- Narcinidae
-
Numbfishes 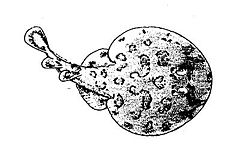
Lesser electric ray, Narcine bancroftii Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Chondrichthyes Subclass: Elasmobranchii Order: Torpediniformes
de Buen, 1926Family: Narcinidae
Gill, 1862The numbfishes are a group of electric rays (order Torpediniformes) in the family Narcinidae.[1] They are bottom-dwelling cartilaginous fishes with large, rounded pectoral fin discs and long tails. They can produce an electric discharge for defense, from which their scientific name is derived (Greek narke, meaning "paralysis").[2]
Members of this family are commonly known as the numbfishes, and are found almost worldwide in warm temperate and tropical continental and continental insular waters. They are strictly marine and are absent from rivers and lakes. They occur in sandy beaches, muddy enclosed bays, estuaries, off coral reefs and river mouths, and on the upper continental slope to a depth of 1,071 meters.[3]
Contents
Description
Small to medium-sized rays, adult numbfishes range from 15 to 66 cm long, though most are less than 50 cm. They have oval, rounded, or shovel-shaped pectoral discs and stout tails of equal or longer length. The snout is moderately elongated, rounded or rounded-angular, differing from the narkids in being supported by broad rostral cartilages. The mouth is straight, with stout, elongated, and highly protrusible jaws and a prominent groove around its periphery. The nostrils are just forward of the mouth and connected to it by a broad groove; the nasal flaps are short but merged into a broad nasal curtain that overlaps the mouth. The teeth are small have a single moderate cusp; the teeth and tooth bands are exposed when the mouth is closed (except in Diplobatis). There are two prominent dorsal fins of roughly equal size, and a large caudal fin.[3][4]
Numbfishes vary in color from whitish, yellowish, brownish, grey-brown, greenish, reddish, or black above, either plain or with small to large spots, blotches, bars or lines, sometimes forming complex eye-shaped spots or ocelli on the pectoral fins. They are usually white underneath, or black in deep-water species. The large, kidney-shaped electric organs are at the base of the pectoral fins and visible through the skin.[3]
Biology and ecology
Numbfishes are slow-swimming bottom-dwellers that feed on small fishes and invertebrates off the bottom; their protrusible jaws aid in removing prey from the substrate. They can generate a moderate shock if disturbed and contact is made with the electric organs; the electrical discharges of narcinids have been measured at 8-37 volts, much less than the electric rays of the genus Torpedo.[2] All species are ovoviviparous, with eggs hatching inside the mother.[3]
Species
- Genus Benthobatis Alcock, 1898
- Genus Diplobatis Bigelow & Schroeder, 1948
- Diplobatis colombiensis Fechhelm & McEachran, 1984 (Colombian electric ray)
- Diplobatis guamachensis Martín Salazar, 1957 (Brownband numbfish)
- Diplobatis ommata (D. S. Jordan & Gilbert, 1890) (Ocellated electric ray)
- Diplobatis pictus G. Palmer, 1950 (Painted electric ray)
- Genus Discopyge Heckel, 1846
- Discopyge castelloi Menni, Rincón & M. L. Garcia, 2008
- Discopyge tschudii Heckel, 1846 (Apron ray)
- Genus Narcine Henle, 1834
- Narcine atzi Carvalho & Randall, 2003
- Narcine bancroftii (E. Griffith & C. H. Smith, 1834) (Lesser electric ray)
- Narcine brasiliensis (Olfers, 1831) (Brazilian electric ray)
- Narcine brevilabiata Bessednov, 1966 (Shortlip electric ray)
- Narcine brunnea Annandale, 1909 (Brown numbfish)
- Narcine entemedor D. S. Jordan & Starks, 1895 (Giant electric ray)
- Narcine insolita Carvalho, Séret & Compagno, 2002
- Narcine lasti Carvalho & Séret, 2002
- Narcine leoparda Carvalho, 2001
- Narcine lingula Richardson, 1846 (Chinese numbfish)
- Narcine maculata (Shaw, 1804) (Darkfinned numbfish)
- Narcine nelsoni Carvalho, 2008 (Eastern Numbfish)
- Narcine oculifera Carvalho, Compagno & Mee, 2002
- Narcine ornata Carvalho, 2008
- Narcine prodorsalis Bessednov, 1966 (Tonkin numbfish)
- Narcine rierai (Lloris & Rucabado, 1991) (Slender electric ray)
- Narcine tasmaniensis Richardson, 1841 (Tasmanian numbfish)
- Narcine timlei (Bloch & Schneider, 1801) (Blackspotted numbfish)
- Narcine vermiculatus Breder, 1928 (Vermiculate electric ray)
- Narcine westraliensis McKay, 1966 (Banded numbfish)
References
- Froese, Rainer, and Daniel Pauly, eds. (2011). "Narcinidae" in FishBase. February 2011 version.
- ^ "Narcinidae". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. http://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=564006. Retrieved March 20, 2006.
- ^ a b Martin, R. Aidan. Electric Rays. ReefQuest Centre for Shark Research. Retrieved on October 12, 2008.
- ^ a b c d Compagno, L.J.V. and Last, P.R. (1999). Narcinidae. Numbfishes. p. 1433-1437. In: K.E. Carpenter and V.H. Niem (eds.) FAO identification guide for fishery purposes. The living marine resources of the Western Central Pacific. Rome: Food and Agricultural Organization.
- ^ Hamlett, William C. (1999). Sharks, Skates, and Rays: The Biology of Elasmobranch Fishes. Baltimore and London: JHU Press. ISBN 0-8018604-8-2.
Categories:- Torpediniformes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
