- Airport crash tender
-
 "FLF Panther" airport crash tender in Germany.
"FLF Panther" airport crash tender in Germany.
An airport crash tender (known in some countries as an airport fire appliance) is a specialised fire engine designed for use at aerodromes and airports in aircraft accidents.
Airport Crash Tenders are extremely powerful machines. They offer relatively good acceleration (for such large, heavy vehicles), are able to negotiate rough terrain outside the runway and airport area, carry large capacities of water, and fire fighting foam, are fitted with powerful high-capacity pumps, and water/foam cannons and capable of delivering firefighting media over long distances.
Newer ARFF vehicles also incorporate Twin Agent nozzles/injection systems to inject a stream of Purple-K dry chemical into the AFFF foam stream "knocking-down" the fire faster. Some also have Halotron tanks with handlines for situations that require a clean agent to be utilized. These features give the airport crash tenders a capability to reach an airplane rapidly, and rapidly put out large fires with jet fuel involved.
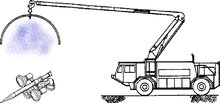
Some tenders have an elevated extended extinguishing arm, giving a possibility to raise a water/foam cannon into the height of approx. 10 – 20 meters. that can puncture through superficial structures of an aeroplane to fight a fire inside the fuselage.[1]
Some arms have reinforced nozzles, called a Snozzle, that, according to the US National Transportation Safety Board is a "piercing nozzle on the fire truck that is used to penetrate an airplane's fuselage and dispense AFFF to extinguish fire inside the cabin or cargo area.[2]
Contents
Standards
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has given standards and recommended practices on rescue fire fighting categories of civil aerodromes.[3][4][5] National aviation authorities may have given even further requirements on aerodrome rescue and fire services.
The rescue fire services are based on a critical aircraft based on a statistical analysis of movements (take-offs and landings) on the airport. The aerodrome category is based on the size of the biggest aircraft taking a movement on the aerodrome. In addition, the number of movements of the critical aircraft is calculated, and the category can be decreased by one if the number of movements is lower than the standard describes. There are also minimum category levels based on e.g. the number of seats in the critical aircraft.[6]
Depending on the airport category, the standards determine the minimum number of rescue fire-fighting vehicles. In addition, requirements are given on the water and foam capacities, discharge rates for foam solutions, and minimum dry chemical powder (complementary agent) amounts, reserve stocks of fire fighting agents, ability to operate on rough terrain, and acceleration of the air crash tenders. The end of each runway has to be achieved in a response time of two minutes, and any part of the movement area has to be achieved in a response time not exceeding three minutes.
Range of airport firefighting vehicles
Airport rescue and firefighting services operate many specialist vehicles to provide emergency cover at airports. They include:-
1) Crash tenders (as described above)
2) "Domestic" type fire appliances. Domestic appliances are similar in function and appearance to fire appliances operated by county fire services / departments. They are not as large or as heavy as airport crash tenders. The units are ordinarily used to respond to fire incidents in airport terminal buildings but also respond to aircraft incidents. The appliances carry Breathing Apparatus, rescue equipment, firefighting media, ladders, cutting equipment.
3) "First attack" or "rapid intervention vehicles"(RIV). RIVs are normally smaller, nimble fire appliances capable of quick acceleration and high speed. They carry less equipment than Domestic and Crash Tenders but arrive first on scene at aircraft incidents to begin rescue and firefighting operations whilst heavier / larger units approach.
4) General purpose vehicles (such as a fire chief's car or general purpose or incident support vehicles).
Examples
- Alvis Salamander
 United Kingdom military, 1950s
United Kingdom military, 1950s - Colet Jaguar series
 United States, commercial, current (K/R 40 Jaguar is "the most powerful crash truck in the world", 3 turbo motors, 2000 HP retarders, 10x8 drive) [7]
United States, commercial, current (K/R 40 Jaguar is "the most powerful crash truck in the world", 3 turbo motors, 2000 HP retarders, 10x8 drive) [7] - Oshkosh Striker
 United States, commercial, current
United States, commercial, current
- Oshkosh Corporation T3000
 United States, commercial
United States, commercial - Oshkosh Corporation T1500
 United States, commercial
United States, commercial
- Oshkosh Corporation T3000
- Rosenbauer Panther, Austria, commercial, current
- Kronenburg, Netherlands, commercial, current
- Scammell 6X6 Airport Crash Tender
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom - Volvo F12
 Sweden
Sweden - Ayaxx Crash Tender
- Morita MAF125A Crash Tender
 Japan
Japan - Douglas Protector II
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom - American-LaFrance O-11A aircraft firefighting truck
 United States
United States - Iveco 380 HP Airport Crash Tender
- Simba 6x6 airport tender
- Simba 8x8 airport tender
- MANSK 8x8 airport tender
- Ziegler Z8 airport tender
- Bachert-Ziegler FLF 3500 airport tender
- Kamaz 6x6 airport tender
- Timoney 6x6 Airport Crash Tender
 Ireland
Ireland - MAN 8x8 airport crash tender
 Germany
Germany - Iveco Magirus Dragon airport tender
- Iveco Magirus SuperDragon airport tender
- Iveco Magirus Impact airport tender
- Amertek RIV (Rescue Intervention Vehicle)
- Waltek C5500-P fire response vehicle
- Waltek RIV 2000
- E-One Titan 6x6
See also
- Firefighter
- Glossary of firefighting terms
- Heavy rescue vehicle
- Water tender
- Water salute
- Aircraft rescue and firefighting
References
- ^ Relyea; Robert G., Garnett; Edward V.: United States Patent Application, February 8, 1993. http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=5301756
- ^ NTSB
- ^ ICAO: Volume 1 - Aerodrome Design and Operations. Annex 14: Aerodrome Rescue and Fire Fighting Service (RFFS) requirements
- ^ ICAO: Airport Services Manual. Part 1 - Rescue and Fire Fighting. 3rd edition, 1990
- ^ Find relevant ICAO standards and recommended practices on SKYbrary
- ^ Categories for Fire Fighting and Minimum Fire Fighting Capacity
- ^ Colet Jaguar series
Gallery of airport crash tenders
-
Crashtender Royal Netherlands Air Force
-
Vehicle at Paderborn-Lippstadt / Germany
-
A Range Rover airport crash tender at RAF Elvington
-
Alvis Salamander airport crash tender fitted with Pyrene equipment
-
Crash tender from Ostrava airport during NATO Day, Czech Republic
-
Crash tender at a C-5 Galaxy crash on April 3, 2006 at Dover Air Force Base, Delaware.
-
Airport crash tender, used by ESS Group, at the Wagga Wagga Airport
Categories:- Firefighting equipment
- Alvis Salamander
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.