- Rafflesia
-
Rafflesia 
Rafflesia arnoldii flower and bud Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae (unranked): Angiosperms (unranked): Eudicots (unranked): Rosids Order: Malpighiales Family: Rafflesiaceae Genus: Rafflesia
R.Br.Species See text.
Rafflesia is a genus of parasitic flowering plants. It contains approximately 28 species (including four incompletely characterized species as recognized by Willem Meijer in 1997), all found in southeastern Asia, on the Malay Peninsula, Borneo, Sumatra, Thailand and the Philippines.[1]
Rafflesia was found in the Indonesian rain forest by an Indonesian guide working for Dr. Joseph Arnold in 1818, and named after Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles, the leader of the expedition. It was discovered even earlier by Louis Deschamps in Java between 1791 and 1794, but his notes and illustrations, seized by the British in 1803, were not available to western science until 1861.[citation needed]
The plant has no stems, leaves or true roots. It is an endoparasite of vines in the genus Tetrastigma (Vitaceae), spreading its absorptive organ, the haustorium, inside the tissue of the vine. The only part of the plant that can be seen outside the host vine is the five-petaled flower. In some species, such as Rafflesia arnoldii, the flower may be over 100 centimetres (39 in) in diameter, and weigh up to 10 kilograms (22 lb). Even the smallest species, R. baletei, has 12 cm diameter flowers. The flowers look and smell like rotting flesh, hence its local names which translate to "corpse flower" or "meat flower" (but see below). The vile smell attracts insects such as flies, which transport pollen from male to female flowers. Most species have separate male and female flowers, but a few have bisexual flowers. Little is known about seed dispersal. However, tree shrews and other forest mammals apparently eat the fruits and disperse the seeds. Rafflesia is an official state flower of Indonesia, also Sabah state in Malaysia, as well as for the Surat Thani Province, Thailand.
The name "corpse flower" applied to Rafflesia is confusing because this common name also refers to the Titan Arum (Amorphophallus titanum) of the family Araceae. Moreover, because Amorphophallus has the world's largest unbranched inflorescence, it is sometimes mistakenly credited as having the world's largest flower. Both Rafflesia and Amorphophallus are flowering plants, but they are still distantly related. Rafflesia arnoldii has the largest single flower of any flowering plant, at least when one judges this by weight. Amorphophallus titanum has the largest unbranched inflorescence, while the Talipot palm (Corypha umbraculifera) forms the largest branched inflorescence, containing thousands of flowers; this plant is monocarpic, meaning that individuals die after flowering.
Contents
Classification
- Species
- Rafflesia arnoldii
- Rafflesia aurantia
- Rafflesia azlanii
- Rafflesia baletei
- Rafflesia bengkuluensis
- Rafflesia cantleyi
- Rafflesia gadutensis
- Rafflesia hasseltii
- Rafflesia keithii
- Rafflesia kerrii
- Rafflesia leonardi
- Rafflesia lobata
- Rafflesia manillana
- Rafflesia micropylora
- Rafflesia mira
- Rafflesia patma
- Rafflesia philippensis
- Rafflesia pricei
- Rafflesia rochussenii
- Rafflesia schadenbergiana
- Rafflesia speciosa
- Rafflesia tengku-adlinii
- Rafflesia tuan-mudae
- Rafflesia verrucosa
- Unverified species
- Rafflesia borneensis
- Rafflesia ciliata
- Rafflesia titan
- Rafflesia witkampii
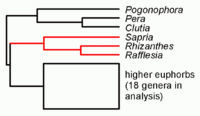
Comparison of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) sequences of Rafflesia with other angiosperm mtDNA indicated that this parasite evolved from photosynthetic plants of the order Malpighiales.[2] Another study from that same year confirmed this result using both mtDNA and nuclear DNA sequences, and showed that three other groups traditionally classified in Rafflesiaceae were unrelated.[3] A more recent study found Rafflesia and its relatives to be embedded within the family Euphorbiaceae, which is surprising as members of that family typically have very small flowers.[4] According to their analysis, the rate of flower size evolution was more or less constant throughout the family except at the origin of Rafflesiaceae, where the flowers rapidly evolved to become much larger before reverting to the slower rate of change.
Malaysian species
Species native to Malaysia include Rafflesia pricei, Rafflesia tengku-adlinii, Rafflesia keithii, and Rafflesia arnoldii. Some Malaysian species, such as R. keithii, begin blooming at night and begin to decompose only 2–3 days after blooming, this after a 6–9 month budding period. Male and female flowers must be open simultaneously for pollination to occur, hence successful pollination is quite rare and some species may be endangered. Rafflesia keithii is found along the eastern slopes of Mount Kinabalu in the Lohan Valley of Sabah.[1]
Philippine species
Since 2002 there has been a tremendous amount of activity by Filipino scientists who have discovered and named several new species of Rafflesia. Before this time there were two species known: R. manillana and R. schadenbergiana, the latter of which was last seen in 1882 on Mt. Apo in Davao Province on Mindanao Island, but was thought to be extinct. The following gives a chronicle of these activities:
- 2002. A Rafflesia was found in the mountains of Antique Province that differed from any previously described. It was named Rafflesia speciosa by Barcelona and Fernando (Kew Bulletin, 57: 647-651, 2002).
- 2005. Another Rafflesia was discovered in the Philippines by Drs. Fernando and Ong on remote Mount Candalaga, Maragusan, Compostela Valley province in Mindanao. It was named Rafflesia mira by Fernando and Ong (2005. Asia Life Sciences 14: 263-270). Another group (Madulid et al. 2005 Acta Manilana 53: 1-6) published another name (R. magnifica) later, thus R. mira stands as the nomenclaturally valid name. R. mira (45–60 cm in diameter), is approximately the same size as R. speciosa (45–56 cm) of Antique Province, but definitely larger than Luzon’s R. manillana (14–20 cm in diameter).[5]
- 2005. During his expedition to Mt. Igtuog and Mt. Sakpaw in the Central Panay mountain range in April 2005, Renee Galang discovered a previously undescribed Rafflesia. This was named R. lobata by Galang and Madulid (2006, Folia Malaysiana 7: 1-8).
- 2006. Danny Balete collected a previously undescribed species of Rafflesia in 1991 in the Bicol Region of southern Luzon. The collection was not recognized as a new species until further field work confirmed that this taxon was different than R. manillana. Several new populations have also been seen in the Camarines Sur Province (Mount Isarog and Mount Iriga)] in the vicinity of Buhi and Iriga City. This was named R. baletei by Barcelona, Cajano, and Hadsall (2006. Kew Bulletin 61: 231-237). The names R. irigaense or R. irigaenses are invalid and refers to the same taxon.
- 2007. In 1994 Pascal Lays rediscovered buds of R. schadenbergiana in South Cotabato. His paper reporting this result has only recently been published. In 2007, Dr. Julie Barcelona visited yet another population of this rare species in Bukidnon. An account of this discovery was published the following year (2008. Flora Malesiana Bulletin, 14: 162-165; see also Parasitic Plant Connection).
- 2007. Mount Banahaw in Luzon, a popular destination for mountaineering and religious groups seemed, until recently, an unlikely spot to find a new species of Rafflesia. But such was the case. Ironically, two papers have been published naming this Rafflesia as a new species. Apparently the first one was by Madulid et al. (2006, Philippine Scientist 43: 43–51 - but only available July 2007) and the second by Barcelona et al. (2007, Blumea 52: 345–350). At this point, it seemed that the correct name was R. banahawensis, not R. banahaw. But more investigation by Julie Barcelona showed that this species was first named by Blanco in his Flora de Filipinas (1845). Thus, the correct name for this species is Rafflesia philippensis Blanco.
- 2007. A description of the Rafflesia from Mount Makiling on Luzon was published as a new species, R. panchoana by D. A. Madulid and coauthors (2007, Acta Manilana 55: 43-47 - but available only in 2008). Comparison to other populations of R. manillana by Dr. Barcelona and coauthors [6] lead them to conclude that this population is R. manillana.
- 2008. In the remote sitio Kinapawan in the coastal town of Lal-lo in Cagayan Valley, a Rafflesia was made known to Filipino botanists. Working with CAVAPPED, CI, and DENR staff, Julie Barcelona traveled to the site and collected the type of this Rafflesia. R. leonardi is similar to R. manillana (of Samar and Luzon) and R. lobata of Panay by the wide diaphragm aperture and flowers that grow on the roots and aerial portion of the vine. It is, however, different in its larger size (to 34 cm), central disk that is nearly smooth or with markedly reduced processes, and the absence of white blotches/windows inside the floral tube. It was determined that this was a new species and was named in honor of the late Leonardo Co who was an expert on the Cagayan flora (2008. Blumea 53: 223-228). It is the 5th Rafflesia found on Luzon and the 8th from the Philippines. In 2010 the name R. banaoana, was published by Pastor Malabrigo, Jr. of the University of the Philippines Los Baños for a Rafflesia found in the Balbalasang-Balbalan National Park in Kalinga, Luzon. This Rafflesia has since been carefully evaluated and found to be conspecific with R. leonardi [7] Popular articles describing R. leonardi can be found in the following references.[8][9]
- 2009. The ninth species of Rafflesia from the Philippines, R. aurantia, was described in Barcelona et al. (Gardens' Bulletin Singapore 61 (1): 17-27), which also includes a summary of the current state of knowledge on Philippine Rafflesia. This species superficially resembles R. tengku-adlinii of northern Borneo but differs in a number of features such as ramenta, disk processes and anther number. The population occurs in the Quirino Protected Landscape, Quirino Province, Luzon.
- 2010. The tenth species of Rafflesia, Rafflesia verrucosa, found in the Philippines was named by Danny Balete and coauthors in the following publication [10] This Rafflesia is noteworthy in having small flowers whose perigone lobes are covered with dense warts (hence the name) as well as by possessing a bisexual flower with other unusual features not seen in any other Rafflesia species.
See also
- Amorphophallus titanum, similar smelling plant, sometimes known as "corpse flower".
- Parasitic plant
- Carrion plant
References
- ^ a b VJR Rafflesia Reserve, Forestry Department Sabah, Malaysia, [1]
- ^ Barkman, T. J.; S.-H. Lim, K. Mat Salleh, J. Nais (January 20, 2004). "Mitochondrial DNA sequences reveal the photosynthetic relatives of Rafflesia, the world's largest flower". PNAS 101 (3): 787–792. doi:10.1073/pnas.0305562101. PMC 321759. PMID 14715901. http://www.pnas.org/cgi/content/abstract/101/3/787?ijkey=b831816f017b346a02ca946d8bec3bff87ef686c&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha.
- ^ Nickrent, D. L.; A. Blarer, Y.-L. Qiu, R. Vidal-Russell, F. E. Anderson. (October 20, 2004). "Phylogenetic inference in Rafflesiales: the influence of rate heterogeneity and horizontal gene transfer". BMC Evolutionary Biology 4: 40: 40. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-4-40. PMC 528834. PMID 15496229. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2148/4/40.
- ^ Davis, C. C.; M. Latvis, D. L. Nickrent, K. J. Wurdack, D. A. Baum (January 11, 2007). "Floral gigantism in Rafflesiaceae". Science 315 (5820): 1812. doi:10.1126/science.1135260. PMID 17218493. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/abstract/1135260v1?maxtoshow=&HITS=10&hits=10&RESULTFORMAT=&fulltext=Rafflesia&searchid=1&FIRSTINDEX=0&resourcetype=HWCIT.
- ^ Haribon Foundation, Raffesia mira: yet another reason to be proud of the Philippines!
- ^ Barcelona, J. F.; P. B Pelser, D. S. Balete, and L. L. Co. (October 2009). "Taxonomy, ecology, and conservation status of Philippine Rafflesia (Rafflesiaceae)". Blumea 54: 77-94: 17. doi:10.3767/000651909X474122. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/nhn/blumea/2009/00000054/F0030001/art00016.
- ^ "An amended description of Rafflesia leonardi and a revised key to Philippine Rafflesia (Rafflesiaceae)". Phytotaxa 24: 11-18. May 2011. http://www.mapress.com/phytotaxa/content/2011/1/pt00024p018.pdf.
- ^ New flower species found in Cagayan
- ^ Rare flower species found only in northern Philippines
- ^ "Rafflesia verrucosa (Rafflesiaceae), a new species of small-flowered Rafflesia from Mindanao, Philippines". Phytotaxa 10: 49-57. September 2010. http://www.mapress.com/phytotaxa/content/2010/1/pt00010p057.pdf.
Further reading
- Jamili Nais (2001). Rafflesia of the world. Kota Kinabalu: Sabah Parks. ISBN 9838120421. OCLC 50043098.
External links
Categories:- Rafflesiaceae
- Parasitic plants
- Flora of Southeast Asia
- Flora of Malesia
- Flora of Indonesia
- Flora of Malaysia
- Flora of Borneo
- Flora of the Philippines
- Flowers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.