- NOνA
-
NOνA (NuMI Off-Axis νe Appearance) is a particle physics experiment designed to detect neutrinos in Fermilab's NuMI (Neutrinos at the Main Injector) beam. Intended to be the successor to MINOS, NOνA will consist of two detectors, one at Fermilab (the near detector), and one in northern Minnesota (the far detector). Neutrinos from NuMI will pass through 810 km of Earth to reach the far detector. NOνA's main goal is to observe the oscillation of muon neutrinos to electron neutrinos. By observing how many neutrinos change from one type to the other, NOνA hopes to accomplish three things:
- Measurement of the mixing angle θ13
- Measurement of the CP-violating phase δ
- Determination of the neutrino mass hierarchy
Contents
Physics goals
Primary goals
Neutrino oscillation is parameterized by the PMNS matrix and the mass squared differences between the neutrino mass eigenstates. Assuming that three flavors of neutrinos participate in neutrino mixing, there are six variables that affect neutrino oscillation: the three angles θ12, θ23, and θ13, a CP-violating phase δ, and any two of the three mass squared differences. There is currently no compelling theoretical reason to expect any particular value of, or relationship between, these parameters.
θ23 and θ12 have been measured to be non-zero by several experiments but the most sensitive search for non-zero θ13 by the CHOOZ collaboration yielded only an upper limit. No measurement of δ has been made. The absolute values of two mass squared differences are known, but because one is very small compared to the other, the ordering of the masses has not been determined.
NOνA will be an order of magnitude more sensitive to θ13 than any previous detector. It will measure it by searching for the transition
 in the Fermilab NuMI beam. If a non-zero value of θ13 is resolvable by NOνA, it will be possible to obtain measurements of δ and the mass ordering by also observing
in the Fermilab NuMI beam. If a non-zero value of θ13 is resolvable by NOνA, it will be possible to obtain measurements of δ and the mass ordering by also observing  δ can be measured because it modifies the probabilities of oscillation in opposite ways for neutrinos and anti-neutrinos. The mass ordering, similarly, can be determined because the neutrinos pass through the Earth, which, through the MSW effect, modifies the probabilities of oscillation differently for neutrinos and anti-neutrinos.[1]
δ can be measured because it modifies the probabilities of oscillation in opposite ways for neutrinos and anti-neutrinos. The mass ordering, similarly, can be determined because the neutrinos pass through the Earth, which, through the MSW effect, modifies the probabilities of oscillation differently for neutrinos and anti-neutrinos.[1]Importance
The neutrino masses and mixing angles are, to the best of our knowledge, fundamental constants of the universe. Measuring them is a basic requirement for our understanding of physics. Knowing the value of the CP violating parameter δ will help us understand why the universe has a matter-antimatter asymmetry. Also, according to the Seesaw mechanism theory, the very small masses of neutrinos may be related to very large masses of particles that we do not yet have the technology to study directly. Neutrino measurements are then an indirect way of studying physics at extremely high energies.[1]
In our current theory of physics, there is no reason why the neutrino mixing angles should have any particular values. And yet, of the three neutrino mixing angles, only θ12 has been resolved as being neither maximal or minimal. If the measurements of NOνA and other future experiments continue to show θ23 as maximal and θ13 as minimal, it may suggest some as yet unknown symmetry of nature.[1]
Relationship to other future experiments
NOνA can potentially resolve the mass hierarchy because it has a very long baseline. It is the only experiment likely to run in the near future that has this ability. Many future experiments that seek to make precision measurements of neutrino properties will rely on NOνA's measurement to know how to interpret their results. One such experiment is T2K, a neutrino beam experiment in Japan similar to NOνA. Like NOνA, it is intended to measure θ13 and δ. It will have a 295 km baseline and will use lower energy neutrinos than NOνA, about 0.8 GeV. Since matter effects are less pronounced both at lower energies and shorter baselines, it will be unable to resolve the mass ordering.[2]
Neutrinoless double beta decay experiments will also benefit from knowing the mass ordering, since the mass hierarchy affects the theoretical lifetimes of this process.[1]
Reactor experiments also have the ability to measure θ13. While they cannot measure δ or the mass ordering, their measurement of the mixing angle is not dependent on knowledge of these parameters. One such proposed experiment is Daya Bay, to be located at the Daya Bay reactor in Hong Kong, which will use a 2 km baseline optimized for observation of the first θ13-controlled oscillation maximum.[3]
Secondary goals
In addition to its primary physics goals, NOνA will be able to improve upon the measurements of the already measured oscillation parameters. NOνA, like MINOS, is well suited to detecting muon neutrinos and so will be able to able to refine our knowledge of θ23.
The NOνA near detector will be used to conduct measurements of neutrino interaction cross sections which are currently not known to a high degree of precision. Its measurements in this area will complement other similar upcoming experiments, such as MINERνA, which also uses the NuMI beam.[4]
Since it is capable of detecting neutrinos from galactic supernovas, NOνA will form part of the Supernova Early Warning System. Supernova data from NOνA can be correlated with that from SuperKamiokande to study the matter effects on the oscillation of these neutrinos.[1]
Design
 Cross section of the earth showing Fermilab, MINOS and NOνA, to scale. The red line is the central axis of the NuMI beam.
Cross section of the earth showing Fermilab, MINOS and NOνA, to scale. The red line is the central axis of the NuMI beam.
To accomplish its physics goals, NOνA needs to be efficient at detecting electron neutrinos, which are expected to appear in the NuMI beam (originally made only of muon neutrinos) as the result of neutrino oscillation.
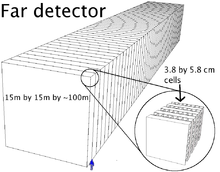
The proposed design is a pair of finely grained liquid scintillator detectors. The near detector will be at Fermilab and will sample the unoscillated beam. The far detector will be in northern Minnesota. The far detector will consist of about 500,000 4 cm × 6 cm × 16m cells filled with liquid scintillator. Each cell will have a loop of bare fiber optic cable to collect the scintillation light, both ends of which lead to an avalanche photodiode for readout. The near detector will have the same general design, but will only be about 1/200 as massive.
Previous neutrino experiments, such as MINOS, have reduced backgrounds from cosmic rays by being underground. However, NOνA will be on the surface and will rely on precise timing information and a well-defined beam energy to reduce backgrounds. It will be situated 810 km from the origin of the NuMI beam and 14 milliradians (12 km) west of the beam's central axis. In this position, it will sample a beam that has a much narrower energy distribution than if it were centrally located, further reducing the effect of backgrounds.[1]
Collaboration
The NOνA experiment includes scientists from a large number of institutions. Different institutions take on different tasks. The collaboration, and subgroups thereof, meets regularly via phone for weekly meetings, and in person several times a year. Participating institutions as of January 2011 are:[5]
- Argonne National Laboratory
- University of Athens
- California Institute of Technology
- University of California, Los Angeles
- Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory
- Harvard University
- Indiana University
- Iowa State University
- Lebedev Physical Institute
- Michigan State University
- University of Minnesota Duluth
- University of Minnesota, Minneapolis
- The Institute for Nuclear Research, Moscow
- Technische Universität München, Munich
- State University of New York, Stony Brook
- Northern Illinois University, DeKalb
- Northwestern University
- Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio de Janeiro
- University of South Carolina, Columbia
- Southern Methodist University
- Stanford University
- University of Tennessee, Knoxville
- Texas A&M University
- University of Texas, Austin
- University of Texas, Dallas
- Tufts University
- University of Virginia, Charlottesville
- The College of William and Mary
- Wichita State University
Current status
In late 2007, NOνA passed a Department of Energy review that grants it "Critical Decision 2", meaning roughly that its design, cost, schedule, and scientific goals have been approved. This also allows for inclusion of project in the Department of Energy congressional budget request. To begin construction, NOνA will still have to pass a "Critical Decision 3" review.
On 21 December 2007, President Bush signed an omnibus spending bill, H.R. 2764, that cut the funding for high energy physics by 88 million dollars from the expected value of 782 million dollars.[6] The budget of Fermilab was cut by 52 million dollars.[7] This bill explicitly states that "Within funding for Proton Accelerator-Based Physics, no funds are provided for the NOνA activity in Tevatron Complex Improvements."[8] So although the NOνA project retained its approval from both the Department of Energy and Fermilab, the lack of funds provided by Congress for the 2008 fiscal year left NOνA with no capital to build its detector, pay its staff, or to continue in the pursuit of scientific results. However, in July 2008, Congress passed and the President Bush signed a supplemental budget bill,[9] which includes funding for NOνA, allowing the collaboration to resume the work.
The NOvA prototype near detector began running at Fermilab in November and registered its first neutrinos from the NuMI beam on 15 December 2010.[10]
References
- ^ a b c d e f "NOνA Proposal to Build a 30 Kiloton Off-Axis Detector to Study Neutrino Oscillations in the Fermilab NuMI Beamline", D.S. Ayres, et al. (NOνA Collaboration), arXiv:hep-ex/0503053
- ^ "Letter of Intent: Neutrino Oscillation Experiment at JHF", The T2K Collaboration, 21 Jan 2003.
- ^ "Daya Bay Neutrino Experiment", J. Cao, arXiv:hep-ex/0509041
- ^ "MINERvA: a dedicated neutrino scattering experiment at NuMI", K. McFarland (MINERνA collaboration), arXiv:physics/0605088
- ^ NOνA webpage: The NOvA Collaboration, retrieved 2011 Jan 27
- ^ American Institute of Physics, FYI Number 121: December 18, 2007, "Budget Cycle Closing With Disappointing DOE Science Outcome", accessed 21 Dec 2007
- ^ Chicago Tribune, 20 Dec 2007, "Fermilab budget slashed by $52 million, layoffs likely", accessed 21 Dec 2007]
- ^ House Amendments to Senate Amendment to H.R. 2764 – State, Foreign Operations, and Related Programs Appropriations Act, 2008 (Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2008), Division C--Energy and Water, page 39 (PDF page 79), accessed 21 Dec 2007. See also the index page for the whole Amendment
- ^ http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=fermilab-saved-from-chopp
- ^ Fermilab Today 21 Dec 2010, accessed 22 Dec 2010
External links
- NOνA's official website
- "NOνA: a neutrino appearance experiment" article in Symmetry magazine
- Photos of the construction of the NOνA detector
Neutrino detectors, experiments, and facilities Discoveries 
Operating Construction Retired Proposed Cancelled See also Categories:- Accelerator neutrino experiments
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.