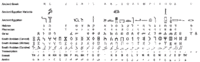- Old South Arabian
-
Old South Arabian Geographic
distribution:Yemen Linguistic classification: Afro-Asiatic Subdivisions: —Old South Arabian (or Epigraphic South Arabian, or Sayhadic) is the term used to describe four extinct, closely related languages spoken in the far southern portion of the Arabian Peninsula. There were a number of other Sayhadic languages (e.g. Awsanic), of which very little evidence survived, however. All those languages were distinct from Classical Arabic, which developed among Arab tribes of the regions of Najd and Hijaz, and most Semitic languages.
The four main Old South Arabian languages were Sabaic, Minaeic (or Madhabic), Qatabanic, and Hadramitic. According to Alice Faber (based on Hetzron's work)[1], together with Ethiopian Semitic languages (such as the contemporary Ge'ez language) and the Modern South Arabian languages (not descended from Old South Arabian but from a sister language), they formed the western branch of the South Semitic languages.
Old South Arabian had its own writing system, the South Arabian alphabet, concurrently used for proto-Ge'ez in the Kingdom of D`mt, ultimately sharing a common origin with the other Semitic abjads, the Proto-Sinaitic alphabet.
The arrival of Islam virtually disintegrated Old South Arabian, as Classical Arabic became the lingua franca of the region. Today, Old South Arabian is extinct, only existing in a few ancient texts and inscriptions. It has, however, contributed to the local Arabic dialects of the region in much the same way that Coptic has contributed to the Egyptian dialect of Arabic.
Bibliography
- A. F. L. Beeston: Sabaic Grammar, Manchester 1984 ISBN 0-9507885-2-X.
- Maria Höfner: Altsüdarabische Grammatik (Porta Linguarum Orientalium, Band 24) Leipzig, 1943.
- Leonid Kogan and Andrey Korotayev: Sayhadic Languages (Epigraphic South Arabian). Semitic Languages. London: Routledge, 1997, p. 157-183.
- N. Nebes, P. Stein: Ancient South Arabian, in: Roger D. Woodard (Hrsg.): The Cambridge encyclopedia of the World's ancient languages Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 2004 ISBN 0-521-56256-2 S. 454-487 (neuester grammatischer Überblick mit Bibliographie).
References
See also
- Modern South Arabian
- South Arabian alphabet
Categories:- Old South Arabian languages
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.