- Dimethyl terephthalate
-
Dimethyl terephthalate 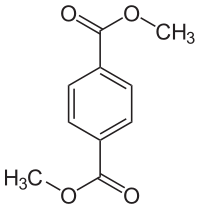 Dimethyl terephthalateSystematic name1,4-Dimethyl benzene-1,4-dicarboxylateOther names1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester
Dimethyl terephthalateSystematic name1,4-Dimethyl benzene-1,4-dicarboxylateOther names1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester
Dimethyl 4-phthalate
Terephthalic acid methyl ester
Dimethyl-p-phthalate
Di-Me terephthalate
Methyl 4-carbomethoxybenzoate
Methyl-p-(methoxycarbonyl)benzoate
Methyl terephthalateIdentifiers Abbreviations DMT CAS number 120-61-6 
PubChem 8441, 12241382 (2H4) ChemSpider 13863300 
EC number 204-411-8 MeSH Dimethyl+4-phthalate RTECS number WZ1225000 Beilstein Reference 1107185 Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- COC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)OC
O=C(OC)c1ccc(cc1)C(=O)OC
Properties Molecular formula C10H10O4 Molar mass 194.18 g mol−1 Exact mass 198.083015792 g mol-1 Appearance white solid Density 1.2 g/cm³, ? Melting point 142 °C, 415 K, 288 °F
Boiling point 288 °C, 561 K, 550 °F
Acidity (pKa) -7.21 Basicity (pKb) -6.60  terephthalate (verify) (what is:
terephthalate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO2CH3)2. It is the diester formed from terephthalic acid and methanol. It is a white solid that melts to give a distillable colourless liquid.[1]
Contents
Production
DMT has been produced in a number of ways. Conventionally and still of commercial value is the direct esterification of terephthalic acid. Alternatively, it can be prepared by alternating oxidation and methyl-esterification steps from p-xylene via methylp-toluate.[1]
Use
DMT is used in the production of polyesters, including polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polytrimethylene terephthalate. It consists of benzene substituted with carboxymethyl groups (CO2CH3) at the 1 and 4 positions. Because DMT is volatile, it is an intermediate is some schemes for the recyclic of PET, e.g. from plastic bottles.
Hydrogenation of DMT affords the diol cyclohexanedimethanol, which is a useful monomer.
References
- ^ a b Richard J. Sheehan "Terephthalic Acid, Dimethyl Terephthalate, and Isophthalic Acid" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_193
External links
This article about an ester is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. - COC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)OC
