- Sfakia
-
Sfakia
Σφακιά
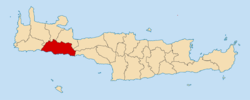
The village of Sfakia.Location Coordinates 35°12′N 24°8′E / 35.2°N 24.133°ECoordinates: 35°12′N 24°8′E / 35.2°N 24.133°E Government Country: Greece Region: Crete Regional unit: Chania Population statistics (as of 2001) Municipality - Population: 2,446 - Area: 467.6 km2 (181 sq mi) - Density: 5 /km2 (14 /sq mi) Other Time zone: EET/EEST (UTC+2/3) Auto: ΧΝ Sfakiá (Greek: Σφακιά) is a mountainous area in the southwestern part of the island of Crete, in the Chania peripheral unit. It is considered one of the few places in Greece to never have been fully occupied by foreign powers. With a 2001 census population of 2,446 inhabitants living on a land area of 467.589 km², Sfakia is one of the largest and least densely populated municipality on the island of Crete. The etymology of its name is disputed. According to the prevailing theory, it relates to its rugged terrain, deriving from the ancient Greek word σφαξ, meaning land chasm or gorge.[1]
Contents
Description
The road from Chania to Sfakiá crosses the island from north to south, through the village of Vryses. From this village the route crosses the White Mountains (Lefká Óri) to Hóra Sfakíon (35°12′N 24°08′E / 35.2°N 24.133°E) by the Libyan Sea. Halfway from Vrisses to Hóra Sfakíon is the fertile plateau of Askifou, surrounded by high mountain peaks. From here to Hóra Sfakíon the road is particularly spectacular. The road hugs the western slope of the Imbros Gorge with breathtaking views. Another scenic route is that leading from Kapsodasos to the plateau of Kallikratis, northeast of Hóra Sfakíon.
There are many beaches in Sfakiá which do not see the numbers of tourists of the northern coast. More adventurous visitors can follow the European hiking footpath E4 which crosses Crete through Sfakiá's mountains. The coastal villages are not connected by a coastal road, and can be reached by ferry boats.
Not far east from Hóra Sfakíon is Frangokastello, literally "Frankish castle". The Venetian fortress here was built in 1371 to deter pirates and unsuccessfully, to control Sfakiá. It is largely ruined but is picturesquely set on a wide sandy beach with the towering White Mountains behind. Daskalogiannis was captured here in 1771.
Accessible only by boat from Sfakiá is Loutro, a small seaside village with some archaeological ruins, a few houses, small hotels and tavernas. Loutro is car-free, you have to park your car in Hóra Sfakíon or Paleohóra. In the north of Sfakiá is the fertile plain of Askyfou. The Sfakía region is crossed by many gorges, among which the famous Samaria Gorge, which run from north to south and all end in the sea. Many of them can be walked, and several even by inexperienced walkers. The region still is inhabited by rare animals, like vultures and eagles, and the kri-kri (or agrimi), the wild Cretan goat. Sfakiá borders to the Libyan Sea, which is inhabited by a diminishing fish population, but occasionally shows dolphins, and even whales.
The local speciality, "Sfakian Pies", are thin pancakes filled with cream cheese and served drizzled with honey.
Resistance
Hóra Sfakíon is famous as one of the centers of the resistance against the occupying forces of both the Venetians and the Turks. The impenetrable White Mountains to the north combined with the rocky beaches on the south helped the locals fight off all invaders. Anopolis, a village near Hóra Sfakíon, is the birthplace of one of the most celebrated Cretan revolutionaries, Daskalogiannis.
A famous legend and unexplained phenomenon describes a procession of visions (Drosoulites) seen in the nearby village Frangokastello as troops that died in the war of independence against the Turks.
Patrick Leigh Fermor wrote about the tall proud Sfakians and their resistance to occupation. Many tales of revolts and uprisings in Crete start in the mountains of western Crete - mountain guerillas, pallikari fighters and rebel assemblies.
After the Battle of Crete during World War II, the locals helped many New Zealand and Australian soldiers escape from here on the night of May 31, 1941, suffering great reprisals. King George II of Greece had already escaped this way when the Germans invaded. Near the village of Komitades is the Church of Panagia Thymiani where the revolution of 1821 began. At the village of Loutro is the ruined "chancellery" where the first revolutionary government of 1821 met.
Sfakiá is notorious for the harshness of the environment and the warlike people. Sfakians themselves are still considered somewhat beyond the reach of the lawmakers and tax collectors of Athens, with vendettas over stolen sheep and women's honour still fought late into the 20th century, with a whole village abandoned.
Stealing and banditry had been considered a way of life in the mountains, even appearing in a Creation myth, which made God Himself a Sfakiot, as recounted by Adam Hopkins:
- ...with an account of all the gifts God had given to other parts of Crete - olives to Ierapetra, Ayios Vasilios and Selinou; wine to Malevisi and Kissamou; cherries to Mylapotamos and Amari. But when God got to Sfakia only rocks were left. So the Sfakiots appeared before Him armed to the teeth. "And us Lord, how are we going to live on these rocks?" and the Almighty, looking at them with sympathy, replied in their own dialect (naturally): "Haven't you got a scrap of brains in your head? Don't you see that the lowlanders are cultivating all these riches for you?"
The Sfakians are also famous for their hospitality and generosity towards guests, resulting in a shift from traditional labour towards tourism, with now many families running their own small hotel or restaurant.
History
The archeology and history of Sfakia is the object of a field survey undertaken by the University of Oxford.[2][3]
References
See also
Administrative division of the Crete Region  Regional unit of HeraklionArchanes–Asterousia • Faistos • Gortyna • Heraklion • Hersonissos • Malevizi • Minoa Pediada • ViannosRegional unit of RethymnoCategories:
Regional unit of HeraklionArchanes–Asterousia • Faistos • Gortyna • Heraklion • Hersonissos • Malevizi • Minoa Pediada • ViannosRegional unit of RethymnoCategories:- Populated places in Chania (peripheral unit)
- Municipalities of Crete
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.