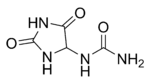
- Diazolidinyl urea
-
Diazolidinyl urea 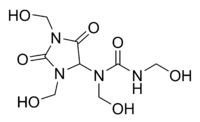 Correct new structure: 1,3-bis(hydroxymethyl)-1-(1,3,4-tris(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dioxoimidazolidin-4-yl)urea
Correct new structure: 1,3-bis(hydroxymethyl)-1-(1,3,4-tris(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dioxoimidazolidin-4-yl)urea
Erroneous old structure: 1-(1,3-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dioxoimidazolidin-4-yl)-1,3-bis(hydroxymethyl)ureaOther namesDiazolidinylurea
Germall IIIdentifiers CAS number 78491-02-8 
PubChem 62277 ChemSpider 56078 
UNII H5RIZ3MPW4 
EC number 278-928-2 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C1N(C(=O)C(N(C(=O)NCO)CO)N1CO)CO
Properties Molecular formula C8H14N4O7 Molar mass 278.22 g/mol Hazards[1] GHS pictograms 
GHS signal word WARNING GHS hazard statements H317 GHS precautionary statements P261, P272, P280, P302+352, P333+313, P321, P363, P501 EU Index not listed Related compounds Related compounds Imidazolidinyl urea  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Diazolidinyl urea is an antimicrobial preservative used in cosmetics. It is chemically related to imidazolidinyl urea which is used in the same way. Diazolidinyl urea acts as a formaldehyde releaser.
It is used in many cosmetics, skin care products, shampoos and conditioners, as well as a wide range of products including bubble baths, baby wipes and household detergents. Diazolidinyl urea is found in the commercially available preservative Germaben.
Commercial diazolidinyl urea is a mixture of different formaldehyde addition products including polymers.[2]
Contents
Chemistry
Synthesis
Diazolidinyl urea is produced by the chemical reaction of allantoin and formaldehyde in the presence of sodium hydroxide solution and heat. The reaction mixture is then neutralized with hydrochloric acid and evaporated:
Structure
Diazolidinyl urea was poorly characterized until recently and still has a wrong CAS structure assigned to it. New data show that the hydroxymethyl functional group of the imidazolidine ring is attached to the carbon, not the nitrogen atom:[2]
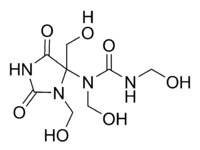

Hoeck structure previous structure Safety
Some people have a contact allergy to imidazolidinyl urea causing dermatitis.[3] Such people are often also allergic to diazolidinyl urea.
References
- ^ HSNO Chemical Classification Information Database (New Zealand Environmental Risk Management Authority), http://www.ermanz.govt.nz/Chemicals/ChemicalDisplay.aspx?SubstanceID=4706, retrieved 2009-09-06.
- ^ a b Lehmann, Søren Vig; Hoeck, Ulla; Breinholdt, Jens; Olsen, Carl Erik; Kreilgaard, Bo (2006). "Characterization and chemistry of imidazolidinyl urea and diazolidinyl urea". Cont. Dermat. 54 (1): 50–58. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2006.00735.x. PMID 16426294.
- ^ Review of toxicological data (NTP NIEHS)
External links
- "Diazolidinyl urea". MEKOS Laboratories AS. http://www.orion-health.co.nz/Info%20Cards/Diazolidinyl%20Urea.htm. Retrieved 2007-03-11.
Categories:- Preservatives
- Disinfectants
- Ureas
- Hydantoins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.