- Parliament of the Czech Republic
-
Parliament of the Czech Republic
Parlament České republiky
Type Type Bicameral Houses - Senate
- Chamber of DeputiesLeadership President of
the SenateMilan Štěch, ČSSD
since 24 November 2010Chair of the
Chamber of
DeputiesMiroslava Němcová, ODS
since 24 June 2010Structure Members 281
- 81 Senators
- 200 Deputies
Senate
Political groupsODS (35 seats)
ČSSD (29 seats)
KDU-ČSL (7 seats)
KSČM (3 seats)
SNK-ED (2 seats)
other (5 seats)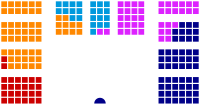
Chamber of
Deputies
Political groupsČSSD (56 seats)
ODS (53 seats)
TOP 09 (41 seats)
KSČM (26 seats)
VV (24 seats)Elections Senate
Voting systemTwo-round system Chamber of
Deputies
Voting systemProportional representation Senate
Last election17-18 October 2008
24-25 October 2008Chamber of
Deputies
Last election28-29 May 2010 Meeting place Palaces in Malá Strana, Prague Website Senate
Chamber of DeputiesCzech Republic 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
the Czech RepublicGovernmentParliamentPolitical partiesAdministrative divisions
The Parliament of the Czech Republic (Czech: Parlament České republiky) is the legislative body of the Czech Republic, based in Prague. It consists of two chambers, both elected in direct elections:
- the Lower House: Chamber of Deputies of the Parliament of the Czech Republic
- the Upper House: Senate of the Parliament of the Czech Republic
The Parliament exercises competences usual in parliamentary systems: it holds and passes bills, has the right to modify the Constitution, ratifies international agreements; if necessary, it declares war, approves presence of foreign military forces in the Czech Republic or a dispatch of Czech military forces abroad. Both chambers also elect the President at a joint session.
History
The tradition of modern parliamentarianism in the Bohemian lands dates back to times of the Habsburg Empire (Austria, then Cisleithanian part of Austria-Hungary), where the Imperial Council (Reichsrat, Říšská rada) was created in 1861.
After proclamation of Czechoslovakia in 1918 its National Assembly undertook legislative duties both of the Imperial Council and State Diets (Bohemian, Moravian, Silesian).[1] In 1938-1939 and between 1945 and 1990 there existed a parliament within non-democratic regimes. As a consequence of federalization of Czechoslovakia (1968), national councils of Czech and Slovak parts of the country were created.
The Chamber of Deputies keeps continuity with the Czech National Council, while the Senate was established in 1996 (with reference to the First Czechoslovak Republic one).
References
- ^ Balík, S.-Hloušek, V.-Holzer, J.-Šedo, J.: Politický systém českých zemí 1848-1989. Brno 2006, p. 81.
Parliament of Europe Sovereign
statesAlbania · Andorra · Armenia · Austria · Azerbaijan · Belarus · Belgium · Bosnia and Herzegovina · Bulgaria · Croatia · Cyprus · Czech Republic · Denmark · Estonia · Finland · France · Georgia · Germany · Greece · Hungary · Iceland · Ireland · Italy · Kazakhstan · Latvia · Liechtenstein · Lithuania · Luxembourg · Macedonia · Malta · Moldova · Monaco · Montenegro · Netherlands · Norway · Poland · Portugal · Romania · Russia · San Marino · Serbia · Slovakia · Slovenia · Spain · Sweden · Switzerland · Turkey · Ukraine · United Kingdom (England • Northern Ireland • Scotland • Wales)
States with limited
recognitionAbkhazia · Kosovo · Nagorno-Karabakh · Northern Cyprus · South Ossetia · Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territoriesÅland · Faroe Islands · Gibraltar · Guernsey · Jan Mayen · Jersey · Isle of Man · Svalbard
Other entities European UnionCategories:- Politics of the Czech Republic
- Government of the Czech Republic
- Parliaments by country
- Bicameral legislatures
- European government stubs
- Czech Republic politics stubs
- Legislature stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

