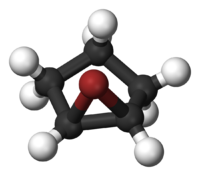
- Halonium ion
-
A halonium ion in organic chemistry is any onium compound (ion) containing a halogen atom carrying a positive charge. This cation has the general structure R-X+-R where X is any halogen and R any organic residue and this structure can be cyclic or an open chain molecular structure. Halonium ions formed from fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine are called fluoronium, chloronium, bromonium, and iodonium, respectively. The simplest halonium ions are of the structure H-X+-H (X = F, Cl, Br, I). Halonium ions often have a three-atom cyclic structure resulting from the formal addition of a halogenium ion X+ to a C=C double bond.[1]
History
Halonium ions were first postulated in 1937 by Roberts and Kimball[2] to account for observed diastereoselectivity in halogen addition reactions to alkenes. They correctly argued that if the initial reaction intermediate in bromination is the open-chain X−–C–C+, rotation around the C–C single bond would be possible leading to a mixture of equal amounts of dihalogen cis isomer and trans isomer, which is not the case. They also asserted that a positively charged halogen atom is isoelectronic with oxygen and that carbon and bromine have comparable ionization potentials.
In 1970 George A. Olah succeeded in preparing and isolating halonium salts[3] by adding a methyl halide such as methyl bromide or methyl chloride in sulfur dioxide at −78°C to a complex of antimony pentafluoride and tetrafluoromethane in sulfur dioxide. After evaporation of sulfur dioxide this procedure left crystals of CH3–X+–CH3SbF−
6, stable at room temperature but not to moisture.Cyclic and acyclic chloronium,[4] bromonium and iodonium ions have been structurally characterised by X-ray crystallography, such as the adamantylideneadamantanebromonium cation, also known as dispiro[adamantane-2,3'-[1λ3]bromirane-3',2''-adamantan]-1'-ylium, shown below.[5]
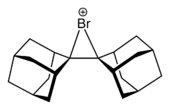
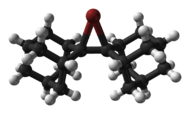
skeletal formula ball-and-stick model Compounds containing trivalent or tetravalent halonium ions do not exist but for some hypothetical compounds stability has been computationally tested [6]
References
- ^ IUPAC Gold Book
- ^ Irving Roberts and George E. Kimball (1937). "The Halogenation of Ethylenes". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 59 (5): 947. doi:10.1021/ja01284a507.
- ^ George A. Olah, John R. DeMember (1970). "Friedel-Crafts chemistry. V. Isolation, carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance, and laser Raman spectroscopic study of dimethylhalonium fluoroantimonates". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 92 (3): 718. doi:10.1021/ja00706a058.
- ^ T. Mori, R. Rathore (1998). "X-Ray structure of bridged 2,2'-bi(adamant-2-ylidene) chloronium cation and comparison of its reactivity with a singly bonded chloroarenium cation". Chem. Commun. (8): 927–928. doi:10.1039/a709063c.
- ^ R. S. Brown, R. W. Nagorski, A. J. Bennet, R. E. D. McClung, G. H. M. Aarts, M. Klobukowski, R. McDonald, B. D. Santarsiero (March 1994). "Stable Bromonium and Iodonium Ions of the Hindered Olefins Adamantylideneadamantane and Bicyclo[3.3.1]nonylidenebicyclo[3.3.1]nonane. X-Ray Structure, Transfer of Positive Halogens to Acceptor Olefins, and ab Initio Studies". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116 (6): 2448–2456. doi:10.1021/ja00085a027.
- ^ The Quest for Tetracoordinated Halonium Ions: A Theoretical Investigation Tobias F. Schneider and Daniel B. Werz Org. Lett., 2010, 12 (21), pp 4844–4847 doi:10.1021/ol102059b
Categories:- Cations
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.