- Brocchi's Cluster
-
 Brocchi's Cluster, also known as the Coathanger: a conspicuous asterism easily seen with binoculars in the constellation Vulpecula.
Brocchi's Cluster, also known as the Coathanger: a conspicuous asterism easily seen with binoculars in the constellation Vulpecula.Collinder 399 (Cr[1] 399) is a random grouping of stars located in the constellation Vulpecula near the border with Sagitta. Collinder 399 is known as Al Sufi's Cluster or Brocchi's Cluster. The brighter members of this star cluster form an asterism also known as the Coathanger.
Contents
History
Before 964, it was first discovered by the Persian astronomer Al Sufi, and described in his Book of Fixed Stars in 964.
In the 17th century, it was independently rediscovered by Italian astronomer Hodierna.
In the 1920s, Brocchi, an amateur astronomer and chart maker for the American Association of Variable Star Observers (AAVSO), created a map of this object for use in calibrating photometers.
In 1931, Swedish astronomer Collinder listed it in his catalogue of open clusters.
Status
The status of this group as a star cluster has changed in recent years. The group was considered to be a cluster for most of the 20th century. Looking at a variety of criteria, however, a study in 1970 concluded that only 6 of the brightest stars formed an actual cluster. Several independent studies since 1998 have now determined that this object is not a true cluster at all, but rather just a chance alignment of stars. These recent studies have generally based their findings on improved measurements of parallax and proper motion provided by the Hipparcos satellite which were first published in 1997.
The "Coathanger"
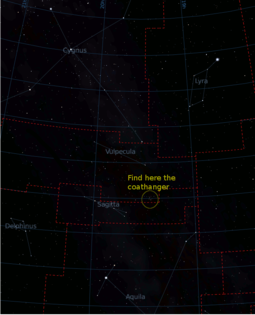 How to find the Coathanger asterism: about 8 degrees NW of the W end of the arrow-shaped Sagitta constellation.
How to find the Coathanger asterism: about 8 degrees NW of the W end of the arrow-shaped Sagitta constellation.
The asterism is made up of 10 stars ranging from 5th to 7th magnitude which form the conspicuous "coathanger", a straight line of 6 stars with a "hook" of 4 stars on the south side. An additional 30 or so fainter stars are sometimes considered to be associated as well.
Under a dark sky, Collinder 399 can be seen with the naked eye as an unresolved patch of light; binoculars or a telescope at very low power are usually needed in order to view the "coathanger" asterism. It is best found by slowly sweeping across the Milky Way along an imaginary line from the bright star Altair toward the even brighter star Vega. About one third of the way toward Vega, the Coathanger should be spotted easily against a darker region of the Milky Way. The asterism is best seen in July-August and north of 20° north latitude it is displayed upside down (as in the picture top right of this page) when it is at its highest point. South of this latitude it is shown upright as the 'hanger' is south of the line of 6 stars.
The asterism and its immediate surroundings are a useful gauge for determining the faintest stars visible in a small telescope as there are a wide range of stellar magnitudes within the cluster easily viewed in one small location of the sky.
Catalogue Data
- Name: Collinder 399
- Right Ascension: 19h 25m 24s
- Declination: +20°11′00″
- Magnitude: 3.6m (visual)
- Diameter: ~60'
- Magnitude of Brightest Star: 5.19m (visual)
External links
- Brocchi's Cluster, Collinder 399 - SEDS
- Collinder 399: The Coat Hanger - Astronomy Picture of the Day
- Collinder 399: The Coat Hanger - Astronomy Picture of the Day
References
- Baumgardt, H. (1998). "The nature of some doubtful open clusters as revealed by HIPPARCOS". Astronomy and Astrophysics 340, 402-414
- Collinder, P. (1931). "On structured properties of open galactic clusters and their spatial distribution". Lund Obs. Ann. No. 2
- Cragin, Murray; Lucyk, James; & Rappaport, Barry (1993). The Deep Sky Field Guide to Uranometria 2000.0 (1st ed). Richmond, VA: Willmann-Bell. ISBN 0-943396-38-7
- Dias, W.S.; Lépine, J.R.D.; & Alessi, B.S. (2001). "Proper motions of open clusters within 1 kpc based on the TYCHO2 Catalogue". Astronomy and Astrophysics 376, 441-447
- Hall, D.S. & VanLandingham, F.G. (1970). "The Nearby Poor Cluster Collinder 399". Pub. of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 82 (487), p. 640-652
- Skiff, Brian (January, 1998). "Brocchi's Cluster Revealed". Sky and Telescope, p. 65-67
Categories:- Astronomical asterisms
- Vulpecula constellation
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

