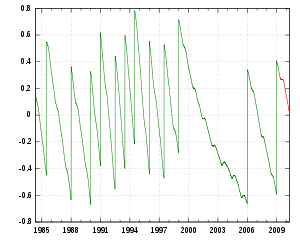
- DUT1
-
The time correction DUT1 (sometimes also written DUT) is the difference between Universal Time (UT1), which is defined by Earth's rotation, and Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which is defined by a network of precision clocks.
- DUT1 = UT1 − UTC
UTC is maintained via leap seconds, such that UTC remains within the range −0.9 s < DUT1 < +0.9 s. The reason for this correction is partly that the rate of rotation of the Earth is not constant, due to tidal braking and the redistribution of mass within the Earth, including its oceans and atmosphere, and partly because the SI second (as now used for UTC) was already, when adopted, a little shorter than the current value of the second of mean solar time.[1]
Forecast values of DUT1 are published by IERS Bulletin A.
Weekly updated values of DUT1 with 0.1 s precision are broadcast by several time signal services, including WWV and MSF. These services transmit one pulse per second of some sort. To represent positive DUT1 values from +0.1 to +0.8 seconds, the pulses sent during seconds 1 through 8 are "emphasized" in some way, generally by transmitting a double pulse. The number of emphasized pulses gives the value of DUT1. Negative DUT1 values, from −0.1 to −0.8 seconds, are similarly represented by emphasizing pulses 9 through 16. For example, a DUT1 value of −0.4 would be transmitted by emphasizing pulses 9 through 12.
The Russian time signal RWM transmits an additional correction dUT1 in 0.02 s increments. Positive values of dUT1 from +0.02 to +0.08 s are encoded by emphasizing pulses 21 through 24; negative values are encoded by emphasizing pulses 31 through 34. The actual value of DUT1 is approximated by the sum of the transmitted DUT1 + dUT1.
The longwave RBU time signal also transmits dUT1.
References and notes
- ITU-R Recommendation TF.460-4: Standard-frequency and time-signal emissions. International Telecommunication Union.
- ^ :(1) In "The Physical Basis of the Leap Second", by D D McCarthy, C Hackman and R A Nelson, in Astronomical Journal, vol.136 (2008), pages 1906–1908, it is stated (page 1908), that "the SI second is equivalent to an older measure of the second of UT1, which was too small to start with and further, as the duration of the UT1 second increases, the discrepancy widens." :(2) In the late 1950s, the cesium standard was used to measure both the current mean length of the second of mean solar time (UT2) (result: 9,192,631,830 cycles) and also the second of ephemeris time (ET) (result: 9,192,631,770±20 cycles), see "Time Scales", by L. Essen, in Metrologia, vol.4 (1968), pp.161–165, on p.162. As is well known, the 9192631770 figure was chosen for the SI second. L Essen in the same 1968 article (p.162) stated that this "seemed reasonable in view of the variations in UT2".
External links
Time measurement and standards Major subjects International standards UTC · UTC offset · UT · ΔT · DUT1 · IERS · ISO 31-1 · ISO 8601 · TAI · 12-hour clock · 24-hour clock · Barycentric Coordinate Time · Civil time · Daylight saving time · Geocentric Coordinate Time · International Date Line · Leap second · Solar time · Terrestrial Time · Time zoneObsolete standards Time in physics Horology Calendar Astronomical · Dominical letter · Epact · Equinox · Gregorian · Hebrew · Intercalation · Islamic · Julian · Leap year · Lunar · Lunisolar · Seven-day week · Solar · Solstice · Tropical year · Weekday determination · Weekday namesArchaeology & geology Astronomical chronology Units of time Related topics Categories:- Time scales
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.