- Grand Bahama
Infobox Islands
name = Grand Bahama
image caption =
image size =
locator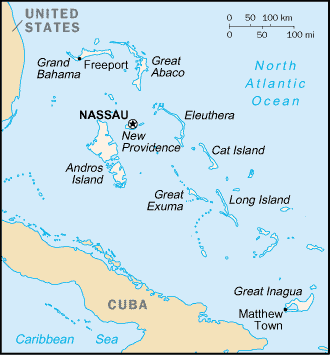
locator
Location map|Bahamas|lat=26.65|long=-78.316667
map_custom = yesnative name =
native name link =
nickname =
location =Atlantic Ocean
coordinates =coord|26|39|N|78|19|W|type:isle
archipelago =Bahamas
total islands =
major islands =
area = 1373 km²
highest mount = 40 ft
elevation =
country = BHS
country admin divisions title =
country admin divisions =
country capital city =
country largest city = Freeport
country largest city population =
country leader title =
country leader name =
population = approx 75,000
population as of = 2007
density = 34
ethnic groups =
additional info =Grand Bahama is one of the northernmost of the islands of the
Bahamas , and the closest major island to theUnited States , lying just 55 mi (90 km) off the state ofFlorida . Grand Bahama is the fourth largest island in the Bahamas island chain of approximately 700 islands and cays. The island is approximately convert|96|mi|km long west to east and convert|17|mi|km at its widest point north to south.Administratively the island consists of the Freeport Bonded Area and the districts of
East Grand Bahama andWest Grand Bahama History
Pre-Contact & Early Spanish Contact
Island's earliest known inhabitants were the
Stone Age hunter-gatherer Siboney Indians, of whom little evidence remains apart from artifacts such as ornamental shells or jewellery. These primitive people eventually disappeared to be replaced by theTaino Arawaks fromSouth America , who travelling in dugoutcanoes eventually colonized most of theCaribbean . The Arawak communities on Grand Bahama, who became known asLucayans (a name that lives on in the popular tourist town of Port Lucaya) were believed to have advanced and well-organized social and political structures, and there were estimated to be approximately 4,000 on Grand Bahama at the time of the arrival of the SpanishConquistadors in 1492. This arrival, and the subsequent claim of the island by Spain shortly after, eventually caused the Lucayans to disappear from Grand Bahama entirely, whether dying through the spreading of Europeandiseases , through the frequent Europeangenocides , or being captured as slaves (usually to mine forgold in the larger Caribbean islands ofHispaniola orCuba , or to dive for pearls inTrinidad ). The disappearance of the Lucayans was rapid, and it is probably for this reason little is known beyond rough estimates about their society. However, in sites such as the Lucayan National Park and Dead Man's Reef there have been numerous artifacts discovered including animal bones, pottery shards, shell beads and evidence of a complex burial system.The Spanish gave the island the name "Gran Bajamar", meaning "Great Shallows", and what the eventual name of the Bahamas islands as a whole is derived from. Grand Bahama's existence for almost two centuries was largely governed by the nature of these "great shallows" - the
coral reefs surrounding the island were treacherous, and repelled its Spanish owners (who largely left it alone apart from for infrequent en-route stops by ships for provisions) while attracting pirates, who would lure ships onto the reefs where they would run aground and be plundered. The Spaniards took little interest in the island after enslaving the nativeLucayan inhabitants.British Rule
The islands were claimed by Great Britain in 1670. Piracy continued to thrive for at least half a century after the British takeover, though the problem was eventually brought under control.
Grand Bahama was to remain relatively quiet until the mid-nineteenth century, with only around 200-400 regular inhabitants in the capital, West End. In 1834, the towns of
Pinder’s Point ,Russell Town andWilliams Town were established by former Bahamian slaves after the abolition of slavery in theBritish empire . The island was still little developed until a brief boom in economic activity during theAmerican Civil War , when it was a center for blockade runners smuggling goods (mostly weaponry, sugar and cotton) to the Confederacy. A second brief smuggling boom occurred during the years of prohibition in the USA.Hawksbill Creek Agreement Era
By the middle of the 20th century, Grand Bahama's population numbered around 500 and the island was one of the least developed of the Bahamas islands. However the island finally gained a stable source of income when in 1955 a
Virginia n financier namedWallace Groves began redevelopment with the Bahamian government to build the city of Freeport under the Hawksbill Creek Agreement and create theGrand Bahama Port Authority Soon after, the ambitious Edward St. George, with the financial help ofSir Jack Hayward , took the company to new frontiers. Seeing the success of Cuba as a tourist destination for wealthy Americans, St. George was eager to develop Grand Bahama in a similar vein. The city grew rapidly, with St. George adding a harbour, an airport (the largest privately owned airport in the world) soon after the city was founded, and the tourist center of Port Lucaya in 1962. Grand Bahama became the second most populous island in the Bahamas (over 50,000 in 2004).Economy
Tourism is the mainstay of the island's economy. The resort area at Port Lucaya and visits bycruise ship s provide the bulk of this activity. Grand Bahama's tourism sector is complemented by an oil bunkering facility owned by Petróleos de Venezuela S.A. and atransshipment /container port partly owned byHong Kong conglomerateHutchison Whampoa and the Grand Bahama Port Authority. There are also quarrying operations on the island and a large shipyard.Important Cities
Freeport is the major city of Grand Bahama Island. As mentioned above, it holds the commercial ship harbour and the main airport. Freeport has many good shops and roads, and is very clean. Foreign investors are just now waking up to the large number of pristine ocean and canal front properties that exist in the Freeport area. As of April 2007, premium waterfront lots can be found for as little as 20% of their counterparts on the Florida coast. Construction in the Freeport area is picking up quickly as a result. An attractive feature of Freeport property is that it's covered by the Hawksbill Creek agreement. Under this agreement, personal real estate is tax free until 2015. Major real estate brokers are [http://kdmgb.com KDM Construction] [http://ladylakebahamas.com Developers] [http://moskorealty.com MOSKO REALTY] , [http://www.hgchristie.com HG Christie] and [http://www.jamessarlesrealty.com James Sarles] . Note that there is no
Multiple Listing Service for Grand Bahama and the web sites can be very out of date.Port Lucaya (not a city to the natives) is an important tourist destination on Grand Bahama Island. It has beautiful beaches and contains several big hotels including the most popular, five-star "Our Lucaya" hotel chain made up of the Sheraton and Westin hotels and the Lanai Suites located at Lighthouse Point. Count Basie Square provides regular live entertainment targeted at cruise ship patrons. Fishing, snorkeling, sight seeing, and "booze cruise" trips leave from Bell Channel Harbour on a daily basis.
West End is officially the capital of Grand Bahama, though Freeport is believed by many to be. It's the oldest city and western most settlement on the island. It first achieved notoriety as a
Rum-running port during prohibition.In the 1950s it became home to the Jack Tar marina and club. However, over the years the marina fell into disrepair and the whole city of West End was of little economic import to Grand Bahama. In 2001, the marina was bought out by a group which renamed it Old Bahama Bay [ [http://www.hotel-online.com/News/PR2001_2nd/May01_OldBahama.html Hotel Online Report] ] . Significant renovations followed including complete refurbishment of the docks, many new canals cut for luxury home sites, luxury condos built, and restaurants built. In March of 2007,
Ginn Resorts took over operation of Old Bahama Bay. Ginn is investing heavily in the West End area, having purchased convert|1720|acre|km2 which it will turn into a luxury resort, marina, and home sites at a cost of 5 billion USD. The project is called [http://www.ginnsurmer.com Ginn Sur Mer] .McLeans Town is the eastern most settlement and a 30 minute ferry ride from the northernmost settlement of the Island of Abaco.
References
External links
* [http://www.bahamas.com Official Tourism Site of The Islands of the Bahamas]
* [http://www.grand-bahama.com Official Site of the Grand Bahama Island Tourism Board]
* [http://www.basragrandbahama.com/ BASRA - Bahamas Air-Sea Rescue Association]
* [http://www.gb-power.com/ Grand Bahama Power Company]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
