- Double-balloon enteroscopy
-
Double-balloon enteroscopy Intervention 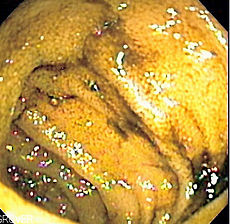
Endoscopic image of normal small bowel.MeSH D058582 Double-balloon enteroscopy, also known as push-and-pull enteroscopy is an endoscopic technique for visualization of the small bowel. It was developed by Hironori Yamamoto in 2001.[1] It is novel in the field of diagnostic gastroenterology as it is the first endoscopic technique that allows for the entire gastrointestinal tract to be visualized in real time.[2]
Contents
Technique
The technique involves the use of a balloon at the end of a special enteroscope camera and an overtube, which is a tube that fits over the endoscope, and which is also fitted with a balloon.[2] The procedure is usually done under general anesthesia, but may be done with the use of conscious sedation.[3] The enteroscope and overtube are inserted through the mouth and passed in conventional fashion (that is, as with gastroscopy) into the small bowel.[1] Following this, the endoscope is advanced a small distance in front of the overtube and the balloon at the end is inflated. Using the assistance of friction at the interface of the enteroscope and intestinal wall, the small bowel is accordioned back to the overtube. The overtube balloon is then deployed, and the enteroscope balloon is deflated. The process is then continued until the entire small bowel is visualized.[4]
The double-balloon enteroscope can also be passed in retrograde fashion, through the colon and into the ileum to visualize the end of the small bowel.[1]
Indications
Double-balloon enteroscopy has found a niche application in the following settings:
- bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract of obscure cause[5]
- iron deficiency anemia with normal colonoscopy and gastroscopy[6]
- visualization and therapeutic intervention on abnormalities seen on traditional small bowel imaging[7]
- ERCP in post-surgical patients with long afferent limbs[8]
Advantages and disadvantages
Double-balloon enteroscopy offers a number of advantages to other small bowel image techniques, including barium imaging, wireless capsule endoscopy and push enteroscopy:
- it allows for visualization of the entire small bowel to the terminal ileum[1]
- it allows for the application of therapeutics[9]
- it allows for the sampling or biopsying of small bowel mucosa, for the resection of polyps of the small bowel,[10] and in the placement of stents or dilatation of strictures of the small bowel.[7]
- it allows for access to the papilla in patients with long afferent limbs after Billroth II antrectomy.
The key disadvantage of double-balloon enteroscopy is the time required to visualize the small bowel; this can exceed three hours, and may require that patients be admitted to hospital for the procedure.[11] There have also been case reports of acute pancreatitis[12] and intestinal necrosis[13] associated with the technique.
References
- ^ a b c d Yamamoto, H; Sekine, Y; Sato, Y; Higashizawa, T; Miyata, T; Iino, S; Ido, K; Sugano, K (2001). "Total enteroscopy with a nonsurgical steerable double-balloon method". Gastrointestinal endoscopy 53 (2): 216–20. doi:10.1067/mge.2001.112181. PMID 11174299.
- ^ a b Yamamoto, H; Sugano, K (2003). "A new method of enteroscopy--the double-balloon method". Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology 17 (4): 273–4. PMID 12704472.
- ^ May, A; Nachbar, L; Wardak, A; Yamamoto, H; Ell, C (2003). "Double-balloon enteroscopy: preliminary experience in patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding or chronic abdominal pain". Endoscopy 35 (12): 985–91. doi:10.1055/s-2003-44582. PMID 14648408.
- ^ Yamamoto, H; Yano, T; Kita, H; Sunada, K; Ido, K; Sugano, K (2003). "New system of double-balloon enteroscopy for diagnosis and treatment of small intestinal disorders". Gastroenterology 125 (5): 1556; author reply 1556–7. doi:10.1016/j.gastro.2003.03.004. PMID 14628813.
- ^ Yen, HH; Chen, YY; Soon, MS; Lin, YM (2007). "An unusual cause of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding". Gut 56 (1): 12, 28. doi:10.1136/gut.2006.094631. PMC 1856651. PMID 16507584. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1856651.
- ^ Chan, AO; Lai, KC (2006). "A patient with long-standing iron-deficient anemia". Nature clinical practice. Gastroenterology & hepatology 3 (2): 112–6; quiz 117. doi:10.1038/ncpgasthep0413. PMID 16456577.
- ^ a b Kita, H; Yamamoto, H (2006). "Double-balloon endoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of small intestinal disease". Best practice & research. Clinical gastroenterology 20 (1): 179–94. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2005.09.004. PMID 16473807.
- ^ Mönkemüller, K; Bellutti, M; Neumann, H; Malfertheiner, P (2008). "Therapeutic ERCP with the double-balloon enteroscope in patients with Roux-en-Y anastomosis". Gastrointestinal endoscopy 67 (6): 992–6. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2007.10.023. PMID 18279869.
- ^ Nishimura, M; Yamamoto, H; Kita, H; Yano, T; Sunada, K; Miyata, T; Sugimoto, T; Iino, S et al. (2004). "Gastrointestinal stromal tumor in the jejunum: diagnosis and control of bleeding with electrocoagulation by using double-balloon enteroscopy". Journal of gastroenterology 39 (10): 1001–4. doi:10.1007/s00535-004-1434-6. PMID 15549455.
- ^ Ohmiya, N; Taguchi, A; Shirai, K; Mabuchi, N; Arakawa, D; Kanazawa, H; Ozeki, M; Yamada, M et al. (2005). "Endoscopic resection of Peutz-Jeghers polyps throughout the small intestine at double-balloon enteroscopy without laparotomy". Gastrointestinal endoscopy 61 (1): 140–7. doi:10.1016/S0016-5107(04)02457-5. PMID 15672077.
- ^ Lo, SK; Mehdizadeh, S (2006). "Therapeutic uses of double-balloon enteroscopy". Gastrointestinal endoscopy clinics of North America 16 (2): 363–76. doi:10.1016/j.giec.2006.03.002. PMID 16644464.
- ^ Honda, K; Mizutani, T; Nakamura, K; Higuchi, N; Kanayama, K; Sumida, Y; Yoshinaga, S; Itaba, S et al. (2006). "Acute pancreatitis associated with peroral double-balloon enteroscopy: a case report". World journal of gastroenterology : WJG 12 (11): 1802–4. PMID 16586559.
- ^ Yen, HH; Chen, YY; Su, WW; Soon, MS; Lin, YM (2006). "Intestinal necrosis as a complication of epinephrine injection therapy during double-balloon enteroscopy". Endoscopy 38 (5): 542. doi:10.1055/s-2006-925184. PMID 16586243.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.