- Vanadyl sulfate
-
Vanadyl sulfate 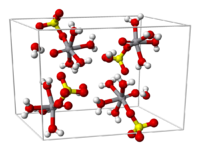
 Oxovanadium(2+) sulfateOther namesBasic vanadium(IV) sulfate
Oxovanadium(2+) sulfateOther namesBasic vanadium(IV) sulfate
Vanadium(IV) oxide sulfate
Vanadium(IV) oxysulfateIdentifiers CAS number 27774-13-6 
Properties Molecular formula VOSO4 Molar mass 163.00 g/mol Appearance Blue crystalline solid Melting point 105 °C decomp.
Solubility in water Soluble Hazards EU Index Not listed Main hazards Irritant Flash point Non-flammble Related compounds Other anions Vanadyl chloride
Vanadyl nitrateOther cations Vanadium(III) sulfate Related compounds Vanadyl acetylacetonate  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Vanadyl(IV) sulfate, VOSO4, is a well known inorganic compound of vanadium. This very hygroscopic blue solid is one of the most common sources of vanadium in the laboratory, reflecting its high stability. It features the vanadyl ion, VO2+, which has been called the "most stable diatomic ion."[1] Vanadyl sulfate is an intermediate in the extraction of vanadium from petroleum residues, a major commercial source of vanadium.[2] Vanadyl sulfate is a component of some food supplements and drugs. Vanadyl compounds mimic the effects of insulin, although humans seem to have no dietary requirement for vanadium.
Synthesis, structure, and reactions
Vanadyl sulfate is most commonly obtained by reduction of vanadium pentoxide with sulfur dioxide:
- V2O5 + 7 H2O + SO2 + H2SO4 → 2 [V(O)(H2O)4]SO4
From aqueous solution, the salt crystallizes as the pentahydrate, the fifth water is not bound to the metal in the solid. Viewed as a coordination complex, the ion is octahedral, with oxo, four equatorial water ligands, and a monodentate sulfate.[1] The V=O bond distance is 160 pm in length, about 50 pm shorter than the V–OH2 bonds. In solution, the sulfate ion dissociates rapidly.
Being widely available, vanadyl sulfate is a common precursor to other vanadyl derivatives, such as vanadyl acetylacetonate:[3]
- [V(O)(H2O)4]SO4 + C5H8O2 + Na2CO3 → [V(O)(C5H7O2)2 + Na2SO4 + 4 H2O + CO2
In acidic solution, oxidation of vanadyl sulfate gives yellow-coloured vanadyl(V) derivatives. Reduction, e.g. by zinc, gives vanadium(III) and vanadium(II) derivatives, which are characteristically green and violet, respectively.
Occurrence in nature
Like most water-soluble sulfates, vanadyl sulfate is only rarely found in nature. Anhydrous form is pauflerite, a mineral of fumarolic origin. Hydrated forms, also rare, include hexahydrate (stanleyite), pentahydrates (minasragrite, orthominasragrite, and anorthominasragrite) and trihydrate - bobjonesite.[citation needed]
References
- ^ a b Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, A. (1984). Chemistry of the Elements. Oxford: Pergamon. p. 1157. ISBN 0-08-022057-6.
- ^ Günter Bauer, Volker Güther, Hans Hess, Andreas Otto, Oskar Roidl, Heinz Roller, Siegfried Sattelberger in "Vanadium and Vanadium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.
- ^ Bryant, Burl E.; Fernelius, W. Conard (1957), "Vanadium(IV) Oxy(acetylacetonate)", Inorg. Synth. 5: 113–16, doi:10.1002/9780470132364.ch30
Categories:- Vanadium compounds
- Sulfates
- Inorganic compound stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
