- Merycoidodon
-
Merycoidodon
Temporal range: Late Eocene–Late Oligocene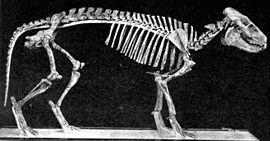
Merycoidodon culbertsoni skeleton Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Artiodactyla Family: †Merycoidodontidae Subfamily: †Merycoidodontinae Genus: †Merycoidodon
Leidy, 1848Type species †Merycoidodon culbertsoni Subgenera and Species[1] †Merycoidodon
- †M. (?M.) presidioensis
- †M. (M.) culbertsoni
†Otarohyus
- †M. (O.) bullatus
- †M. (O.) major
unassigned
- †M. dunagani
Synonyms - †Blickohyus Schultz and Falkenbach, 1968
- †Genetochoerus Schultz and Falkenbach, 1968
- †Oreodon Leidy, 1851
- †Otionohyus Schultz and Falkenbach, 1968
- †Paramerycoidodon Schultz and Falkenbach, 1968
- †Prodesmatochoerus Schultz and Falkenbach, 1954
- †Promesoreodon Schultz and Falkenbach, 1949
- †Subdesmatochoerus Schultz and Falkenbach, 1954
Merycoidodon ("Ruminating teeth") is an extinct genus of terrestrial herbivore of the family Merycoidodontidae, subfamily Merycoidodontinae (oreodont), more popularly known by the name Oreodon ("Hillock teeth") endemic to North America during the Late Eocene-Early Miocene subepochs (38—16.3 mya) existing for approximately 21.7 million years.[2]
Contents
Taxonomy
Merycoidodon was named by Leidy (1848). Its type is Merycoidodon culbertsoni. It was considered a nomen nudum by Cope (1884); it was considered a nomen dubium by Sinclair (1924); it was considered a nomen vanum by Lander (1998). It was assigned to Merycoidodontidae by Joseph Leidy (1848), Thorpe (1937), Scott (1940), Galbreath (1953), Toohey (1959) and Stevens and Stevens (1996).[3][4]
Most researchers in paleobiology and paleontology, however, now use the antecedent genus Merycoidodon to refer to this Oligocene epoch oreodont. The name "Oreodon" is actually a synonym of the fish genus Orodus, and is, thus, not a valid scientific name.
Taxonomically speaking, Merycoidodon (a.k.a. Oreodon) belongs to the family "Merycoidodontidae" (once known as "Oreodontidae"), a group of artiodactyls related to camels that were endemic to North America. Its ancestors date back to the Eocene and its last descendants are known from the Pliocene, so that oreodonts, broadly speaking, lived throughout the whole of the Tertiary era.
Morphology
Merycoidodon would have somewhat resembled a pig in appearance, but had a longer body, at about 1.4 metres (4.6 ft), and short limbs. The fore limbs had five toes (although the first one was vestigial), while the hind limbs had four. Given the shape of the limbs, it is unlikely that the animals would have been able to run fast. Unlike modern ruminants, they had a full set of teeth, although the molars were adapted for grinding up tough vegetation. Notably, they had strong, and very striking, canines.[5]
The skulls of Mercyoidodon have a pit in front of the eyes. Similar pits are found in the skulls of modern deer, where they contain a scent gland used for marking territory. Although Merycoidodon was not directly related to deer, it seems likely that it possessed a similar gland, which may imply that it, too, was territorial.[5]
Oreodonts lived in large herds and moved about from place to place. They seem to have had a predilection for well-watered regions, where food was plentiful and succulent. The number of fossils found implies that, at one time, oreodonts were as plentiful in south Dakota as zebras are today in the steppes of North Africa.
Four specimens were examined by M. Mendoza for body mass and estimated to have a weight of:
- Specimen 1: 139.2 kg (306.8 lbs).
- Specimen 2: 94.6 kg (208.5 lbs).
- Specimen 3: 112.8 kg (248.6 lbs).
- Specimen 4: 131.3 kg (289.4 lbs).[6]
Fossil distribution
Fossils have been uncovered as far north as Alberta, Canada to Florida and Texas, and Oregon.
References
- ^ Stevens, M.S.; Stevens, J.B. (1996). "Merycoidodontinae and Miniochoerinae". In Prothero, D.R.; and Emry, R.J. (eds.). The terrestrial Eocene-Oligocene transition in North America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 498–573. ISBN 0521433878.
- ^ PaleoBiology Database: Merycoidodon, basic info
- ^ B. Lander. 1998. Oreodontoidea. In C. M. Janis, K. M. Scott, and L. L. Jacobs (eds.), Evolution of Tertiary mammals of North America 402-425
- ^ L. Toohey. 1959. The species of Nimravus (Carnivora, Felidae). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 118
- ^ a b Palmer, D., ed (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 271. ISBN 1-84028-152-9.
- ^ M. Mendoza, C. M. Janis, and P. Palmqvist. 2006. Estimating the body mass of extinct ungulates: a study on the use of multiple regression. Journal of Zoology
- Benes, Josef. Prehistoric Animals and Plants. Pg. 219. Prague: Artua, 1979.
External links
Categories:- Oreodonts
- Eocene mammals
- Oligocene mammals
- Miocene extinctions
- White River Fauna
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.





