- Messier 79
-
Messier 79 
Observation data (J2000 epoch) Class V Constellation Lepus Right ascension 05h 24m 10.59s[1] Declination -24° 31′ 27.3″[1] Distance 41 kly[citation needed] (12 kpc) Apparent magnitude (V) +8.56[1] Apparent dimensions (V) 8,7' Physical characteristics Other designations M79, NGC 1904, GCl 10[1] See also: Globular cluster, List of globular clusters Messier 79 (also known as M79 or NGC 1904) is a globular cluster in the Lepus constellation. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1780. M79 is at a distance of about 41,000 light years away from Earth and 60,000 light years away from the Galactic Center.
Like Messier 54 (the other extragalactic globular on Messier's list), it is thought that M79 is not native to the Milky Way galaxy at all, but instead to the Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy which is currently experiencing a very close encounter with the Milky Way—one it is unlikely to survive intact. This is, however, a contentious subject as astronomers are still debating the nature of the Canis Major dwarf galaxy itself.[2]
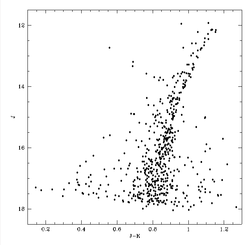
Color-magnitude diagram
This color-magnitude diagram was made using infrared images of Messier 79 in two bands- J and K. J-band magnitude is plotted along y-axis and color, J-K, is plotted along x-axis. The image was created using Peter Stetson standard for clouded-field photometry, Daophot.[3]
From the diagram it is evident that, most of the stars in this cluster are red giants. The elongated branch is Red giant branch. Stars in the upper left sequence extending outwards from the branch and some stars at the very low temperature end are actually foreground stars.
Altogether 3 regions of HRD are present here: low mass end of the main sequence, complete red giant branch and horizontal branch. In infrared red stars are brighter, that's why red stars are brighter in this diagram making the lower main sequence shallower than usual. On the other hand the horizontal branch becomes steeper in this diagram due to IR effects (on the HB the blue end is fainter and the red end is brighter).
References
- ^ a b c d "SIMBAD Astronomical Database". Results for NGC 1904. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/Simbad. Retrieved 2006-11-17.
- ^ López-Corredoira, M.; Momany, Y.; Zaggia, S.; Cabrera-Lavers, A. (2007). "Re-affirming the connection between the Galactic stellar warp and the Canis Major over-density". Astronomy and Astrophysics 472 (3): l47. arXiv:0707.4440. Bibcode 2007A&A...472L..47L. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20077813.
- ^ This diagram is made by Astromundus students attending the lectures and workshop of Peter Stetson, the writer of Daophot, standard codes for clouded-filed photometry. Date: June 2011, University of Rome Tor Vergata
External links
- Messier 79, SEDS Messier pages
- Messier 79, Galactic Globular Clusters Database page
- Messier 79 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
Messier objects List M1 · M2 · M3 · M4 · M5 · M6 · M7 · M8 · M9 · M10 · M11 · M12 · M13 · M14 · M15 · M16 · M17 · M18 · M19 · M20 · M21 · M22 · M23 · M24 · M25 · M26 · M27 · M28 · M29 · M30 · M31 · M32 · M33 · M34 · M35 · M36 · M37 · M38 · M39 · M40 · M41 · M42 · M43 · M44 · M45 · M46 · M47 · M48 · M49 · M50 · M51 · M52 · M53 · M54 · M55 · M56 · M57 · M58 · M59 · M60 · M61 · M62 · M63 · M64 · M65 · M66 · M67 · M68 · M69 · M70 · M71 · M72 · M73 · M74 · M75 · M76 · M77 · M78 · M79 · M80 · M81 · M82 · M83 · M84 · M85 · M86 · M87 · M88 · M89 · M90 · M91 · M92 · M93 · M94 · M95 · M96 · M97 · M98 · M99 · M100 · M101 · M102 · M103 · M104 · M105 · M106 · M107 · M108 · M109 · M110See also  Book:Messier objects ·
Book:Messier objects ·  Category:Messier objects
Category:Messier objects  Portal:Astronomy
Portal:AstronomyCoordinates:
 05h 24m 10.59s, −24° 31′ 27.3″Categories:
05h 24m 10.59s, −24° 31′ 27.3″Categories:- Globular clusters
- Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy
- Lepus constellation
- Messier objects
- NGC objects
- Star cluster stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.