- Bromobimane
-
Bromobimane 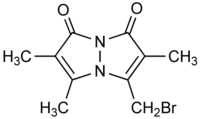 3-(bromomethyl)-2,5,6-trimethyl-1H,7H-
3-(bromomethyl)-2,5,6-trimethyl-1H,7H-
pyrazolo[1,2-a]pyrazole-1,7-dioneOther namesBromobimane, mBBrIdentifiers CAS number 71418-44-5 PubChem 114810 ChemSpider 102775 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C1\C(=C(/N2/C(=C(\C(=O)N12)C)CBr)C)C
Properties Molecular formula C10H11BrN2O2 Molar mass 271.11 g mol−1 Melting point 152–154 °C
Solubility in water in MeOH, DMF, DMSO Hazards Main hazards alkylating agent  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Bromobimane (or monobromobimane) is a heterocyclic compound and bimane dye that is used as a reagent in biochemistry. It alkylates thiol groups, replacing the H with a fluorescent tag (λemission = 478 nm). Its alkylating properties are comparable to iodoacetamide.[1]
References
- ^ Paul C. Chinn, Vincent Pigiet, and Robert C. Fahey (1986). "Determination of thiol proteins using monobromobimane labeling and high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis: Application to Escherichia coli thioredoxin". Analytical Biochemistry 159 (1): 143–149. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(86)90319-2. PMID 3544950.
Categories:- Alkylating agents
- Organobromides
- Lactams
- Hydrazides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
