- Sde Dov Airport
-
Sde Dov Airport
שדה דב
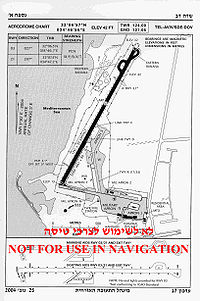
مطار سدي دوفAircraft on final approach at Sde Dov IATA: SDV – ICAO: LLSD Location of airport in Israel Summary Airport type Public Operator Israel Airports Authority Serves Israel Location Tel Aviv, Israel Elevation AMSL 42 ft / 13 m Coordinates 32°6′38.99″N 34°46′46.01″E / 32.1108306°N 34.7794472°E Website Runways Direction Length Surface ft m 03/21 5,712 1,741 Asphalt Statistics (2007) Total Passenger Movements 703,649 Total Aircraft Movements 36,427 Sde Dov Airport (Hebrew: שדה דב, lit. Dov Field, Arabic: مطار سدي دوف), also known as Dov Hoz Airport (Hebrew: נמל התעופה דב הוז, Nemal HaTe'ufa Dov Hoz, Arabic: مطار دوف هوز) (IATA: SDV, ICAO: LLSD) is an airport located in Tel Aviv, Israel which mainly handles scheduled domestic flights to Eilat and (Ovda), northern Israel (Haifa and the Galilee), and the Israeli Golan Heights.[1] It is Tel Aviv's largest airport and the second largest in the area, after Ben Gurion International Airport. The airport is named after Dov Hoz, one of the pioneers of Jewish aviation. The airport will close at some point in the future after an agreement was struck repurposing land which houses it for luxury residential apartments. Commercial flights will move to Ben Gurion Airport near the city of Lod, southeast of Tel Aviv.[2] The airport is a focus city for Arkia Israel Airlines and Israir Airlines.
Contents
History
Early history
In 1937, the mayor of Tel Aviv Israel Rokach asked the British mandate authorities for permission to create an airport in Palestine, promising to solve the transportation problem of Jews during the Arab revolt of 1936–39 when travelling around the region by ground was difficult and dangerous. Works began on a plot of land north of the Yarkon River, Tel Aviv in 1938 and once completed, the airport served regular flights to Haifa, with the option of flights to Beirut.[3] In 1940, the airport's name was changed to Sde Dov, in memory of Dov Hoz, one of the pioneers of Jewish aviation.[4]
In the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, the airport served as a base to the Israeli Air Force. It was a central base, home to 21 aircraft at the time. The first military flight was made in December, 1947, when Pinchas Ben Porat flew an RWD-13 to Beit Eshel to rescue an injured soldier.[5][6]
After the war
Following the 1948 war the Arab orchards to the east of Tel Aviv were opened for development, and the military started using the Sde Dov airport on a regular basis. The airport regained its commercial operations, initially serving domestic flights, mostly to single customers, on Piper Cub aircraft. It later expanded operations to scheduled service on larger aircraft to various parts of Israel. As a result of the land availability, an additional, north–south, runway was built with no opposition. By 1960, land in Tel Aviv became scarce, and the municipality demanded that the airport be relocated northward, so as to allow residential development in its place. However, a committee that investigated in 1961 the options for such a relocation found no feasible site in proximity to Tel Aviv and suggested that flights be moved to Lod airport (now known as Ben Gurion Airport), and that road access from Tel Aviv to Lod is improved. This option, however, was blocked by the Israel Defense Forces.[3]
The government set up a second committee in 1968 who suggested that the old east–west runway be closed and the airport's area reduced, allowing for development to the east of the airport. They suggested that this is replaced by a new runway in the sea, adjacent to the beach. The runway was closed, and a high density upper-middle income neighborhood was built to the east of the airport, although the new runway was never constructed due to the high cost involved.[3]
As the new residential area suffered from aircraft noise, residents joined in the demand that the airport be relocated. Despite this, the number of flights to the airport increased as the newly formed Israel Airports Authority strived to reduce congestion at Ben Gurion Airport by shifting all domestic turbo-prop flights to Sde Dov. Once again, the only feasible alternative proposed at this point was to build a runway in the sea and again, the high cost of this project meant that it never happened. This was a large issue in the area during the whole of the 1980s.[3]
Recent history and relocation plans
The early 1990s saw a rapid rise in land values in the Tel Aviv area following the massive immigration wave from the ex-Soviet Union and the rapid economic growth fueled by the peace prospects in 1993–1996 and subsequent hi-tech boom. This brought the issue of relocation back to light.[3] Despite this, however, in 1997, Sde Dov was declared an International Airport for private flights.[7] In the future, the Main Terminal, the aircraft parking aprons and the aircraft hangars will be transferred to an area near the Tel Baruch Beach which will enable the construction of new traffic routes to North Tel Aviv.[8]
Statistics for Sde Dov Airport
(not including Air Force traffic) [9]Year Total Passengers Total operations 2000 831,748 37,489 2001 879,922 38,884 2002 808,774 38,624 2003 757,817 37,674 2004 666,879 35,716 2005 662,951 34,687 2006 628,888 31,958 2007 703,649 36,427 The issue remained unresolved until late 2006 when it was announced that the airport would be vacated to make way for residential redevelopment.[10] It is unclear, however, when this will actually take place as the Tel Aviv municipality opposes closing the airport. Initially the plan was to relocate the entire airport (runway as well as terminal facilities) onto an artificial island to be built offshore.[11]
When Sde Dov does close, its military terminal would be relocated to the Palmachim Airbase and civilian activities would be relocated to Ben Gurion Airport.[2] With capacity at Ben Gurion projected to reach a maximum over the next few decades however, the concept of building an airport offshore in the Tel Aviv region may yet be revived in the future. Sde Dov itself is operating near to capacity, however, with annual passenger movements around 700,000 and a potential capacity of 950,000.[7]
The airport today
Today, Sde Dov Airport mostly handles domestic flights within Israel, as well as light-aircraft activity and limited international flights, mostly to nearby Cyprus. The airport has two terminals. The IAF still takes up about 40% of overall movements (take-offs and landings), and uses the airport as a base for some of its operations, as well as a convenient hub for military and government passenger traffic. Due to its location in the centre of Israel, air-force and civilian pilots alike cross the airspace controlled by Sde Dov's air traffic control tower from north to south and vice versa in order to reach their destination, without landing at Sde Dov. This increases significantly the air traffic density above and around the airport, and efforts have been made to keep "crossing traffic" away from the approach and departure patterns in order to minimise their effect on air traffic safety at Sde Dov. The airport has seven check-in desks and 45 aircraft stands.[7]
Airlines and destinations
Airlines Destinations Arkia Israel Airlines Eilat, Haifa, Ovda, Dead Sea (Coming Soon) Ayit Aviation and Tourism Rosh Pina Elrom Airways Ein Yahav Israir Eilat External links
References
- ^ "Scheduled Flights". Israel Airports Authority. http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/Templates/InsidePages/ScheduleFlightsTemplate.aspx?NRMODE=Published&NRORIGINALURL=%2fRashat%2fen-US%2fAirports%2fSdeDov%2fInformationforTravelers%2fScheduleFlights%2ehtm&NRNODEGUID=%7b0AE46CA1-7A07-4442-A40F-85DC202EE736%7d&NRCACHEHINT=Guest. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- ^ a b "Tel Aviv airport to make way for luxury project". http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3420369,00.html. Retrieved 2007-07-03.
- ^ a b c d e "The Sde Dov Airport". Hebrew University. http://geography.huji.ac.il/emppp/israel%20conflict/envcnf.apn.htm. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- ^ Huldai: Sde Dov airport is here to stay for at least 15 years, Haaretz
- ^ Aloni, Shlomo (2001). Arab-Israeli Air Wars 1947-82. Osprey Publishing. p. 7. ISBN 1841762946. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=mO02czQ9jyYC&pg=PA7&dq=sde+dov+airport+Pinchas+Ben+Porat&sig=oA-Nt_POUEUNySyQacSOwRs43Fc.
- ^ Cohen, Eliezer (1993). Israel's Best Defense. New York: Orion Books. pp. 504. ISBN 0-517-587904.
- ^ a b c "Sde Dov (Dov Hoz) Airport". Airports Worldwide. http://www.airports-worldwide.com/israel/sde_dov_israel.htm. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- ^ "Development Plans". IAA. http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/SdeDov/AbouttheAirport/DevelopmentPlans/. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- ^ "Sde Dov Airport Statistics". http://www.iaa.gov.il/Rashat/en-US/Airports/SdeDov/AbouttheAirport/Statistics/. Retrieved 2007-05-05.
- ^ "Sde Dov to be vacated, state gets half of Big Bloc". Haaretz. http://www.haaretz.com/hasen/spages/793988.html. Retrieved 2007-05-05.
- ^ "An Airport on an Artificial Island". http://telavivinf.com/info/infoitem.asp?item=345&lang=eng. Retrieved 2007-05-05.
Airports Border Terminals Egypt: Nitzana · Taba
Gaza Strip: Karni · Kerem Shalom
Jordan: Allenby Bridge · Arava · Jordan RiverDefunct/Former Properties  Israeli airports
Israeli airportsInternational Domestic Bar Yehuda · Be'er Sheva · Eilat · Ein Yahav · Fik · Haifa · Herzliya · Megiddo · Mitzpe Ramon · Rosh Pina Ben Ya'akov · Sde Dov · Yotvata
Military Former Categories:- Airports in Israel
- Transport in Tel Aviv
- Israeli Air Force bases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.