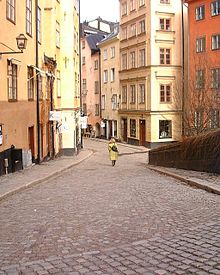- Österlånggatan
-
Österlånggatan (Swedish: Eastern Long Street) is a street in Gamla stan, the old town of Stockholm, Sweden. Stretching southward from Slottsbacken to Järntorget, it forms a parallel street to Baggensgatan and Skeppsbron. Major sights include the statue of Saint George and the Dragon on Köpmanbrinken and the restaurant Den Gyldene Freden on number 51, established in 1722 and mentioned in Guinness Book of Records as one of the oldest with an unaltered interior.
Contents
History
Like Västerlånggatan, Österlånggatan used to pass outside of the city walls and was for many centuries one of the city's major streets. (See Västerlånggatan for more details.) When Skeppsbron, the broad street and quay running to the east of Österlånggatan, was created during the 17th century, Österlånggatan lost much of the importance it used to have.[1] Compared to Västerlånggatan, Österlånggatan is today a relatively quiet street notwithstanding the many restaurants and shops, in sharp contrast to the neighbourhood when the street formed the backyard of the dock district, crowded with sailors, taverns, travellers, and traders.[2]
During the 13th century, Österlånggatan was little more than the eastern shoreline, and archaeological excavations have unveiled the original beaten track some three metres below today's pavement. The shore line was, however, gradually pushed eastward by land fillings of gravel and rubbish. In the 14 century, the street had become the 'long street east of the wall' (e.g. Österlånggatan), far from the water, paved and lined-up with workshops, shops, and dwellings. German merchants lived in and around Järntorget, while Swedish merchant's from Bergslagen, the mining district north of the capital, resided on Österlånggatan, and only a few of the noble families settled here during the Middle Ages. One of them was Gunilla Johansdotter Bese (1473–1553), who lived in the now closed alley still carrying her name, Fru Gunillas Gränd, between Numbers 43 and 45.[2]
Many taverns from 17th century are known in the street: Riga on Number 19; Holländska Dyn ("Dutch Slough") on Number 21; Förgylda Draken ("Gilded Dragon") on Number 27; Tre Kungar ("Three Kings") on Number 28; Sveriges Wapen ("Swedish Arms") on Number 29; and Stjärnan ("The Star") in the Rococo building on Number 45. Of all these taverns, only Den Gyldene Freden ("The Golden Peace") on Number 51 remains, but can hardly give a hint of the filth, stench, rows, and misery once hidden behind the romantic names.[2]
The shipping trade gradually disappeared and by the early 20th century virtually everything associated with it on Österlånggatan was gone. Since the 1980s, the street have gradually been transformed into a quiet shopping street.[2]
A walk north to south
Slottsbacken - Köpmanbrinken
The northern end of Österlånggatan forms a discreet and informal back door to the old town; recessed in a corner of the prestigious Slottsbacken it can be hard to even discover, and as the narrow northern end is squeezed between tall façades, its easy to misinterpret the street as yet another of the many alleys. The first block is, however, flanked by two buildings worth a brief note: On the right side is the rear face of the Royal Coin Cabinet, housing a royal collection begun in the 16th century, and on the left is Number 1, a building started in 1897 and completed in 1950 to the plans of Ivar Tengbom (1878–1968), more famous as the architect behind Stockholm School of Economics and Stockholm Concert Hall — the windows facing Telegrafgränd, the first alley, gives a clear idea of what the building looked like at the time, in sharp contrast to the 18th-century stone portal on the opposite side of the alley.[3][4]
The first façade of Number 3-7 dates back to the 1760s with many later additions, for example the large northern window was the same size as the small southern until the 1960s while its large 18th-century shutters show there once was a door here. In contrast, the plain façades of Number 5 and 7 have an old feeling but is mostly a product of a later restorations: in 1963 the old mouldings and two of the original four windows of N.5 where removed, and the door of N.7 was placed where the southern window now is until the mid 1930s.[4] The second alley, Skeppar Karls Gränd is named after Skipper Karl who bought a building in the alley in the 16th century, the alley at the time facing the big fish market and the adjacent waterfront where his ships were moored.
On Number 6-8 is the House of Banér, the major portal of which is on the opposite side, facing Bollhusgränd, while the 'modest' portal on this side carries the arm of Per Banér and Hebbla Fleming. On the façade is also the fire bird Phoenix taking off surrounded by flames, the symbol of the fire insurance company created to tackle the fires frequently ravaging the old town, owned by its costumers and still residing on Mynttorget.[5] The cartouches are from the 17th century, while the portals and remaining façade is from the 18th century.[6] Number 10-12 were merged in the 1760s when the top of the building was added and the building got much of its present appearance, save for the enlarged shop windows and some original decorations now gone.[7]
In Number 9 is the vault of Bredgränd ("Broad Alley"), not really wide viewed from Österlånggatan, but actually one of the wider in the opposite end. In the alley remains of the city wall from the late Middle Ages have been found, 2 metres wide at the base narrowing off towards the top, it was made of stone, brick and wood taken from timbered houses.[citation needed] Both plain façades of Number 11-13 date back to the 17th century and are largely unaltered since the 1870s, except for some joineries and minor details.[8]
The alley Kråkgränd, named after the magistrate Knut Nilsson Kråka who lived there in the early 17th century. The alley have also been named after the magistrate Johan Persson who in 1638 took over a property said to be located "on the upper corner in a vault over the alley".[9] Under the first five small building behind Number 15 are the merged medieval cellars of the restaurant Fem Små Hus ("Five Small Houses") started in 1969. The basement of the block have, however, served as a tavern for several hundreds years — two illegal inns were reported in 1694.[10][11]
Köpmanbrinken
Köpmanbrinken ("Merchant's Slope") is leading up to Köpmantorget, its railing featuring the statue of Saint George and the Dragon, a copy from 1912 of the original located in the Stockholm Cathedral. Where the statue is today there used to be an entire block triangular in shape. One of the three buildings it contained was used as a synagogue for a few years in the late 18th century, but as this collapsed on May 1, 1821, the entire block was demolished. Buildings collapsed somewhat frequently in the area as the underlying soil, composed entirely of land filling, slid eastward and pulled the layers of gravel under the buildings in the process. Also in 1821, a wall in 8 Köpmanbrinken, reported as "looking rather trustworthy", was however transformed into a ruin in a snap, flying debris smashing windows on the opposite side of the street.[5]
On the opposite side, on either side of Number 17, are two relatively new alleys: Nygränd ("New Alley"), which notwithstanding the name is from the 16th century, and Brunnsgränd ("Well's Alley"), which notwithstanding the name contains no well. The explanation for this is former location of the biggest market square in Stockholm between these two alleys, called Fisketorget ("Fisher's Square"). It stretched down from the city gate located where Köpmantorget is today, to the waterfront between 1413 and around 1520. During the 14th century it was even named Fiskestrand ("Fishery Shore") and stretched north to Skeppar Karls Gränd.[12] The well beneath the statue of Saint George (both created in 1912) is often erroneously associated with Brunnsgränd, but the well which gave the alley its name is found inside the block north of it.[5]
The present building on Number 17 is the design of the architect Carl Malmström. Built in 1902 and inspired by the building on 10 Skeppsbron (possibly by Nicodemus Tessin the Younger), it featured shops on street level, flanked by pilasters topped by volutes, offices on the second floor behind the low rounded arches and the bar windows, with dwellings above and storage below. Originally, the entrance was flanked by two minor doors facing the street (the door still is still there), and was slightly more elaborated. The green colour of the building would have pleased neither of the two architects, but obviously was to the taste of today's catering business, judging from the restaurant residing there - Pontus in the Green House.[13]
Köpmanbrinken - Benickebrinken
The middle section of the street contains numerous alleys stretching east while the block on the opposite side forms a continuous block, the extent of which is caused by the medieval city wall which stretched behind the block, along the fronts facing Baggensgatan.[14]
While the sandstone on ground level of number 19 is 18th century in style, it was unveiled in the 1960s, the building however received much of its present appearance in 1876. During the following decades, the proprietors then started to add and relocate the doors of the building, sealing one door to replace a window with a new door, ten years later reverting the arrangement — in many aspects typical for the faith of the buildings in the old town. The building was occupied by the tavern Riga during the 17th and 18th century, and during 60 years from 1917 by a sail loft.[15] South of Number 19 is Skottgränd, an alley named after the Scotsmen who settled here in the 17th century, supposedly to own their living either as merchants or warriors. On Number 2 was the tavern Bacchus in the early 18th century, Number 6 was a storage as the still operational derrick show, and over the door of Number 3 is the inscription NON DOMUS DOMINUM SED DOMINUS DOMUM, roughly: 'A dominion doesn't make a lord, but a lord makes a domesticity'. One of the two shuttered windows on the southern side has iron detailing 17th century in style, but both of them are from 1873 when the façade of Number 21 was completed together with its portal feature featuring sculptural leaf garland and ductile wooden decorations. Next to the vault leading to Stora Hoparegränd (a name derived from hooper, the profession of making barrels) is just enough space for the narrow front door of Number 23; the portal of which is 18th century in style but was added to the building probably in the mid-19th century, a few decades before the shop door got flanked by its fluted wooden pilasters.[16]
The imposing old building on the opposite side, Number 14, featuring an oriel, a Renaissance frieze, and a Baroque portal was built in 1888 to the design of Isak Gustaf Clason, an architect known for the uninhibited use of historical styles from various epochs for different commissions — the 'Nordic Renaissance' of the Nordic Museum on Djurgården is arguably the best example.[5] The façade, unaltered except for the pediments over the doors removed in 1966, was inspired by the buildings of the old town, and the eclectic pioneering style of the architect is regarded as a first decisive step away from the well-established manners of the 19th century to rebuild old structures using the cast iron constructions introduced throughout the city during this time (see Riddarholmskyrkan). The façade is full of quotations from various historical periods, together humbly adapting to the heterogeneous environment, while the large stone vaults are adjusting the relation between the street and the interior.[17][18]
The façades of Number 25-27 are insidiously similar in appearance. The first have been repeatedly rebuilt — old doors removed, windows enlarged, the plain plastered surface added in the early 20th century, and the concrete portal in the 1970s — while the rough-cast façade and stone portal of the other is overall 18th century in character and largely unaltered since 1757.[19] Not much different is Number 16 on the opposite side of the street, the four cast iron pilasters and the fair-faced plaster of which is unaltered since 1889, while there was originally a depressed rounded arch over the double sliding doors of the front door.[20]
Between Drakens Gränd and the vault of Ferkens Gränd (named after the German word for pig, Ferkel) is Number 29-31; the stone pilasters, double doors, and simple profiled borders of the former are from 1850, while the latter is much unaltered since it was enlarged in 1834, as with many other building the shop windows have been enlarged during the 19th and 20th centuries.[21] Much due to the shutters and plain stone portals of Number 18 on the opposite side, this façade have kept its simple character since the 18th century when the building served as an outhouse (e.g. a shed), even though the door shutters were added in the 19th century and the doors are from the 1970s.[22]
While Number 33 is probably much the product of a paring which removed the moulding and detailing from 1939, the light 18th-century character of the fair-faced plaster façade and its narrow doors and windows is left pretty intact. In contrast, the dark and rough surface of Number 35, which probably reflects the appearance of the façade in 1778, hardly gives a hint of the three small original windows facing the street, or the shop window installed in 1916, wider than the present, notwithstanding the fact the main door is 18th century in style.[23] Similarly, the narrow Gustavian wooden portal, most likely from 1777, on Number 20 on the opposite side, gives the entire façade a simple and ancient character, but gives no hint of the three round arched wall openings depicted on an elevation in 1852 when the top floors of the building were added.[24] And again, Number 22 have kept much of its simple appearance from the 18th century, notwithstanding the large shop windows of the gallery, most likely from the mid- or late 19th century.[25]
On either side of Number 37 are Lilla Hoparegränd ("Smaller Heaper's Alley", a corruption of "Hoper's Alley", e.g. hooper indicating a profession, 'maker of barrels') and Pelikansgränd ("Pelican's Alley"), both forking off from Gaffelgränd ("Fork alley"). While the building is standing on a medieval wall, the façade is from the 18th century, and the portal from the 17th century. The latter was probably cut by Johan Wendelstam, a German sculptor who arrived to Stockholm in 1641 to became the Guild Master within a few years, and also cut one of the portals on Stortorget. The client was apparently Dutch as the inscription on the gable stone reads: Gaet het wel men heeft veel vrinden kert het luck wie kan se vinden ("When luck stands by one have a lot of friends, but when luck turns where are they then?"). Behind the front door is an entrance hall featuring a richly profiled sandstone column carrying a cross-vault.[5][26] The façade of Number 24 dates back to 1862, the shutters and wooden panels from that time however replaced by the rough-cast plaster probably in 1945, and the windows enlarged since.[27] The rusticated façade of Number 26 dates back to the enlargement in 1846, at the time it was however perfectly symmetric, a balance manipulated in 1973 when the enlarged opening and wooden panel of the restaurant entrance was added. The northern door, still featuring some original details, gives a fair impression of what the façade looked like in the 19th century.[28] The façade of Number 28, arguably one of the oldest still existent residential properties in Stockholm, is mostly from 1874 with some details replaced in 1969.[29]
Seemingly old-fashion, the façade of Number 39-41 had both a cornice and channelled rustication until 1967, presumably similar to that of N.26, while the portal and doors are from the late 19th century. Like most of the blocks on this side of the street, this one is standing on land fillings containing historical layers stretching down more than 15 metres, the sliding and compression of which have resulted in the buildings sinking with about 0,5 metres per century, and the 6–8 metres long piling from the 15th century leaning some 20 degrees towards the waterfront. Archaeological excavations in this block have documented the remains of human structures from the late 13th century, while the oldest settlements appears in historical records in 1420. These building flanked an alley passing through the block down to a landing bridge by the water. During the late 15th century a second city wall in wood was built here, during the 1580s replaced by a more permanent wall in stone. No later than 1499, Sten Sture the Elder transferred the lot now forming the southern part of the façade to the Order of Saint John, which had a church built here, inaugurated in 1514, and demolished in 1530 following the Reformation. A wall from and the graveyard of this church was rediscovered under the alley Johannesgränd passing south of the block; King Gustav Vasa is known to have looted the graveyard to assemble raw material to produce saltpetre used for gunpowder, a deed commented: "Not Christian is thus shoot one's forefathers in the air" (Ej är kristeligt i väder så skjuta sina förfäder).[30][31]
Benickebrinken-Järntorget
The façade of Number 45 is perfectly preserved since the construction of the building in 1762, including the shape and size of the door and the windows, the channelled rustication of the central wall projection and its compressed arch, but excluding the rustication on the corners, and the well adapted joinery from 1939. In the building preceding the present was the tavern Stjärnan ("The Star"), still in operation in the 19th century.[32]
Northern and southern Benickebrinken ("Slope of Benicke") leading up to Svartmangatan ("Black Man's Street") are named after the innkeeper Jören Benick who in the middle of the 16th century ran a tavern here named Solen ("The Sun") after the symbol hanging in the street. His tavern was located in a block demolished in the 19th century which used to run between Österlånggatan and the two then extremely narrow slopes. The tavern was preceded by the Blackfriars monastery located south of the slopes 1330s-1520s, the graveyard of which was discovered under the southern slope, while the extent of it is still marked by two lines of paving stones in Prästgatan passing south of the block.[33][34][35]
An archaeological excavation in 2000 in the block behind Number 47-51 have revealed several foundation works of old buildings and of the second city wall (15th-16th century) and one of its defensive towers, a corner of which was located in the alley Packhusgränd passing north of the block.[36] The troubadour Carl Michael Bellman often used living individuals as prototypes for the numerous people appearing in his Bacchanalian songs, and the model for Ulla Winblad, a promiscuous woman, was Maria Kristina Kiellström who took the name Winblad ("Wine leaf") from her stepmother. While its not known how well acquainted she was with Bellman, she did marry his friend Erik Nordström with whom she settled in Norrköping in 1772. As her husband died in custody, she moved back to Stockholm in 1782 and settled on Number 47. In the meantime the songs of Bellman had made her famous and everyone was charmed by her return to the capital. She was less flattered however, and it is said she gave Bellman a blow at one occasion and her second husband is reported to have regularly complained he had married that 'lecherous woman'. Her reaction is somewhat understandable, considering the often burlesque lyrics in the songs. Below are 3 of the 21 verses of his 48th epistle named Varuti avmålas Ulla Winblads hemresa från Hessingen i Mälaren en sommarmorgon 1769 ("In which is depicted Ulla Winbladh's journey home from Hessingen in Lake Mälaren a summer's morning 1769"), describing the trip back to Stockholm from Stora Essingen in a rowing boat passing by Marieberg where at the time was located a saltpetre work and a penitentiary.[37][38]
Ulla, fästman på dig ser. Ulla, your fiancé is looking at you. Kom, min Norströms lilla, Come, my darling of Norstöm's, sätt dig brevid mej, sitt ner, sit by my side, sit down, fritt din låga stilla! let your flare freely fade! Vi har alla lika rang. We are all of equal rank. Lustigt! Hör basuners klang! Amusing! Hear trumpets blast! Prosit och contentement! Bless you and contentment! Dyrbar ögonvila. Dear delightful sight. [...] [...] Såg du nu Marieberg, Now, did you notice Marieberg, så se längre neder; then look further down; med en gul och bleknad färg yellow and pale in colour sig ett tjäll utbreder. extends a humble abode. Fönstren glittra. Kännen I Glittering windows. Smell thou ej salpetersjuderi? not the saltpetre works? En gång, Ulla — raljeri! — Some day, Ulla — raillery! — palten dit dig leder. bobby will take you there. [...] [...] Norström stjälper sin peruk Norström tips his wig av sin röda skalla, off his red pate, och min Ulla, blek och sjuk, and my Ulla, faint and ill, lät sin kjortel falla, let her skirt fall, klev så bredbent i paulun; thus straddle-legged stepped into bed; Movitz efter med basun: Movitz after with the trumpet: maka åt dig, Norström! Frun get away, Norström! The lady hör ju till oss alla. do belong to all of us. On Number 51 is the restaurant Den Gyldene Freden ("The Golden Peace"), named after the Treaty of Nystad in 1721 and in opened in 1722, it remains the oldest and most famous restaurant in Sweden. Carl Michael Bellman use to work in the Custom House on the opposite side and while he is likely to have visited the place occasionally, he is not likely ta have been a regular there. He is however associated with the establishment, and he actually saved it from being closed down more than a hundred years after his death. The society preserving his memory, Bellmans minne ("Memory of Bellman"), meet regularly in the restaurant and when the painter Anders Zorn at one of their sessions in February 1919, was told the old restaurateur was about to retire and would discontinue the business, Zorn bought for SEK 150,000, had it restored for SEK 250,000, and later bequeathed it to the Swedish Academy together with a requirement the latter should appoint the members of a foundation which should manage the property and use the annual yield to award a prominent poet the prize Bellmanpriset.[40][41]
An archaeological excavation in 1993, in the intersection with Prästgatan and Tullgränd just south of Södra Benickebrinken, unveiled a bricked wall 0,5 metres under the current street. This section of Österlånggatan used to be much narrower, and the wall is what remains of a building once located on Number 34-36 on the western side of the street, demolished together with a triangular block located between Österlånggatan and the two slopes north of the intersection when the southern part of the street was widened in 1898.[35] The building was known as Kyskendal ("Chastity Valley"), described as a "Cupid's tempel filled with priestesses from basement to attic", while the basement was the location for the tavern Krypin ("Creep/Crawl-In"), mentioned by C M Bellman in his 23rd epistle.
On Number 53 is Norra Bankohuset ("Northern [National] Bank Building"), built in 1770 and enlarged in 1880, it used to house the note-printing works and money depot of the Bank of Sweden until its relocation to the present Parliament Building in 1906. The window gratings on ground level and the small windows above still reminds of its former function. The defective foundation works caused huge crevices in fronts facing the alley, and while the damaged have been repaired, there are still windows inclined windows in the alley as a reminder. The small portal facing Österlånggatan is from the early 19th century.[42][43] An arched passage over Norra Bankogränd connects the building to Södra Bankohuset, the former main building of the national bank facing Järntorget.
See also
References
- ^ (in Swedish) Stockholms gatunamn (2nd ed. ed.). Stockholm: Kommittén för Stockholmsforskning. 1992. ISBN 91-7031-042-4.
- ^ a b c d Glase, Béatrice; Gösta Glase (1988) (in Swedish). Gamla stan med Slottet och Riddarholmen (3rd ed. ed.). Stockholm: Bokförlaget Trevi. ISBN 91-7160-823-0.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 34–35. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/s34_155Aeolus1_Cassiopea13.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ a b Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 119–125. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/s34_155Aeolus1_Cassiopea13.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ a b c d e Glase, Béatrice; Gösta Glase (1988) (in Swedish). Gamla stan med Slottet och Riddarholmen (3rd ed. ed.). Stockholm: Bokförlaget Trevi. ISBN 91-7160-823-0.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 762–764. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 770–775. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 597–602. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Fredrik Ulrik Wrangel (1912). "Stockholmiana I-IV". Project Runeberg. pp. 391. http://runeberg.org/wrangsto/0501.html. Retrieved 2007-03-07.
- ^ Glase, Béatrice; Gösta Glase (1988) (in Swedish). Gamla stan med Slottet och Riddarholmen (3rd ed. ed.). Stockholm: Bokförlaget Trevi. ISBN 91-7160-823-0.
- ^ "Fem Små Hus". Fem Små Hus. 2007. http://www.femsmahus.se/. Retrieved 2007-03-07.
- ^ Lindgren, Rune (1992) (in Swedish). Gamla stan förr och nu. Stockholm: Rabén & Sjögren. ISBN 91-29-61671-9.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (200-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 432–435. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/s410_506Deucalion1Iphigenia4.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Lindgren, Rune (1992) (in Swedish). Gamla stan förr och nu. Stockholm: Rabén & Sjögren. ISBN 91-29-61671-9.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (200-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 115–118. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/s34_155Aeolus1_Cassiopea13.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 825–830. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 805–807. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Olof Hultin, ed (1999) (in Swedish). Guide till Stockholms arkitektur (2nd ed. ed.). Stockholm: Arkitektur Förlag AB. ISBN 91-86050-41-9.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 156–160. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/s156_254Castor10Cepheus.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 802–804. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 79–86. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/s34_155Aeolus1_Cassiopea13.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 800–801. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 590–596. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 798–799. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 796–798. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 126–127. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/s34_155Aeolus1_Cassiopea13.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 793–795. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 790–792. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 776–777. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ John Hedlund (1999-1998). "GLAUCUS 3, 4, 5 & 6". Stockholm City Museum. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/2002-5.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 480–481. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/s410_506Deucalion1Iphigenia4.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Maria Lorentzi (2002-2003). "Butiksfasader i Gamla stan. Inventering". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 822–824. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/748_843Pandora2Pygmalion3.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Martin Stugart (2007?-01-12). "Varifrån har Norra och Södra Benickebrinken i Gamla stan fått sina namn.". Dagens Nyheter. http://www.dn.se/DNet/jsp/polopoly.jsp?d=1467&a=599782. Retrieved 2007-02-25.
- ^ Glase, Béatrice; Gösta Glase (1988) (in Swedish). Gamla stan med Slottet och Riddarholmen (3rd ed. ed.). Stockholm: Bokförlaget Trevi. ISBN 91-7160-823-0.
- ^ a b Barbro Århem (1993). "Prästgatan, Österlånggatan, Södra Benickebrinken". Stockholm City Museum. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/forvaltningen/media/pdf/Prastgatan.pdf. Retrieved 2007-02-25.
- ^ Mikael Johansson (2001). "Argus 8". Stockholm City Museum. pp. 1–11. http://www.stadsmuseum.stockholm.se/media/pdf/argus8.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Martin Stugart (2003-07-11). "Var bodde de kända personerna i Bellmans visor?". Dagens Nyheter. http://www.dn.se/DNet/jsp/polopoly.jsp?a=159950. Retrieved 2007-03-08.
- ^ Huldén, Lars (1994) (in Swedish). Carl Michael Bellman (2nd ed. ed.). Stockholm: Natur och Kultur. ISBN 91-27-03767-3.
- ^ Hassler, Göran (1990) (in Swedish). Bellman, en antologi (3rd ed. ed.). Litteraturfrämjandet. ISBN 91-7448-512-1.
- ^ Glase, Béatrice; Gösta Glase (1988) (in Swedish). Gamla stan med Slottet och Riddarholmen (3rd ed. ed.). Stockholm: Bokförlaget Trevi. ISBN 91-7160-823-0.
- ^ Lindorm, Per-Erik (1951) (in Swedish). Stockholm genom sju sekler. Stockholm: Sohlmans.
- ^ Glase, Béatrice; Gösta Glase (1988) (in Swedish). Gamla stan med Slottet och Riddarholmen (3rd ed. ed.). Stockholm: Bokförlaget Trevi. ISBN 91-7160-823-0.
- ^ Olof Hultin, ed (1999) (in Swedish). Guide till Stockholms arkitektur (2nd ed. ed.). Stockholm: Arkitektur Förlag AB. ISBN 91-86050-41-9.
External links
- hitta.se - Location map and virtual walk
- Stockholm City Museum - Shop façades consensus 2002-2003
- Stockholmskällan - Historical photos
Coordinates: 59°19′25.8″N 18°04′25.2″E / 59.323833°N 18.073667°E
Categories:- Streets in Stockholm
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.