- Cutchogue, New York
-
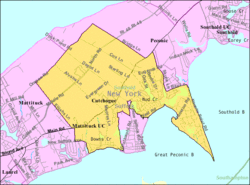
Cutchogue — CDP — Cutchogue Library Coordinates: 41°0′38″N 72°28′25″W / 41.01056°N 72.47361°WCoordinates: 41°0′38″N 72°28′25″W / 41.01056°N 72.47361°W Country United States State New York County Suffolk Town Southold Area - Total 8.5 sq mi (22.1 km2) - Land 8.1 sq mi (21.0 km2) - Water 0.4 sq mi (1.1 km2) Elevation 30 ft (9 m) Population (2000)[1] - Total 2,849 - Density 351.7/sq mi (135.8/km2) Time zone Eastern (EST) (UTC-5) - Summer (DST) EDT (UTC-4) ZIP code 11935 Area code(s) 631 FIPS code 36-19466 GNIS feature ID 0947961 Cutchogue is a census-designated place (CDP) in Suffolk County, New York (USA). The population was 2,849 at the 2000 census.[1]
Cutchogue CDP roughly represents the area of Cutchogue hamlet (unincorporated community) in the town of Southold.
Contents
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the community has a total area of 8.5 square miles (22 km2), of which, 8.1 square miles (21 km2) of it is land and 0.4 square miles (1.0 km2) of it (4.93%) is water.
History
The name Cutchogue is derived from an Algonquin word meaning "principal place." Many of the local Native Americans lived at Fort Corchaug before English-American settlers began arriving in 1640. The Old House, built in 1649, is the oldest English-style house in the village. In fact, it is one of the best surviving examples of English domestic architecture in the United States, and it was named a National Historic Landmark. Famous early residents include political figure Parker Wickham and his nephew John Wickham. Cutchogue is also the birthplace of composer Douglas Moore. Hargrave Vineyard, the first winery on Long Island, was established in Cutchogue in 1973. The Long Island Merlot Alliance which promotes wine making using the merlot grape, the principal Long Island grape, is based in Cutchogue.
Demographics
As of the census of 2000, there were 2,849 people, 1,120 households, and 801 families residing in the CDP. The population density was 351.7 per square mile (135.8/km²). There were 1,680 housing units at an average density of 207.4/sq mi (80.1/km²). The racial makeup of the community was 93.86% White, 2.42% African American, 0.04% Native American, 0.53% Asian, 1.72% from other races, and 1.44% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 5.69% of the population.[1]
There were 1,120 households, out of which 27.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 62.3% were married couples living together, 6.7% had a female householder with no husband present, and 28.4% were non-families. 25.1% of all households were made up of individuals and 13.9% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.48 and the average family size was 2.93.[1]
In the CDP the population was spread out with 21.5% under the age of 18, 5.1% from 18 to 24, 24.7% from 25 to 44, 28.3% from 45 to 64, and 20.5% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 44 years. For every 100 females there were 98.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 94.9 males.[1]
The median income for a household in the community was $65,469, and the median income for a family was $71,611. Males had a median income of $51,103 versus $34,432 for females. The per capita income for the CDP was $35,042. About 2.0% of families and 5.6% of the population were below the poverty line, including 5.8% of those under age 18 and 3.4% of those age 65 or over.[1]
Albert Einstein and Cutchogue
An avid sailor, Albert Einstein once called Little Peconic Bay in Cutchogue "the most beautiful sailing ground I ever experienced."[2] In the summers of 1938 and 1939 he rented a cottage on Old Cove Road, now called West Cove Road, on Nassau Point, and spent many hours alone in a little sailboat he called Tineff (Yiddish for "worthless").
While in Cutchogue on August 2, 1939, pipe-smoking Einstein was visited by fellow Jewish physicists from Hungary Leo Szilard (who had produced a nuclear chain reaction in a laboratory at Columbia University) and Eugene Wigner (who both had been put up to it by Niels Bohr, and found his house after asking directions from a 7-year-old boy on the street), and signed the famous July 16 Letter to President Roosevelt, alerting him to the new developments in nuclear physics and hinting that the Germans might be working on an atomic bomb, urging him to launch his own program. The letter is widely credited with setting in motion the Manhattan Project, the US government effort that built the first atomic bomb.
After Szilard explained the concept of a nuclear chain reaction to him, Einstein gave the famous reply, "Daran habe ich gar nicht gedacht!" ("I really never thought of that before").[3]
Schools
References
- ^ a b c d e f "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ KILGANNON, COREY (21 July 2007). "No Sailor, for Sure, but He Had Relativity Down Cold". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2007/07/21/nyregion/21einstein.html. Retrieved 27 February 2011.
- ^ Isaacson, Walter (2008). Einstein: His Life and Universe. Simon and Schuster. pp. 472. ISBN 0743264738. http://books.google.com/books?id=cdxWNE7NY6QC&pg=PA472&lpg=PA472&dq=einstein+%22I+never+thought+of+that%22#v=onepage&q=einstein%20%22I%20never%20thought%20of%20that%22&f=false.
Town of Southold, New York County Villages CDP Hamlets Cutchogue · East Marion · Fishers Island · Laurel · Mattituck · New Suffolk · Orient · Peconic · SoutholdWebsite: southold.northfork.netCategories:- Southold, New York
- Census-designated places in New York
- Hamlets in New York
- Populated places in Suffolk County, New York
- Place names in New York of Native American origin
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.