- Cyclohexanedimethanol
-
Cyclohexanedimethanol  [4-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexyl]methanolOther names1,4–Cyclohexanedimethanol; CHDM; 1,4-Bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane
[4-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexyl]methanolOther names1,4–Cyclohexanedimethanol; CHDM; 1,4-Bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexaneIdentifiers CAS number 105-08-8 
PubChem 7735 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - OCC1CCC(CO)CC1
Properties Molecular formula C8H16O2 Molar mass 144.21 g/mol Appearance White waxy solid Density 1.02 g/ml Melting point 41-61 °C, 314-334 K, 106-142 °F
Boiling point 284-288 °C, 557-561 K, 543-550 °F
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cyclohexanedimethanol (CHDM) is an organic compound with formula C6H10(CH2OH)2. It is a colorless low-melting solid used in the production of polyester resins. Commercial samples consist of a mixture of cis and trans isomers, as seen for other disubstituted derivatives of cyclohexane.
Production
CHDM is produced by catalytic hydrogenation of dimethyl terephthalate (DMT). The reaction conducted in two steps beginning with the conversion of DMT to the diester dimethyl 1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylate (DMCD). In the second step DMCD is further hydrogenated to CHDM. The cis/trans ratio of CHDM is differ according to the catalyst, 80:20 for Cu4Ru12 catalyst, 65:35 in case of the RuPt catalyst, 88:12 for the Ru-Sn catalyst [1], 30:70 in case of the copper chromite catalyst usually used in industrial processing.[2]
- C6H4(CO2CH3)2 + 3 H2 → C6H10(CO2CH3)2
- C6H10(CO2CH3)2 + 4 H2 → C6H10(CH2OH)2 + 2 CH3OH
Most of the commercial CHDM has cis/trans ratio of 30:70. The leading producers in CHDM are Eastman Chemicals and SK Chemicals.
Applications
Via the process called polycondensation, CHDM is a precursor to polyesters. It is one of the most important co-monomers for production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), or polyethylene terephalic ester (PETE), from which plastic bottles are made.[3][4]
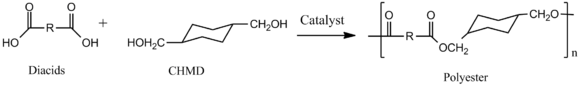 Thermoplastic polyesters containing CHDM exhibit enhanced strength, clarity, and solvent resistance. The exact properties of the polyesters vary from the high melting crystalline poly(1,4-cyclohexylenedimethylene terephthalate), PCT, to the non-crystalline copolyesters with the combination of ethylene glycol and CHDM in the backbone. The properties of these polyesters is also dependent on the cis/trans ratio of the CHDM monomer.[5] CHDM has low melting point and reduce the degree of crystallinity of PET homopolymer. These PET is known as glycol modified polyethylene terephthalate, PETG. PETG is used in many fields, electronics, automobiles, barrier, and medicals etc. So the resin can be plastically formed with lower force and /or with low heat requirement. These reasons stabilize the polymer from degradation and reduce final products acetaldehyde level to acceptable level.
Thermoplastic polyesters containing CHDM exhibit enhanced strength, clarity, and solvent resistance. The exact properties of the polyesters vary from the high melting crystalline poly(1,4-cyclohexylenedimethylene terephthalate), PCT, to the non-crystalline copolyesters with the combination of ethylene glycol and CHDM in the backbone. The properties of these polyesters is also dependent on the cis/trans ratio of the CHDM monomer.[5] CHDM has low melting point and reduce the degree of crystallinity of PET homopolymer. These PET is known as glycol modified polyethylene terephthalate, PETG. PETG is used in many fields, electronics, automobiles, barrier, and medicals etc. So the resin can be plastically formed with lower force and /or with low heat requirement. These reasons stabilize the polymer from degradation and reduce final products acetaldehyde level to acceptable level.Reference
- ^ J. M. Thomas; R. Raja (2002). "The materials Chemistry of Inorganic Catalyst". Australian journal of Chemistry 54: 551–560. doi:10.1071/CH01150.
- ^ S.R. Turner; Y. Li (2010). "Synthesis and Properties of Cyclic Diester Based Aliphatic Copolyesters". Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry 48: 2162–2169. doi:10.1002/pola.23985.
- ^ S.R. Turner (2004). "Development of amorphous copolyesters based on 1,4- cyclohexane-dimethanol". Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 42: 5847–5852. doi:10.1002/pola.20460.
- ^ S. Andjelic; D.D. Jamiolkowski; R. Bezwada (2007). "Mini-review The Polyoxaesters". Polymer International 56: 1063–1077. doi:10.1002/pi.2257.
- ^ S. R. Turner, R.W. Seymour; T.W. Smith (2001). "Cyclohexanedimethanol Polyesters". Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology. doi:10.1002/0471440264.pst257.
Categories:- Monomers
- Diols
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
