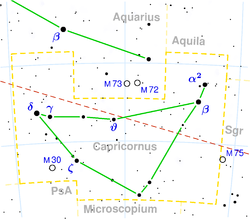
- Gamma Capricorni
-
Coordinates:
 21h 40m 05.5s, −16° 39′ 44″
21h 40m 05.5s, −16° 39′ 44″γ Capricorni Observation data
Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS)Constellation Capricornus Right ascension 21h 40m 05.4563s[1] Declination −16° 39′ 44.308″[1] Apparent magnitude (V) +3.69 Characteristics Spectral type F0p[2] U−B color index +0.22[3] B−V color index +0.32[3] Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) −31.2[4] km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: 187.39[1] mas/yr
Dec.: −22.33[1] mas/yrParallax (π) 23.48 ± 1.10[1] mas Distance 139 ± 7 ly
(43 ± 2 pc)Details Surface gravity (log g) 3.95[5] Temperature 7,520[5] K Metallicity ![\begin{smallmatrix}\left[\frac{Fe}{H}\right]\ =\ 0.5\end{smallmatrix}](9/8b96f0b512a9dcac4ad45b224f60454d.png) [5]
[5]Rotational velocity (v sin i) 40[6] km/s Other designations Gamma Capricorni (γ Cap, γ Capricorni) is a giant star in the constellation Capricornus. It has the traditional name Nashira, which comes from the Arabic سعد ناشرة - sa'd nashirah for "the lucky one" or "bearer of good news".
In Chinese, 壘壁陣 (Lěi Bì Zhèn), meaning Line of Ramparts, refers to an asterism consisting of γ Capricorni, κ Capricorni, ε Capricorni, δ Capricorni, ι Aquarii, σ Aquarii, λ Aquarii, φ Aquarii, 27 Piscium, 29 Piscium, 33 Piscium and 30 Piscium.[7] Consequently, γ Capricorni itself is known as 壘壁陣三 (Lěi Bì Zhèn sān, English: the Third Star of Line of Ramparts.)[8]
Because it is near the ecliptic, γ Capricorni can be occulted by the Moon, and (rarely) by planets.
γ Capricorni is a blue-white A-type (A7III) giant star with a mean apparent magnitude of +3.69. It is approximately 139 light years from Earth. It is classified as an Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum type variable star and its brightness varies by 0.03 magnitudes.
Nashira as the name
Nashira (AK-85) is once of United States navy ship.
References
- ^ a b c d e Perryman, M. A. C. et al (July 1997). "The HIPPARCOS Catalogue". Astronomy & Astrophysics 323: L49–L52. Bibcode 1997A&A...323L..49P.
- ^ a b "HD 206088 -- Variable Star of alpha2 CVn type". SIMBAD. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=HD+206088. Retrieved 2009-11-12.
- ^ a b Johnson, H. L.; Iriarte, B.; Mitchell, R. I.; Wisniewskj, W. Z. (1966). "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars". Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory 4 (99). Bibcode 1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- ^ Wilson, Ralph Elmer (1953). General catalogue of stellar radial velocities. Carnegie Institution of Washington. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1953QB901.W495...... Retrieved 2007-05-14.
- ^ a b c Burkhart, C.; Coupry, M. F. (September 1991). "The A and Am-Fm stars. I - The abundances of Li, Al, Si, and Fe". Astronomy and Astrophysics 249 (1): 205−216. Bibcode 1991A&A...249..205B.
- ^ Royer, F.; Grenier, S.; Baylac, M.-O.; Gómez, A. E.; Zorec, J. (October 2002). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars in the northern hemisphere. II. Measurement of v sin i". Astronomy and Astrophysics 393: 897–911. arXiv:astro-ph/0205255. Bibcode 2002A&A...393..897R. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020943.
- ^ (Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN 978-986-7332-25-7.
- ^ (Chinese) 香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表, Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
Bayer Flamsteed 1 (ξ1) • 2 (ξ2) • 3 • 4 • 5 (α¹, Prima Giedi) • 6 (α², Secunda Giedi) • 7(σ) • 8 (ν, Alshat) • 10 (π) • 11 (ρ) • 15 (υ) • 16 (ψ) • 17 • 18 (ω) • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 (η) • 23 (θ) • 24 (A) • 25 (χ) • 26 • 27 • 28 (φ) • 29 • 30 • 31 • 32(ι) • 33 • 34 (ζ) • 35 • 36 (b) • 37 • 38 • 39 (ε) • 40 (γ, Nashira) • 41 • 42 • 43 (κ) • 44 • 45 • 46 (c) • 47 • 48 (λ) • 49 (δ, Deneb Algedi) • 50 • 51 (μ)List Categories:- Variable star stubs
- Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variables
- Bayer objects
- Capricornus constellation
- F-type main sequence stars
- Stars with proper names
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.