- Discrete signal
-
(Discrete here means "constituting a separate entity" and is distinct from "discreet"; a "discreet signal" is one not intended to be seen by others.)
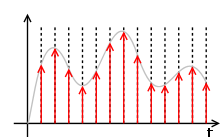
A discrete signal or discrete-time signal is a time series consisting of a sequence of qualities. In other words, it is a type series that is a function over a domain of discrete integral.
Unlike a continuous-time signal, a discrete-time signal is a function of a continuous argument; however, it may have been obtained by sampling from a discrete-time signal, and then each value in the sequence is called a sample. When a discrete-time signal obtained by sampling is a sequence corresponding to uniformly spaced times, it has an associated sampling rate; the sampling rate is not apparent in the data sequence, and so needs to be associated as a separate data item.
Contents
Acquisition
Discrete signals may have several origins, but can usually be classified into one of two groups:[1]
- By acquiring values of an analog signal at constant or variable rate. This process is called sampling.[2]
- By recording the number of events of a given kind over finite time periods. For example, this could be the number of people taking a certain elevator every day.
Digital signals
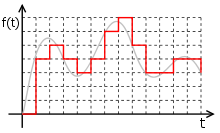
A digital signal is a discrete-time signal for which not only the time but also the amplitude has been made discrete; in other words, its samples take on only values from a discrete set.
The process of converting a continuous-valued discrete-time signal to a digital (discrete-valued discrete-time) signal is known as analog-to-digital conversion. It usually proceeds by replacing each original sample value by an approximation selected from a given discrete set (for example by truncating or rounding, but much more sophisticated methods exist), a process known as quantization. This process loses information, and so discrete-valued signals are only an approximation of the converted continuous-valued discrete-time signal, itself only an approximation of the original continuous-valued continuous-time signal.
Common practical digital signals are represented as 8-bit (256 levels), 16-bit (65,536 levels), 32-bit (4.3 billion levels), and so on, though any number of quantization levels is possible, not just powers of two.
See also
- Aliasing
- Anti-aliasing filter
- Digital-to-analog converter
- Digital control
- Digital frequency
- Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem
- Whittaker–Shannon interpolation formula
- Sampling (signal processing)
- Ideal sampler
References
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.