- Urnfield culture numerals
-
Numeral systems by culture Hindu-Arabic numerals Western Arabic (Hindu numerals)
Eastern Arabic
Indian family
TamilBurmese
Khmer
Lao
Mongolian
ThaiEast Asian numerals Chinese
Japanese
SuzhouKorean
Vietnamese
Counting rodsAlphabetic numerals Abjad
Armenian
Āryabhaṭa
CyrillicGe'ez
Greek (Ionian)
HebrewOther systems Aegean
Attic
Babylonian
Brahmi
Egyptian
Etruscan
InuitKharosthi
Mayan
Quipu
Roman
Sumerian
UrnfieldList of numeral system topics Positional systems by base Decimal (10) 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 20, 24, 30, 36, 60, 64 List of numeral systems 0 / 1 // 2 /// 3 //// 4 \ 5 /\ 6 //\ 7 ///\ 8 ////\ 9 \\ 10 /\\ 11 //\\ 12 ///\\ 13 ////\\ 14 \\\ 15 /\\\ 16 //\\\ 17 ///\\\ 18 ////\\\ 19 \\\\ 20 /\\\\ 21 //\\\\ 22 ///\\\\ 23 ////\\\\ 24 \\\\\ 25 /\\\\\ 26 //\\\\\ 27 ///\\\\\ 28 ////\\\\\ 29 During the beginning of the Urnfield culture, around 1200 BC, a series of votive sickles of bronze with marks that have been interpreted as a numeral system, appeared in Central Europe.
Contents
Discovery
In 1946 a deposit with more than 250 sickles corresponding to the period 1500–1250 BC was discovered in Frankleben (in the region of Merseburg–Querfurt). This discovery was part of a series of deposits from the Urnfield culture found close to the Saale, where some 600 sickles and other objects have been retrieved. The sickles are thought to have been created and buried in deposits with ritual ends, due to the lack of signs of use.
On the sickles, a series of marks in two positions called attention: simple strokes, under the button that sticks out, near where a handle ought to be, and more complex signs, in the corner of the blade or on the base. The basic strokes have been interpreted as a numeral system.
Other objects that show these marks have been discovered, like the Ruthen stamp (from the end of the Bronze Age), which shows the symbol ////\\\\\ and the Coswig vessel (between 1200–1000 BC), which also shows the symbol ////\\\\\, accompanied by other symbols. In the case of the Coswig vessel, it gives the impression that it was made by a trained hand which wrote a complex series of signs on the fresh clay surface.
The numeral system
The discovered numeral system is in base five, i.e. quinary. The units digit are written with a stroke from the top-right to the bottom-left «/» and the fives place with a stroke from the top-left to the bottom-right «\». The numbers from 1 = / to 29 = ////\\\\\ have been found.
Interpretation
These embossed marks, unique in objects from the Bronze Age, were introduced in cast-iron molds and were not created on finished objects. The marks on the clay molds were done sometimes by hand, others with stamps, and corrected wrong symbols indicates an intention and a previous planning. The marking system for the clay on the cast is similar to Mesopotamian cuneiform.
That numbers past 29 have not been found, when theoretically the system can be used to write unlimited numbers, has been interpreted to be because of the lunar cycle of 29.5 days. The cultures that use a lunar calendar habitually decide between 29 and 30 days for their calendar and correct the annual difference in various ways. If this interpretation is accepted, each ravine represents one day of the lunar cycle.
The shape of the sickle is similar to a crescent moon, which explains the significance of this object in the worship of the Urnfield culture.
With this, the symbol found on the Ruthen stamp and the Coswig vase has been interpreted, 29 = ////\\\\\, as a symbol of the lunar cycle. In general, it is believed that the writing encodes the lunar cycle as the agricultural cycle linked with the moon and the Sun.
Other symbols
Another series of symbols exists which appears around the sickles and still has not been interpreted. However it is clear that these symbols follow determined rules that are valid in all the influential territory.
Some of those symbols can be put in groups from one to four by what has been proposed as a type of base five numeral system.
40 41 42 43 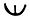 44
4445 46 47 48 49 50 51  52
52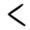 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56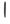 57
57● 58 59 60 61 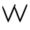 62
62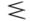 63
63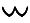 64
6465 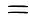 66
66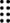 67
67●● 68 69 70 71 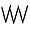 72
72 73
73 74
7475  76
76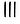 77
77●●● 78 79 80 81 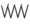 82
8283 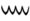 84
84 85
85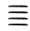 86
86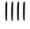 87
87●●●● 88 89 There still exist some symbols that have not been put in any group:
 16
16 22
22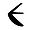 25
25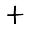 26
26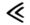 33
33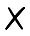 36
36 42
42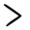 43
43 69
69The numbers 22, 25, 33, 36, 43 and 69 and 24, 52, 53, 54, 56, 62, 63, 64, 66, 73, 74, 84 and 86 appear on the base of the sickle. The numbers 16, 26 and 42 and 44, 52, 54, 55, 57, 58, 62, 64, 67, 68, 72, 74, 77, 78, 82, 84, 85, 87 and 88 appear on the angle of the sickle. The numbers 52, 54, 62, 64, 74 and 84 appear in both places.
Hypothesis of the runes
This writing has been related to the German runes, not only due to the geographic but also the agricultural and lunar character that the two possess. It has been affirmed that the runes often appear together with other non-runic symbols, even in combination on the same object. Also, ᛃ j, ᛜ ng and also ᚷ g do not have connections to the Etruscan alphabet from which the Runic alphabet supposedly comes. On the other hand, the letters ᛃ j, ᛜ ng and ᚲ k are distinguished from the rest of the runes by their smaller size. The runes are also characterized by possessing names in addition to representing a sound.
Under the hypothesis that the names of some runes were taken from previous symbols, the names of those runes could give clues about the meaning of the symbols. In this way, if the symbol that has more combinations with others , the one that appears most frequently and the most characteristic are selected, you can make the following equivalence:
Symbol Rune Equivalence Meaning 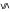 22
22ᛃ jera year 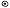 69
69ᛜ ingwaz god 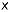 36
36ᚷ gebô present This is just an interesting hypothesis that perhaps will never be confirmed.
External links
References
- This article draws heavily on the December 16, 2006 version of the corresponding article in the Spanish-language Wikipedia.
- Meller, Harald (Ed.), Der geschmiedete Himmel, Ed. Landesamt für Denkmalpflege und Archäologie Sachsen-Anhalt (2006) ISBN 3-8062-1907-9
See also
Categories:- Bronze Age Europe
- European archaeology
- Numerals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
