispublic/f?p=gnispq:3:::NO::P3_FID:1213954. Retrieved March 22, 2009.
- ^ "Duncan Island". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. August 2, 1979. http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gnispublic/f?p=gnispq:3:::NO::P3_FID:1173598. Retrieved March 20, 2009.
- ^ "Lewistown". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. August 2, 1979. http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gnispublic/f?p=gnispq:3:::NO::P3_FID:1213631. Retrieved March 22, 2009.
- ^ "Hollidaysburg". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. August 2, 1979. http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gnispublic/f?p=gnispq:3:::NO::P3_FID:1177213. Retrieved March 22, 2009.
- ^ "Johnstown". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. August 2, 1979. http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gnispublic/f?p=gnispq:3:::NO::P3_FID:1213975. Retrieved March 21, 2009.
- ^ "Pittsburgh". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. August 2, 1979. http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gnispublic/f?p=gnispq:3:::NO::P3_FID:1213644. Retrieved March 21, 2009.
- ^ "Kittanning". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. August 2, 1979. http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gnispublic/f?p=gnispq:3:::NO::P3_FID:1214737. Retrieved March 21, 2009.
Further reading
For more on the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad, see William Hasell Wilson, The Columbia-Philadelphia Railroad and Its Successor (1896). A reprint of this booklet was issued in 1985. See also John C. Trautwine, Jr., The Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad of 1834, in Philadelphia History, Vol. 2, No. 7 (Philadelphia, PA: City History Soc. of Philadelphia, 1925). This is a pamphlet written for The City History Society of Philadelphia and read at the meeting of March 15, 1921.
External links
Chartered 1846 · Main Line (1857) · Northern Central (1861-1976) · Baltimore and Potomac (1867-1902) · Pan Handle (1847-1956) · Pittsburgh, Fort Wayne and Chicago (1851-1976) · United New Jersey (1871-1976) · Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore (1836-1902) · Philadelphia, Baltimore and Washington (1902-1976)Categories:- Canals in Pennsylvania
- Defunct Pennsylvania railroads
- Predecessors of the Pennsylvania Railroad
- Railway companies established in 1828
- Railway companies disestablished in 1857
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.