- Flight 19
-
Flight 19 
Artist's depiction of five Avengers.Occurrence summary Date December 5, 1945 Type Disappearance Site Off the eastern coast of Florida, United States (Bermuda Triangle) Crew 14 Fatalities 14 Survivors None Aircraft type TBF Avenger Operator  United States Navy
United States NavyDestination NAS Fort Lauderdale Flight 19 was the designation of five TBM Avenger torpedo bombers that disappeared on December 5, 1945 during a United States Navy-authorized overwater navigation training flight from Naval Air Station Fort Lauderdale, Florida. All 14 airmen on the flight were lost, as were all 13 crew members of a PBM Mariner flying boat assumed to have exploded in mid-air while searching for the flight. Navy investigators could not determine the cause for the loss of Flight 19 but said the aircraft may have become disoriented and ditched in rough seas after running out of fuel.
The pulp magazine Argosy published an account of the incident. Subsequently, writers on the paranormal such as Charles Berlitz and Richard Winer added their own research to associate the incident with the Bermuda Triangle.[not verified in body] The flight also features in the 1977 science fiction film Close Encounters of the Third Kind.
Contents
Flight 19 undertook a routine navigation and combat training exercise in VTB-type aircraft.[1] The assignment was called "Navigation problem No. 1", a combination of bombing and navigation, which other flights had completed or were scheduled to undertake that day.[2] The flight leader was United States Navy Lieutenant Charles Carroll Taylor who had about 2,500 flying hours, mostly in aircraft of this type, while his trainee pilots had 300 total, and 60 flight hours in the Avenger.[2] Taylor had recently arrived from NAS Miami where he had also been a VTB instructor. The student pilots had recently completed other training missions in the area where the flight was to take place.[2] They were US Marine Captains Edward Joseph Powers and George William Stivers, US Marine Second Lieutenant Forrest James Gerber and USN Ensign Joseph Tipton Bossi.
The aircraft were four TBM-1Cs, BuNo 45714, 'FT3', BuNo 46094, 'FT36', BuNo 46325, 'FT81', BuNo 73209, 'FT117', and one TBM-3, BuNo 23307, 'FT28'.
Each aircraft was fully fueled, and during pre-flight checks it was discovered they were all missing clocks. Navigation of the route was intended to teach dead reckoning principles, which involved calculating among other things elapsed time. The apparent lack of timekeeping equipment was not a cause for concern as it was assumed each man had his own watch.[2] Takeoff was scheduled for 13:45 local time, but the late arrival of Taylor delayed departure until 14:10.[2] Weather at NAS Fort Lauderdale was described as "... favorable, sea state moderate to rough."[2] Taylor was supervising the mission, and a trainee pilot had the role of leader out front.
Called "Naval Air Station, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, navigation problem No. 1,"[3] the exercise involved three different legs, but the actual flight should have flown four. After take off, they flew on heading 091° (almost due east) for 56 nmi (64 mi; 104 km) until reaching Hen and Chickens Shoals where low level bombing practice was carried out. The flight was to continue on that heading for another 67 nmi (77 mi; 124 km) before turning onto a course of 346° for 73 nmi (84 mi; 135 km), in the process over-flying Grand Bahama island. The next scheduled turn was to a heading of 241° to fly 120 nmi (140 mi; 220 km) at the end of which the exercise was completed and the Avengers would turn left to then return to NAS Ft. Lauderdale.[2]
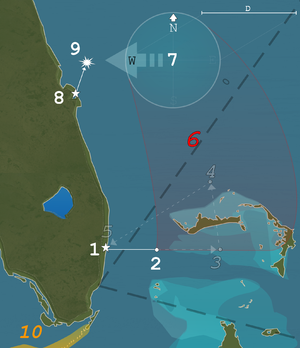 Map of Flight 19's navigation exercise and final position on December 5, 1945. D. 100 nautical miles (190 km) 0. The Bermuda Triangle 1. Start exercise at NAS Fort Lauderdale 14:10. 2. Drop bombs at Hen and Chickens shoals until around 15:00. 3. Proceed on new heading 346° for 73 nautical miles (140 km). 4. Fly on third heading 241° for 120 nautical miles (220 km) to point north of NAS Fort Lauderdale. 5. Return to NAS Fort Lauderdale 26°N 80°W / 26°N 80°W 6. 15:00–17:50 exact position unknown. 7. 17:50 radio triangulation establishes flight's position to within 100 nautical miles (190 km) of 29°N 79°W / 29°N 79°W and their last reported course, 270°. 8. PBM-5 (BuNo 59225) takes off from NAS Banana River 19:27. 9. 19:50 PBM-5 explodes near 28°N 80°W / 28°N 80°W. 10. The Florida Keys, where Taylor thought he was.
Map of Flight 19's navigation exercise and final position on December 5, 1945. D. 100 nautical miles (190 km) 0. The Bermuda Triangle 1. Start exercise at NAS Fort Lauderdale 14:10. 2. Drop bombs at Hen and Chickens shoals until around 15:00. 3. Proceed on new heading 346° for 73 nautical miles (140 km). 4. Fly on third heading 241° for 120 nautical miles (220 km) to point north of NAS Fort Lauderdale. 5. Return to NAS Fort Lauderdale 26°N 80°W / 26°N 80°W 6. 15:00–17:50 exact position unknown. 7. 17:50 radio triangulation establishes flight's position to within 100 nautical miles (190 km) of 29°N 79°W / 29°N 79°W and their last reported course, 270°. 8. PBM-5 (BuNo 59225) takes off from NAS Banana River 19:27. 9. 19:50 PBM-5 explodes near 28°N 80°W / 28°N 80°W. 10. The Florida Keys, where Taylor thought he was.
Radio conversations between the pilots were overheard by base and other aircraft in the area. The practice bombing operation was carried out because at about 15:00 a pilot requested and was given permission to drop his last bomb.[2] Forty minutes later, another flight instructor, Lieutenant Robert F. Cox in FT-74, forming up with his group of students for the same mission, received an unidentified transmission.[3]
A male asked Powers, one of the students, for his compass reading. Powers replied: "I don't know where we are. We must have got lost after that last turn." Cox then transmitted; "This is FT-74, plane or boat calling 'Powers' please identify yourself so someone can help you." The response after a few moments was a request from the others in the flight for suggestions. FT-74 tried again and a man identified as FT-28 (Taylor) came on. "FT-28, this is FT-74, what is your trouble?" "Both of my compasses are out", Taylor replied, "and I am trying to find Fort Lauderdale, Florida. I am over land but it's broken. I am sure I'm in the Keys but I don't know how far down and I don't know how to get to Fort Lauderdale."[2]
FT-74 informed the NAS that aircraft were lost, then advised Taylor to put the sun on his port wing and fly north up the coast to Fort Lauderdale.[2] Base operations then asked if the flight leader's aircraft was equipped with a standard YG (IFF transmitter), which could be used to triangulate the flight's position, but the message was not acknowledged by FT-28. (Later he would indicate that his transmitter was activated.) Instead, at 16:45, FT-28 radioed: "We are heading 030 degrees for 45 minutes, then we will fly north to make sure we are not over the Gulf of Mexico." During this time no bearings could be made on the flight, and IFF could not be picked up. Taylor was told to broadcast on 4805 kilocycles. This order was not acknowledged so he was asked to switch to 3,000 kilocycles, the search and rescue frequency. Taylor replied – "I cannot switch frequencies. I must keep my planes intact."[2]
At 16:56 Taylor was again asked to turn on his transmitter for YG if he had one. He did not acknowledge but a few minutes later advised his flight "Change course to 090 degrees (due east) for 10 minutes." About the same time someone in the flight said "Dammit, if we could just fly west we would get home; head west, dammit."[2] This difference of opinion later led to questions about why the students did not simply head west on their own.[4] It has been explained that this can be attributed to military discipline.[4]
As the weather deteriorated, radio contact became intermittent, and it was believed that the five aircraft were actually by that time more than 200 nmi (230 mi; 370 km) out to sea east of the Florida peninsula. Taylor radioed "We'll fly 270 degrees west until landfall or running out of gas"[2] and requested a weather check at 17:24. By 17:50 several land based radio stations had triangulated Flight 19's position as being within a 100 nmi (120 mi; 190 km) radius of 29°N 79°W / 29°N 79°W;[2] Flight 19 was north of the Bahamas and well off the coast of central Florida, but nobody transmitted this information on an open, repetitive basis.[2]
At 18:04 Taylor radioed to his flight "Holding 270, we didn't fly far enough east, we may as well just turn around and fly east again". By that time, the weather had deteriorated even more and the sun had since set. Around 18:20, Taylor's last message was received. He was heard saying "All planes close up tight ... we'll have to ditch unless landfall ... when the first plane drops below 10 gallons, we all go down together."[2][1] At the same time, in the same area, SS Empire Viscount, a British-flagged tanker, radioed that she was in heavy seas and high winds northeast of the Bahamas, where Flight 19 was about to ditch.[2]
PBM-5 (BuNo 59225)
PBM-5 (BuNo 59225) 
PBM-5 Mariner VP-50 Blue Dragons (BuNo 59256) in April 1956-similar to BuNo 59225. (Note: "BuNo" stands for Bureau Number.[5])Occurrence summary Date December 5, 1945 Type Presumed mid-air explosion Site 28°35′N 80°15′W / 28.59°N 80.25°W Crew 13 Fatalities 13 Survivors None Aircraft type PBM-5 Mariner Operator  United States Navy
United States NavyFlight origin NAS Banana River Destination NAS Banana River Earlier, as it became obvious the flight was indeed lost, several air bases, aircraft, and merchant ships were alerted. A PBY Catalina left after 18:00 to search for Flight 19 and guide them back if they could be located.[2] After dark, two PBM Mariner seaplanes originally scheduled for their own training flights were diverted to perform square pattern searches in the area west of 29°N 79°W / 29°N 79°W. PBM-5 BuNo 59225 took off at 19:27 from Banana River Naval Air Station (now Patrick Air Force Base), called in a routine radio message at 19:30 and was never heard from again.[2]
At 19:50, the tanker SS Gaines Mills reported seeing a mid-air explosion, then flames leaping 100 ft (30 m) high and burning on the sea for 10 minutes. The position was 28°35′N 80°15′W / 28.59°N 80.25°W. Captain Shonna Stanley, reported searching for survivors through a pool of oil, but found none. The escort carrier USS Solomons also reported losing radar contact with an aircraft in the same position and time.[2]
Investigation
A 500-page Navy board of investigation report published a few months later made several observations.
- Taylor had mistakenly believed that the small islands he passed over were the Florida Keys, so his flight was over the Gulf of Mexico and heading northeast would take them to Florida. It was determined that Taylor had passed over the Bahamas as scheduled, and he did in fact lead his flight to the northeast over the Atlantic. The report noted that some subordinate officers did likely know their approximate position as indicated by radio transmissions stating that flying west would result in reaching the mainland.
- Taylor, although an excellent combat pilot and officer with the Navy, had a tendency to "fly by the seat of his pants," getting lost several times in the process.[citation needed] It was twice during such times that he had to ditch his plane in the Pacific and be rescued.
- Taylor was not to fault because the compasses stopped working.
- The loss of PBM-5 BuNo 59225 was attributed to a mid-air explosion.[3]
This report was subsequently amended "cause unknown" by the Navy after Taylor's mother contended that the Navy was unfairly blaming her son for the loss of five aircraft and 14 men, when the Navy had neither the bodies nor the airplanes as evidence.[citation needed]
Had Flight 19 actually been where Taylor believed it to be, landfall with the Florida coastline would have been reached in a matter of 10 to 20 minutes or less, depending on how far down they were. However, a later reconstruction of the incident showed that the islands visible to Taylor were probably the Bahamas, well northeast of the Keys, and that Flight 19 was exactly where it should have been. The board of investigation found that because of his belief that he was on a base course toward Florida, Taylor actually guided the flight further northeast and out to sea. Further, it was general knowledge at NAS Fort Lauderdale that if a pilot ever became lost in the area to fly a heading of 270° west (or in evening hours toward the sunset if the compass had failed). By the time the flight actually turned west, they were likely so far out to sea they had already passed their aircraft's fuel endurance. This factor combined with bad weather, and the ditching characteristics of the Avenger,[1] meant that there was little hope of rescue, even if they had managed to stay afloat.
It is possible that Taylor overshot Castaway Cay and instead reached another land mass in southern Abaco Island. He then proceeded northwest as planned. He fully expected to find the Grand Bahama Island laying in front of him as planned. Instead, he eventually saw a land mass to his right side, the northern part of Abaco Island. Believing that this landmass to his right was the Grand Bahama Island and his compass was malfunctioning, he set a course to what he thought was southwest to head straight back to Fort Lauderdale. However, in reality this changed his course further northwest, toward open ocean.
To further add to his confusion, he encountered a series of islands north of Abaco Island, which looks very similar to the Key West Islands. Eventually, to Taylor's horror, he was still in the middle of the ocean instead of over Fort Lauderdale. The control tower then suggested that Taylor's team should fly west, which would have taken them to the landmass of Florida eventually. Instead of following his compass, Taylor headed for what he thought was west, but in reality was northwest, almost parallel to Florida.
After trying that for a while and no land in sight, Taylor decided that it was impossible for them to fly so far west and not reach Florida. He believed that he might have been near the Key West Islands. What followed was a series of serious confusions between Taylor, his team and the control tower. Taylor was not sure whether he was near Bahama or Key West, and he was not sure which direction was which due to compass malfunction. The control tower informed Taylor that he could not be in Key West since the wind that day did not blow that way. Some of his teammates believed that their compass was working. Taylor then set a course northeast according to their compass, which should take them to Florida if they were in Key West. When that failed, Taylor set a course west according to their compass, which should take them to Florida if they were in Bahama. If Taylor stayed this course he would have reached land before running out of fuel. However, at some point Taylor decided that he had tried going west enough. He then once again set a course northeast, thinking they were near Key West after all. Finally, his flight ran out of fuel and may have crashed into the ocean somewhere north of Abaco Island and east of Florida.[6]
In 1986, the wreckage of an Avenger was found off the Florida coast during the search for the wreckage of the Space Shuttle Challenger.[citation needed] Aviation archaeologist Jon Myhre raised this wreck from the ocean floor in 1990. He was convinced it was one of the missing planes, but positive identification could not be made. In 1991, the wreckage of five Avengers was discovered off the coast of Florida, but engine serial numbers revealed they were not Flight 19. They had crashed on five different days all within 1.5 mi (2.4 km) of each other.[7] Records revealed that the various discovered aircraft, including the group of five, were declared either unfit for maintenance/repair or obsolete, and were simply disposed of at sea.[7]
Records also showed training accidents between 1942 and 1945 accounted for the loss of 95 aviation personnel from NAS Fort Lauderdale[8] In 1992, another expedition located scattered debris on the ocean floor, but nothing could be identified. In the last decade[when?], searchers have been expanding their area to include farther east, into the Atlantic Ocean but the remains of Flight 19 have still never been confirmed found.
Men of Flight 19 and PBM-5 BuNo 59225
Charles Carroll Taylor
The flight leader, Lieutenant Charles Carroll Taylor (born October 25, 1917), graduated from Naval Air Station Corpus Christi in February 1942 and became a flight instructor in October of that year.
Aircraft
numberPilot Crew Series Nr. FT-28 Charles C. Taylor, Lieutenant, USNR George Devlin, AOM3c, USNR
Walter R. Parpart, ARM3c, USNR23307 FT-36 E. J. Powers, Captain, USMC Howell O. Thompson, SSgt., USMCR
George R. Paonessa, Sgt., USMC46094 FT-3 Joseph T. Bossi, Ensign, USNR Herman A. Thelander, S1c, USNR
Burt E. Baluk, JR., S1c, USNR45714 FT-117 George W. Stivers, Captain, USMC Robert P. Gruebel, Pvt., USMCR
Robert F. Gallivan, Sgt., USMC73209 FT-81 Robert J. Gerber, 2nd LT, USMCR William E. Lightfoot, Pfc., USMCR* 46325 BuNo 59225 Walter G. Jeffery, Ltjg, USN Harrie G. Cone, Ltjg, USN
Roger M. Allen, Ensign, USN
Lloyd A. Eliason, Ensign, USN
Charles D. Arceneaux, Ensign, USN
Robert C. Cameron, RM3, USN
Wiley D. Cargill, Sr., Seaman 1st, USN
James F. Jordan, ARM3, USN
John T. Menendez, AOM3, USN
Philip B. Neeman, Seaman 1st, USN
James F. Osterheld, AOM3, USN
Donald E. Peterson, AMM1, USN
Alfred J. Zywicki, Seaman 1st, USN59225 * This particular plane was one crew member short. The airman in question, Marine Corporal Allan Kosnar, had been given special permission not to fly that day.References
- ^ a b c Mayell, Hillary (December 15, 2003) Bermuda Triangle: Behind the Intrigue, National Geographic News. Verified 2008-03-10
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t McDonell, Michael (June 1973), "Lost Patrol", Naval Aviation News, p. 8–16.
- ^ a b c d United States Navy, (December 7, 1945) Board of Investigation Into 5 missing TBM airplanes and one PBM airplane convened by Naval Air Advanced Training Command, NAS Jacksonville, Florida, excerpt
Hosted by ibiblio.org. Verified 2008-03-08 - ^ a b Goodridge, Elisabeth (November 17, 2005) Flight 19 crew honored by House; disappearance began notion of Bermuda Triangle, Associated Press
- ^ United States Navy, Background on Naval Aircraft Bureau (Serial) Numbers Department of the Navy – Naval Historical Center
- ^ National Geographic, Naked Science (2006), Episode: Bermuda Triangle.
- ^ a b Dive to Bermuda Triangle (2004); telecast on The Science Channel, February 17, 2006
- ^ Air Station Fort Lauderdale Historical Association 95 young Americans lost their lives at the NAS Fort Lauderdale base during 1942-1945
Verified 2010-12-13
External links
- Flight 19 and Bermuda Triangle
- US Naval History and Heritage Command: Flight 19 - The Lost Patrol
- BBC: Flight 19 - The Lost Patrol
- Naval Air Station Fort Lauderdale Museum Flight 19 - The Lost Patrol
Jul 28 B-25 Empire State Building crash
Oct 05 National Airlines Flight 16
Nov 03 Honolulu Clipper forced landing
Dec 06 Flight 19Incidents resulting in at least 50 deaths shown in italics. Deadliest incident shown in bold smallcaps. Bermuda Triangle  1918: USS Cyclops (AC-4)
1918: USS Cyclops (AC-4)
 1921: Carroll A. Deering
1921: Carroll A. Deering 1925: SS Cotopaxi
1925: SS Cotopaxi
 1941: USS Proteus (AC-9)
1941: USS Proteus (AC-9) 1941: USS Nereus (AC-10)
1941: USS Nereus (AC-10)
 1963: SS Marine Sulphur Queen
1963: SS Marine Sulphur Queen Flight 19
Flight 19
 NC16002Categories:
NC16002Categories:- 1945 in the United States
- Bermuda Triangle
- Aviation accidents and incidents in 1945
- Unexplained disappearances
- Military units and formations of the United States Navy
- Missing aircraft
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
