- National Council of the Slovak Republic
-
National Council of the Slovak Republic Type Type Unicameral Leadership Speaker Pavol Hrusovsky, Christian Democratic Movement
since 13 October 2011Structure Members 150 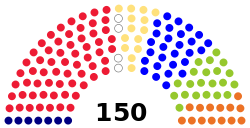
Political groups Smer (62)
SDKÚ–DS (28)
Freedom and Solidarity (21)
Christian Democratic Movement (14)
Most–Híd/OKS (14)
Slovak National Party (7)Elections Voting system Open list proportional representation with a 5% election threshold Last election 12 June 2010 Meeting place Bratislava Website www.nrsr.sk Slovakia 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
SlovakiaNational CouncilDivisionsForeign Policy
Other countries · Atlas
Politics portal
Slovakia's parliament has been called the 'National Council' since 1 October 1992. From 1969 to 1992, its predecessor, the parliament of the Slovak part of Czechoslovakia, was called the Slovak National Council (Slovenská národná rada).
The National Council approves domestic legislation, constitutional laws, and the annual budget. Its consent is required to ratify international treaties, and is responsible for approving military operations. It also elects individuals to some positions in the executive and judiciary as specified by law.
The parliament building is situated on the castle hill, next to Bratislava Castle in Alexander Dubček Square.
Contents
Functions
The 150-seat unicameral National Council of the Slovak Republic is Slovakia's sole constitutional and legislative body. It considers and approves the Constitution, constitutional statutes and other legal acts. It also approves the state budget. It elects some officials specified by law as well as the candidates for the position of a Justice of the Constitutional Court of the Slovak Republic and the Prosecutor General. Prior to their ratification, the parliament should approve all important international treaties. Moreover, it gives consent for dispatching of military forces outside of Slovakia's territory and for the presence of foreign military forces on the territory of the Slovak Republic.
Decision making
The parliament may vote only if a majority of all its members (76) are present. To pass a decision the approval of a simple majority of all MPs present is required (i.e. at least 39 votes). Almost all legal acts can be adopted by this relative majority. An absolute majority (76 votes) is required to pass a vote of no-confidence in the Cabinet or its members, or to elect and recall the Speaker or the Deputy Speakers. A qualified majority of 3/5 of all deputies (at least 90 votes) is required for the adoption of a constitution or a constitutional statute.
Speakers
For the speakers see: List of speakers of Slovak parliaments
Еlections
Members of the parliament are elected directly for a 4-year term, under the proportional system. Although the suffrage is universal, only a citizen who has the right to vote, has attained 21 years of age and has permanent residency in the Slovak Republic is eligible to be elected. Similarly to the Netherlands and Israel, the whole country forms one multi-member constituency. The election threshold is 5%. Voters may indicate their preferences within the semi-open list. Parliamentary elections were last held on 12 June 2010.
Latest election
Summary of the 12 June 2010 Slovak National Council election results Parties Ideology Votes % Seats ± Direction – Social Democracy Social democracy 880,111 34.79 62 +12 Slovak Democratic and Christian Union – Democratic Party Conservatism 390,042 15.42 28 −3 Freedom and Solidarity Classical liberalism 307,287 12.14 22 * Christian Democratic Movement Christian democracy 215,755 8.52 15 +1 Most–Híd Hungarian minority interest 205,538 8.12 14 * Slovak National Party Slovak nationalism 128,490 5.07 9 −11 Party of the Hungarian Coalition Hungarian minority interest 109,638 4.33 0 −20 People's Party – Movement for a Democratic Slovakia National conservatism 109,480 4.32 0 −15 Party of the Democratic Left Democratic socialism 61,137 2.41 0 0 People's Party – Our Slovakia Nationalism 33,724 1.33 0 * Communist Party of Slovakia Communism 21,104 0.83 0 0 Union – Party for Slovakia Conservatism 17,741 0.70 0 * Paliho Kapurková, Cheerful Political Party Frivolous political party 14,576 0.57 0 * European Democratic Party Pro-Europeanism 10,332 0.40 0 * New Democracy National conservatism 7,962 0.31 0 * Party of the Roma Coalition Roma minority interest 6,947 0.27 0 * Union of the Workers of Slovakia Communism 6,196 0.24 0 0 AZEN – Alliance for Europe of the Nations National conservatism 3,325 0.13 0 * Total (turnout 58.83%) 2,529,385 — 150 — * Did not stand in previous election Source: Statistics Bureau of Slovakia Buildings
 Building of the National Council of the Slovak Republic next to Bratislava Castle.
Building of the National Council of the Slovak Republic next to Bratislava Castle.
The main parliament building is situated next to the Bratislava Castle on the castle hill. The building is insufficiently large to accommodate all officials and representatives. This is because it was built during the Czecoslovak period, when the legislature usually met in Prague.[1] The secondary parliament building, which was the main building until 1994, is situated next to the Trinitarian Church below the castle hill in Bratislava.
References
External links
Parliament of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities - European Union
Coordinates: 48°08′31″N 17°05′50″E / 48.14194°N 17.09722°E
Categories:- Government of Slovakia
- Parliaments by country
- Unicameral legislatures
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Slovak National Council — The Slovak National Council is the name of different types of supreme bodies in the history of Slovakia. They existed within the Kingdom of Hungary or Czechoslovakia or the WWII Slovak Republic or were bodies of Slovak exiles: *Slovak National… … Wikipedia
National Council — may refer to: Contents 1 Conservation 2 Economics 3 Education 4 Politics 4.1 Legislative … Wikipedia
National parliaments of the European Union — European Union This article is part of the series: Politics and government of the European Union … Wikipedia
Confederation of Trade Unions of the Slovak Republic — KOZ SR Full name Confederation of Trade Unions of the Slovak Republic Native name Konfederácia odborových zväzov Slovenskej republiky Members 570,000 Country Slovakia … Wikipedia
Slovak National Council's Declaration of Independence of the Slovak Nation — The Slovak National Council s Declaration of Independence of the Slovak Nation was a resolution of the Slovak National Council on 17 July 1992, by which members of the Council demanded Slovakia s independence. This event was part of a process,… … Wikipedia
Slovak Republic (1939–1945) — Infobox Former Country native name = Slovenská republika ¹ conventional long name = Slovak Republic common name = Slovakia continent = Europe government type = Republic status = Client state empire = Germany status text = Client state of Nazi… … Wikipedia
Slovak parliamentary election, 2006 — Infobox Election election name = Slovak parliamentary election, 2006 country = Slovakia type = parliamentary ongoing = no previous election = Slovak parliamentary election, 2002 previous year = 2002 next election = Slovak parliamentary election,… … Wikipedia
Council of the European Union — Not to be confused with European Council or Council of Europe. Council of the European Union name in other official languages … Wikipedia
Parliament of the Czech Republic — Parlament České republiky Type Type … Wikipedia
Slovak Socialist Republic — From 1969 to 1990, the Slovak Socialist Republic ( Slovenská socialistická republika in Slovak; abbreviated SSR) was the official name of that part of Czechoslovakia that is Slovakia today. The name was used from January 1 1969 until March… … Wikipedia

