- Party of the Democratic Revolution
-
Party of the Democratic Revolution
Partido de la Revolución Democrática
Leader Jesus Zambrano[1] Founded May 5, 1989 Headquarters Mexico City, Mexico Ideology Democratic socialism
Social democracy
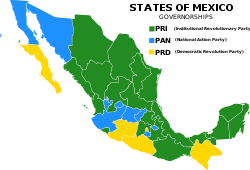
Social progressivismPolitical position Left-wing International affiliation Socialist International Continental affiliation Foro de São Paulo Official colours Yellow Seats in the Chamber of Deputies 72 / 500Seats in the Senate 31 / 128Governorships 5 / 32Website http://www.prd.org.mx Politics of Mexico
Political parties
ElectionsThe Party of the Democratic Revolution (Spanish: Partido de la Revolución Democrática, PRD) is a democratic socialist party in Mexico and one of 2 Mexican affiliates of the Socialist International. The PRD is a member of the Broad Progressive Front alliance.
Contents
History
Founded in Mexico City on May 5, 1989 by Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas, Heberto Castillo, Marco Rascon Cordova, Gilberto Rincón Gallardo, Porfirio Muñoz Ledo, other prominent PRI members and left-wing politicians. The party was originally founded by including many smaller left-wing parties such as the Partido Comunista Mexicano (PCM, Mexican Communist Party), Partido Socialista Unificado de México (PSUM, Unified Socialist Party of Mexico), Partido Mexicano Socialista (PMS, Socialist Mexican Party) and Partido Mexicano de los Trabajadores (PMT, Mexican Workers' Party). The PMS donated its registration with the Federal Electoral Commission (CFE) to enable the new party to be established.
It was proclaimed to be the party of the 6 de julio (July 6), referring to the date of the 1988 presidential election where it is alleged that Cárdenas, the candidate of a coalition of center-left parties called National Democratic Front (Frente Democrático Nacional) won the election but was denied victory by fraudulent means. Victory was instead handed to PRI candidate, Carlos Salinas.
Electoral presence
The party only has electoral presence in central and Southern Mexico, whereas in the North its voting averages is only 5%. It has won gubernatorial races in some states including Baja California Sur, Chiapas, Guerrero and Michoacán. although, most of them have been obtained with former members of the PRI). It has also maintained control over the Federal District (Mexico City) since 1997, with 3 former members of the PRI. In the 2003 local elections, 13 of the Federal District's 16 boroughs (delegaciones) were won by PRD candidates; in the 2006 election, that figure rose to 14.
In the 2000 presidential election the Alianza por México (the "Alliance for Mexico", comprising the PRD and four smaller parties) candidate Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas won 16.6% of the popular vote and 15 seats in the Senate. Three years later in the 2003 legislative elections the party won 17.6% of the popular vote and 95 seats in the Chamber of Deputies.
In the 2006 legislative elections the party won 127 out of 500 seats in the Chamber of Deputies and 26 out of 128 Senators.
Video Scandals
Main article: VideoscandalsThe party had enjoyed a reputation of honesty unmatched by its competitors, until the "Video Escándalos" (Video Scandals) a series of videos where notable party members were taped receiving cash funds or betting large sums of money in a Las Vegas casino. Party members who were seen on the video tapes were expelled from the party, but those who were supposedly associated are still active members.
Later, another video was recorded by Cuba's government where Carlos Ahumada states that members of the PRI and PAN were planning the situation presented in the first video as part of a plot against Andrés Manuel López Obrador to get him away as possible presidential candidate[citation needed].
Recent history
The former mayor of Mexico City, Andrés Manuel López Obrador, was the presidential candidate for the "Coalición por el Bien de Todos" (Coalition for the Good of All) in the 2006 presidential elections. After the general election of July 2, 2006, and a recount of the 9.09% of the ballot tally sheets which supposedly presented irregularities, the Federal Electoral Institute recorded the vote results in favor of Felipe Calderón by a margin of 0.58 percent.[2] These results were later validated by the Federal Electoral Tribunal. However, PRD claims that there was election fraud. The claims of election fraud have been rejected by the Federal Electoral Tribunal (TEPJF), which considered these "evidently inadmissible" ("notoriamente improcedente") and certified PAN's candidate Felipe Calderón as the winner.
The PRD had called for demonstrations and set up camps in the capital's main square blocking one of its main avenues (Paseo de la Reforma) for six weeks to demand for a recount of all votes which was not granted. The camps were later dismantled after confrontation with the Mexican Army was likely and Obrador was declared "Legitimate President" by his followers in a "public open vote" (people in the main square raising their hands). Obrador does not recognize the legitimacy of Calderón.
In 2008 after bitter infighting within the party Jesús Ortega, an opponent of Andrés Manuel López Obrador, was elected party president. In the 2009 legislative elections, López Obrador supported two smaller parties while mainatining his ties to PRD.
See also
References
External links
Political parties in Mexico 
Portal:Politics - List of political parties - Politics of Mexico Categories:- Party of the Democratic Revolution
- Political parties established in 1989
- Political parties in Mexico
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.