- Cystamine
-
Cystamine 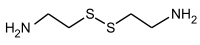 2,2'-Dithiobis(ethylamine)Other names2,2'-Dithiobisethanamine
2,2'-Dithiobis(ethylamine)Other names2,2'-Dithiobisethanamine
2-Aminoethyl disulfide
DecarboxycystineIdentifiers Abbreviations AED CAS number 51-85-4 
PubChem 2915 ChemSpider 2812 
UNII R110LV8L02 
ChEMBL CHEMBL61350 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - S(SCCN)CCN
Properties Molecular formula C4H12N2S2 Molar mass 152.28 g/mol[1] Appearance Viscous oil Boiling point Decomposes
Solubility in water Miscible Solubility in Ethanol Soluble  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cystamine is an organic disulfide. It is formed when cystine is heated, the result of decarboxylation. Cystamine is an unstable liquid and is generally handled as the dihydrochloride salt, C4H12N2S2·2HCl, which is stable to 203-214 °C at which point it decomposes. Cystamine is toxic if swallowed or inhaled and potentially harmful by contact.
References
- ^ Merck Index, 12th Edition, 2846.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
