- Charge at Krojanty
-
Battle of Krojanty Part of the Invasion of Poland 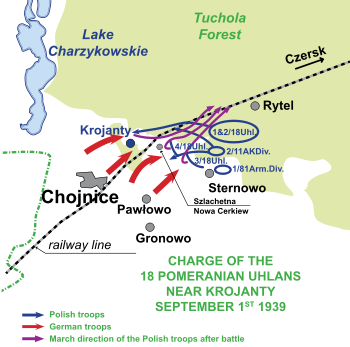
Date September 1, 1939 Location Near Krojanty, Pomerania Result Indecisive Belligerents  Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany Poland
PolandCommanders and leaders  Hans Gollnick
Hans Gollnick
 Mauritz von Wiktorin
Mauritz von Wiktorin Kazimierz Mastalerz †
Kazimierz Mastalerz †Strength ~800
76th Infantry Regiment
Armored reconnaissance vehicles
30 guns~250
18th Pomeranian Uhlans
1st & 2nd squadrons,
1 platoon of 3rd and 4th sq.Casualties and losses 11 killed
9 wounded19-25 killed
40-50 wounded- Westerplatte
- Danzig
- The Border
- Krojanty
- Chojnice
- Grudziądz
- Lasy Królewskie
- Mokra
- Danzig Bay
- Pszczyna
- Mława
- Tuchola Forest
- Jordanów
- Borowa Góra
- Mikołów
- Węgierska Górka
- Tomaszów Mazowiecki
- Wizna
- Łódź
- Przemyśl
- Piotrków
- Różan
- Radom
- Łomża
- Wola Cyrusowa
- Warsaw
- Gdynia
- Hel
- Bzura
- Jarosław
- Kałuszyn
- Węgrów
- Wilno
- Lwów
- Modlin
- Kobryń
- Brześć
- Kępa Oksywska
- Tomaszów Lubelski
- Wólka Węglowa
- Kampinos Forest
- Janów, Wereszyca, and Hołosko
- Krasnystaw
- Grodno
- Łomianki
- Sarny
- Cześniki
- Krasnobród
- Władypol
- Szack
- Wytyczno
- Parczew
- Kock
The Charge, battle[1] or skirmish of Krojanty[2] was a cavalry charge that occurred during the Invasion of Poland in the Second World War. It took place on the evening of September 1, 1939, near the Pomeranian village of Krojanty. Polish soldiers advanced east along the former Prussian Eastern Railway to railroad crossroads 7 kilometres from the town of Chojnice (Konitz) where elements of the Polish cavalry attacked the German Wehrmacht infantry battalion. During the attack the cavalry received machine gun fire from German armoured personnel carriers stationed nearby and was forced to retreat. Delay of the German advance is claimed as successful completion of the Poles' mission.
Happening on the first day of the war, it was one of its first clashes, and part of the larger Battle of Tuchola Forest. The incident became notable as reporters visiting the site soon after saw the dead bodies of horses and cavalrymen which led to false reports of Polish cavalry attacking German tanks. Nazi propaganda[3] took advantage of this, suggesting that the Poles attacked intentionally, believing that the German still had the dummy tanks the Versailles treaty restrictions had permitted them. The scene of Polish cavalry charging the Panzers with their lances has become a myth.[4]
Contents
Before the battle
Polish units were engaged in battle from 0500 against elements of German 76th Infantry Regiment (Colonel Hans Gollnick) of 20th Motorised Division under Lt. Gen. Mauritz von Wiktorin, which operated on the left (northern) flank of XIX Panzer Corps under Gen. Heinz Guderian. Early in the day Polish cavalry had intercepted German infantry moving towards the Free City of Danzig (Gdańsk) and slowed their progress.
At 0800 the Germans broke through Polish Border Guard units south of the Polish cavalry, which forced the Polish units in the area to start a retreat towards a secondary defence line at the river Brda (Brahe). 18th Pomeranian Uhlans Regiment (18. Pułk Ułanów Pomorskich) was ordered to cover the retreat.
The battle
The 18th Pomeranian Uhlans spotted a group of German infantry resting in a clearing in the Tuchola Forest heath near the railroad crossroads of Chojnice - Runowo Pomorskie line.
Colonel Kazimierz Mastalerz decided to take the enemy by surprise and ordered Eugeniusz Świeściak, commander of the 1st squadron, to execute a cavalry charge at 1900 hours, leading two squadrons, about 250 strong. Most of the two other squadrons, and their TKS/TK-3 tankettes, were held back in reserve.
The charge was successful: the German infantry unit was dispersed, and the Poles occupied the clearing. However German armored reconnaissance vehicles appeared from the forest road, probably part of Aufklärungs-Abteilung 20, and soon the Polish units came under heavy machine gun fire, probably from Leichter Panzerspähwagen equipped with MG 34, or Schwerer Panzerspähwagen equipped also with a 20 mm gun. The Poles were completely exposed and began to gallop for cover behind a nearby hillock.[5]
Commander Świeściak was killed, as was Mastalerz, who tried to save him. About a third of the Polish force was dead or wounded. On the other hand, the German advance was halted long enough to allow the withdrawal of Polish 1st Rifle battalion and National Defence battalion Czersk from the nearby battle of Chojnice.
The Polish cavalry charge impressed the Germans and caused a delay in the offensive of the German 20th Motorised Infantry Division which considered a tactical retreat. This was however prevented by personal intervention of Gen. Guderian, who in his memoirs stated that he encountered his staff "wearing helmets, preparing an anti-tank gun for a possible Polish cavalry attack,"[6] and that "the panic of the first day of war was overcome quickly".[7]
-
German Schwerer Panzerspähwagen
Aftermath and the myth
Main article: Polish cavalry#Cavalry charges and propagandaThe Polish cavalry charge stopped the German pursuit for the day, and the units of Czersk Operational Group were able to withdraw southwards unopposed. Also, it took the Germans several hours to reorganise and continue the advance. On September 2, 1939, the 18th Pomeranian Uhlans Regiment was decorated by Gen. Grzmot-Skotnicki, the commander of the Operational Group, with his own Virtuti Militari medal for valour shown in this combat.
The same day, German war correspondents were brought to the battlefield, together with two journalists from Italy. They were shown the corpses of Polish cavalrymen and their horses, as well as German tanks that had arrived at the place after the battle. One of the Italian correspondents, Indro Montanelli, sent home an article, in which he described the bravery and heroism of Polish soldiers, who charged German tanks with sabres and lances. Although such a charge did not happen and there were no tanks used during the combat, the myth was used by German propaganda during the war. German propaganda magazine Die Wehrmacht reported on 13 September that the Poles had gravely underestimated German weapons, as Polish propaganda had suggested that German armored vehicles were only covered with sheet metal, leading to a grotesque attack. After the end of World War II it was still used by Soviet propaganda as an example of stupidity of pre-war Polish commanders, who allegedly did not prepare their country for the war and instead wasted the blood of their soldiers.
George Parada states:[8]
Contrary to German propaganda, Polish cavalry brigades never charged tanks with their sabres or lances as they were equipped with anti-tank weapons such as 37 mm Bofors wz.36 (exported to UK as Ordnance Q.F. 37 mm Mk I) antitank guns, that could penetrate 26 mm of armour at 600 m at 30 degrees. The cavalry brigades were in the process of being reorganized into motorized brigades.
Another weapon was anti-tank rifle model 1935 (karabin przeciwpancerny wz. 35). Its calibre was 7.92 mm and it could penetrate 15 mm of armour at 300 m at 30 degrees. In 1939, the Germans were mainly equipped with the small Panzer I and Panzer II models which were vulnerable to such weapons.
References
- ^ Translation of Polish term bitwa pod Krojantami as used in Marek Getter, Adam Tokarz, Wrzesień 1939 w książce, prasie i filmie : poradnik bibliograficzny, Stowarzyszenie Bibliotekarzy Polskich, 1970, p.101 and others
- ^ Zaloga describes the battle as small skirmish near the hamlet of Krojanty. Steven J. Zaloga, The Polish Army 1939-45 (Men-at-Arms 117), p.8
- ^ Cover of Hitler Youth magazine Der Pimpf, Nationalsozialistische Jungenblätter, 10/1939, Archive.org
- ^ If a single image dominates the popular perception of the Polish campaign of 1939, it is the scene of Polish cavalry bravely charging the Panzers with their lances. Like many other details of the campaign, it is a myth that was created by German wartime propaganda and perpetuated by sloppy scholarship. Yet such myths have also been embraced by the Poles themselves as symbols of their wartime gallantry, achieving a cultural resonance in spite of their variance with the historical record. - Steven J. ZALOGA: Poland 1939 - The birth of Blitzkrieg. Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2002. Panzerworld.net
- ^ Steven J. Zaloga, The Polish Army 1939-45 (Men-at-Arms 117), p.9, Osprey Publishing, Oxford 1982, S. 8
- ^ Heinz Guderian: Erinnerungen eines Soldaten, "Die lange Straße war leer. Weit und breit fiel kein Schuß. Umso erstaunter war ich, als ich unmittelbar vor Zahn angerufen wurde und die Männer meines Stabes im Helm damit beschäftigt fand, eine Panzerabwehrkanone in Stellung zu bringen. Auf meine Frage, was sie dazu veranlaßt hätte, erhielt ich die Antwort, polnische Kavallerie sei im Anmarsch und müsse jeden Augenblick eintreffen.", 1951, p. 63, Books.Google.com
- ^ Heinz Guderian: Erinnerungen eines Soldaten, "Ich setzte mich nun an den Anfang des in der Nacht herausgezogenen Regiments und führte es selbst bis an den Kamionka-Ubergang nördlich Groß-Klonia, um es von dort auf Tuchel anzusetzen. Der Angriff der 2. (mot.) Division kam nunmehr schnell in Fluß. Die Panik des ersten Kriegstages war überwunden. Die Panzer-Aufklärungs-Abteilung 3 war in der Nacht bis an die Weichsel gelangt. Auf dem Gutshof Poledno in der Nähe von Schwetz hatte sie leider durch Unvorsichtigkeit empfindliche ...", 1951, p. 63 [1]
- ^ George Parada, Invasion of Poland (Fall Weiss), Achtungpanzer.com
Further reading
- Janusz Piekalkiewicz: Polenfeldzug - Hitler und Stalin zerschlagen die Polnische Republik, Augsburg 1997.
External links
- The Mythical Polish Cavalry Charge
- (Polish) Detailed account of the battle
- (Polish) History of 18th Uhlans Regiment
Coordinates: 53°43′32″N 17°37′55″E / 53.72556°N 17.63194°E
Categories:- Battles of the Polish September Campaign
- Polish cavalry
- Cavalry charges
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




