- PARP2
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 2 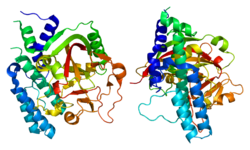
PDB rendering based on 1gs0.Available structures PDB 3KCZ, 3KJD Identifiers Symbols PARP2; ADPRT2; ADPRTL2; ADPRTL3; PARP-2; pADPRT-2 External IDs OMIM: 607725 MGI: 1341112 HomoloGene: 4004 GeneCards: PARP2 Gene EC number 2.4.2.30 Gene Ontology Molecular function • DNA binding
• NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity
• transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groupsCellular component • nucleus
• nucleoplasm
• nucleolusBiological process • DNA repair
• base-excision repair
• protein ADP-ribosylationSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 10038 11546 Ensembl ENSG00000129484 ENSMUSG00000036023 UniProt Q9UGN5 O88554 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001042618.1 NM_009632.2 RefSeq (protein) NP_001036083.1 NP_033762.1 Location (UCSC) Chr 14:
20.81 – 20.83 MbChr 14:
51.43 – 51.44 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PARP2 gene.[1][2][3]
This gene encodes poly(ADP-ribosyl)transferase-like 2 protein, which contains a catalytic domain and is capable of catalyzing a poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation reaction. This protein has a catalytic domain which is homologous to that of poly (ADP-ribosyl) transferase, but lacks an N-terminal DNA binding domain which activates the C-terminal catalytic domain of poly (ADP-ribosyl) transferase. The basic residues within the N-terminal region of this protein may bear potential DNA-binding properties, and may be involved in the nuclear and/or nucleolar targeting of the protein. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found.[3]
Interactions
PARP2 has been shown to interact with XRCC1.[4]
References
- ^ Johansson M (Aug 1999). "A human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase gene family (ADPRTL): cDNA cloning of two novel poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase homologues". Genomics 57 (3): 442–5. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5799. PMID 10329013.
- ^ Yelamos J, Schreiber V, Dantzer F (Apr 2008). "Toward specific functions of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-2". Trends Mol Med 14 (4): 169–78. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2008.02.003. PMID 18353725.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: PARP2 poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 2". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=10038.
- ^ Schreiber, Valérie; Amé Jean-Christophe, Dollé Pascal, Schultz Inès, Rinaldi Bruno, Fraulob Valérie, Ménissier-de Murcia Josiane, de Murcia Gilbert (Jun. 2002). "Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-2 (PARP-2) is required for efficient base excision DNA repair in association with PARP-1 and XRCC1". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (25): 23028–36. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202390200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11948190.
Further reading
- Bashford CL, Chance B, Lloyd D, Poole RK (1981). "Oscillations of redox states in synchronously dividing cultures of Acanthamoeba castellanii and Schizosaccharomyces pombe". Biophys. J. 29 (1): 1–11. Bibcode 1980BpJ....29....1B. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85114-9. PMC 1328658. PMID 7260241. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1328658.
- Berghammer H, Ebner M, Marksteiner R, Auer B (1999). "pADPRT-2: a novel mammalian polymerizing(ADP-ribosyl)transferase gene related to truncated pADPRT homologues in plants and Caenorhabditis elegans". FEBS Lett. 449 (2–3): 259–63. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00448-2. PMID 10338144.
- Amé JC, Rolli V, Schreiber V et al. (1999). "PARP-2, A novel mammalian DNA damage-dependent poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (25): 17860–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.25.17860. PMID 10364231.
- Still IH, Vince P, Cowell JK (2000). "Identification of a novel gene (ADPRTL1) encoding a potential Poly(ADP-ribosyl)transferase protein". Genomics 62 (3): 533–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.6024. PMID 10644454.
- Schreiber V, Amé JC, Dollé P et al. (2002). "Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-2 (PARP-2) is required for efficient base excision DNA repair in association with PARP-1 and XRCC1". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (25): 23028–36. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202390200. PMID 11948190.
- Saxena A, Wong LH, Kalitsis P et al. (2003). "Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 2 localizes to mammalian active centromeres and interacts with PARP-1, Cenpa, Cenpb and Bub3, but not Cenpc". Hum. Mol. Genet. 11 (19): 2319–29. doi:10.1093/hmg/11.19.2319. PMID 12217960.
- Malanga M, Althaus FR (2004). "Poly(ADP-ribose) reactivates stalled DNA topoisomerase I and Induces DNA strand break resealing". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (7): 5244–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.C300437200. PMID 14699148.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: Large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1356129.
- Maeda Y, Hunter TC, Loudy DE et al. (2006). "PARP-2 interacts with TTF-1 and regulates expression of surfactant protein-B". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (14): 9600–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M510435200. PMID 16461352.
- Chevanne M, Calia C, Zampieri M et al. (2007). "Oxidative DNA damage repair and parp 1 and parp 2 expression in Epstein-Barr virus-immortalized B lymphocyte cells from young subjects, old subjects, and centenarians". Rejuvenation Res 10 (2): 191–204. doi:10.1089/rej.2006.0514. PMID 17518695.
PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 14 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

