- Forskolin
-
Forskolin 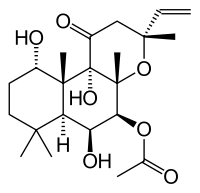 (3R,4aR,5S,6S,6aS,10S,10aR,10bS)-6,10,10b-trihydroxy-3,4a,7,7,10a-pentamethyl-1-oxo-3-vinyldodecahydro-1H-benzo[f]chromen-5-yl acetate
(3R,4aR,5S,6S,6aS,10S,10aR,10bS)-6,10,10b-trihydroxy-3,4a,7,7,10a-pentamethyl-1-oxo-3-vinyldodecahydro-1H-benzo[f]chromen-5-yl acetateIdentifiers CAS number 66428-89-5 PubChem 47936 ChemSpider 43607 
UNII 1F7A44V6OU 
DrugBank DB02587 ChEBI CHEBI:42471 
ChEMBL CHEMBL52606 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(=O)O[C@H]1[C@H]([C@@H]2[C@]([C@H](CCC2(C)C)O)([C@@]3([C@@]1(O[C@@](CC3=O)(C)C=C)C)O)C)O
- InChI=1S/C22H34O7/c1-8-19(5)11-14(25)22(27)20(6)13(24)9-10-18(3,4)16(20)15(26)17(28-12(2)23)21(22,7)29-19/h8,13,15-17,24,26-27H,1,9-11H2,2-7H3/t13-,15-,16-,17-,19-,20-,21+,22-/m0/s1

Key: OHCQJHSOBUTRHG-KGGHGJDLSA-N
InChI=1/C22H34O7/c1-8-19(5)11-14(25)22(27)20(6)13(24)9-10-18(3,4)16(20)15(26)17(28-12(2)23)21(22,7)29-19/h8,13,15-17,24,26-27H,1,9-11H2,2-7H3/t13-,15-,16-,17-,19-,20-,21+,22-/m0/s1
Key: OHCQJHSOBUTRHG-KGGHGJDLBB
Properties Molecular formula C22H34O7 Molar mass 410.5 g mol−1 Solubility soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, chloroform and DMSO[1]  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Forskolin (also called Coleonol) is a labdane diterpene that is produced by the Indian Coleus plant (Coleus forskohlii). Forskolin is commonly used to raise levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP) in the study and research of cell physiology. Forskolin resensitizes cell receptors by activating the enzyme adenylyl cyclase and increasing the intracellular levels of cAMP. cAMP is an important signal carrier necessary for the proper biological response of cells to hormones and other extracellular signals. It is required for cell communication in the hypothalamus/pituitary gland axis and for the feedback control of hormones. It[clarification needed] acts by activating protein kinase A. Further reading: function of protein kinase A
Contents
Biosynthesis
- As with other members of the large diterpene family of natural products, forskolin is derived from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). Forskolin, however, contains some unique functional elements, key among them is the presence of a tetrahydopyran derived heterocyclic ring. This ring is synthesized after the formation of the trans-fused carbon ring systems are formed by a carbocation mediated cyclization. The remaining tertiary carbocation is quenched by a molecule of water. After deprotonation, the remaining hydroxyl group is free to form the heterocyclic ring. This cyclization can occur either by attack of the alcohol oxygen onto the allylic carbocation formed by loss of diphosphate, or by an analogous SN2' like displacement of the diphosphate.[2] This forms the core ring system A of forskolin.
- The remaining modifications of the core ring system A can putatively be understood as a series of oxidation reactions to form a poly-ol B which is then further oxidized and esterified to form the ketone and acetate ester moieties seen in forskolin. However, because the biosynthetic gene cluster has not been described this putative synthesis could be incorrect in the sequence of oxidation/esterification events, which could occur in almost any order.
Potential medical use
- Applied with rolipram, forskolin provides a route[further explanation needed] to inhibition of colon cancer cell growth and survival. [3] These two drugs also work together to induce long-term potentiation in neuronal populations. [4]
- Forskolin is a vasodilator.
- To date, there have been more than two clinical studies examining the effectiveness of forskolin as a weight loss aid. Only one has been subject to peer-review and published in a medical journal. This clinical study also observed forskolin's role in significantly increasing lean mass, bone mass, and testosterone in the subjects involved.[5] This research has led to companies marketing forskolin as a bodybuilding supplement.
- Forskolin may be helpful to control the underlying cause of glaucoma[citation needed]. The sometimes successful use of forskolin to reduce intraocular pressure may be due to its unique ability to stimulate adenylate cyclase activity and increase cAMP which regulates and activates critical enzymes required for the cellular energy required to move fluid out of the eye.
- Increase skin's natural resistance to burning under UV light (see links below)
- Stimulate a tanning response when applied topically[citation needed].
- Reduce urinary tract infections and enhance the ability of antibiotics to kill bacteria that normally survive.
Forskolin can also be used to promote nerve repair by increasing cAMP concentrations. Forskolin can activate or upregulate the proliferation of Schwann cells in culture, together with Fibroblast growth factor or Transforming Growth Factor-Beta.
Various experimental studies are underway in using Forskolin as an adjuvant in treatment for diseases such as Parkinsons and/or nerve damage caused by trauma/accident.
References
- ^ http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/etc/medialib/docs/Sigma/Product_Information_Sheet/f6886pis.Par.0001.File.tmp/f6886pis.pdf
- ^ P.M. Dewick Medicinal Natural Products 3rd Ed. 2009, 232
- ^ McEwan DG, Brunton VG, Baillie GS, Leslie NR, Houslay MD, Frame MC. (June 2007) "Chemoresistant KM12C Colon Cancer Cells Are Addicted to Low Cyclic AMP Levels in a Phosphodiesterase 4-Regulated Compartment via Effects on Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase.", Cancer Research Volume 67, Issue 11.
- ^ Nikolai Otmakhov, Lena Khibnik, Nonna Otmakhova, Stephen Carpenter, Shervin Riahi, Brent Asrican and John Lisman. (January 2004) "Forskolin-Induced LTP in the CA1 Hippocampal Region Is NMDA Receptor Dependent", Journal of Neurophysiology Volume 91, Issue 1.
- ^ Michael P. Godard, Brad A. Johnson, Scott R. Richmond (August 2005) "Body Composition and Hormonal Adaptations Associated with Forskolin Consumption in Overweight and Obese Men", Obesity Research Vol. 13 No. 8.
- Aaron H. Bubolz, Hongwei Li, Qingping Wu, and Yanping Liu. Enhanced oxidative stress impairs cAMP-mediated dilation by reducing Kv channel function in small coronary arteries of diabetic rats. Article
External links
Categories:- Diterpenes
- Alkenes
- Ketones
- Alcohols
- Acetate esters
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
