- List of Arizona hurricanes
An Arizona hurricane is a
tropical cyclone originating in the easternPacific Ocean that affects theU.S. state ofArizona . Usually, the storm makes landfall in the Mexican states ofBaja California orSonora and the remaining moisture affects the state. However, a few storms have crossed into Arizona still with tropical storm strength.Tropical storms in Arizona are infrequent, since the predominant storm track carries most storms that form in the Eastern Pacific either parallel or away from the Pacific coast of northwestern Mexico. As a result, most storms that could affect Arizona are carried away from the United States, with only 6% of all Pacific hurricanes entering US territory.cite web|first=Kristen L.|last=Corbosiero|title=The Contribution of Eastern North Pacific Tropical Cyclones to the Warm Season Rainfall Climatology of the Southwestern United States|year=2003|publisher=
University of Albany |accessdate=2006-03-20|url=http://web.archive.org/web/20060505070334/http://www.atmos.albany.edu/student/kristen/monsoon.html Accessed through theWayback Machine .] However, Arizona still can expect experiencing the effects of tropical cyclones once every five years, in average. Many, but not all, of these systems also impacted California.torms
Tropical storms are one of Arizona's main sources of rainfall, and they infuse the
monsoon over the southwestern United States.cite web | title=Hydrologic Conditions in Arizona During 1999–2004: A Historical Perspective | publisher=United States Geological Survey | author = Arizona Water Science Center | accessdate=2006-03-20 | month=September | year=2005 | url=http://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2005/3081/pdf/FS2005-3081WEB.pdf] However, all of the storms that have impacted Arizona have formed in the latter parts of thePacific hurricane season , and only storm remnants have affected the state before August.torm systems
Several of these tropical cyclones have caused deaths or heavy property damage, usually due to
flood ing caused byrain .Before 1960
Records of tropical cyclones in the East Pacific before 1950 are sparse, but there were still several storms that produced rainfall over Arizona in this period.
The first known tropical disturbance to affect the state occurred in August 1921, when a remnant low of a tropical cyclone moved into the western portions of the state.cite web | author = Williams, Jack | url = http://www.usatoday.com/weather/whhcalif.htm | title = Background: California's tropical storms | date =
May 17 ,2005 | publisher =USA Today | accessdate = 2008-05-16] The next month, onSeptember 30 ,1921 , a tropical depression that had tracked parallel to the Mexican coastline moved into Arizona, causing heavy rainfall.cite journal | url = http://docs.lib.noaa.gov/rescue/mwr/057/mwr-057-02-0043.pdf | title = Tropical Cyclones of the Eastern North Pacific Ocean | journal =Monthly Weather Review | author = Hurd, Willis E. | month = February | year = 1929 | volume = 57 | issue = 2 | accessdate = 2008-05-16 | format = PDF] This tropical storm caused more than three inches of rainfall along theColorado River valley, with 3.65 in (93 mm) of rain reported in Yuma. Throughout the state, Flagstaff saw 1.50 in (38 mm) of rainfall, while 1.24 in (31 mm) of precipitation fell in Prescott, 0.68 in (17 mm) in Tucson, and 0.56 in (14 mm) in Phoenix.Five years later, the remnants of another September storm hit the state, but this time, the precipitation was heaviest on the southeastern portion of the state. The 1926 storm caused over 5 in (127 mm) of rain in the vicinity of Douglas. In September 1927, the remnants of another tropical system caused 1–2 in (25–50 mm) of rainfall throughout the state.
In August 1935, the remnants of an unnamed tropical storm that landed on Southern California caused torrential rain and flooding across Arizona, especially along the
Santa Cruz River and Rillito Creek on Southern Arizona. The rainfall due to the storm still holds the monthly rainfall record at the National Weather Service office inTucson .1939 saw two tropical systems enter the state during the same month. On
September 4 ,1931 , the remnants of a former hurricane entered southwest Arizona, near Yuma. More than 5.00 in (127 mm) of precipitation fell in northwest Arizona, with many parts of the state collecting more than an inch of rain. This same system produced more than twice the average annual rainfall in Imperial Valley, California. On the 11th, the remnants of separate system passed, again, over southwest Arizona.No tropical cyclones are known to have affected Arizona in the 1940s. However, in the 1950s, the remnants of two more storms passed over the state. In
August 24 ,1951 , the moisture from a hurricane that made landfall inBaja California moved over the state, producing more than 5.00 (127 mm) of precipitation over southwestern Arizona. Flagstaff saw 4.00 in (102 mm) of rain, with similar totals measured at Prescott (3.95 in, 100 mm) and Phoenix (3.24 in, 82 mm). The storm also washed out several roadways near Gila Bend, isolating the city from motorists. Overall, the storm caused $750,000 (1951USD ) in property damage. Three years later, the remnants of another hurricane moved over Arizona from the south during the month of July. Damage from this storm is unknown.1970s
In September 1970, the remnants of Tropical Storm Norma became Arizona's deadliest storm when they contributed to the disaster known as the "Labor Day storm of 1970". As Norma dissipated, moisture from the cyclone was entrapped in a large extratropical low. The resulting rainfall caused flooding that killed 23 people and significant damage. Two years later, the remnants of Hurricane Joanne caused flooding that caused $10 million (1972 USD) in property damage and eight deaths.
On
September 11 1976 , Hurricane Kathleen killed a man when a gust of wind blew a palm tree down onto his mobile home. Severe flooding and hailstorms also resulted.While most of the rainfall from the storm fell in California,cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Hurricane Kathleen - September 7-12, 1976 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/kathleen1976.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] 2.87 in (73 mm) fell at theDavis Dam on theColorado River . The next month, Hurricane Liza brought light rain to the state, with the state maxima being 1.48 in (38 mm) on Willow Beach.In August of the following year, Hurricane Doreen caused severe flooding in Yuma County and near
Bullhead City . A rain gauge near Yuma saw more than 7 in (180 mm) of precipitation during the storm.cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Hurricane Doreen - August 15-18, 1977 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/doreen1977.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] In October 1977, the remnants of Hurricane Heather caused 8.30 in (211 mm) of rain in Nogales.cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Hurricane Heather - October 5-8, 1977 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/heather1977.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15]1980s
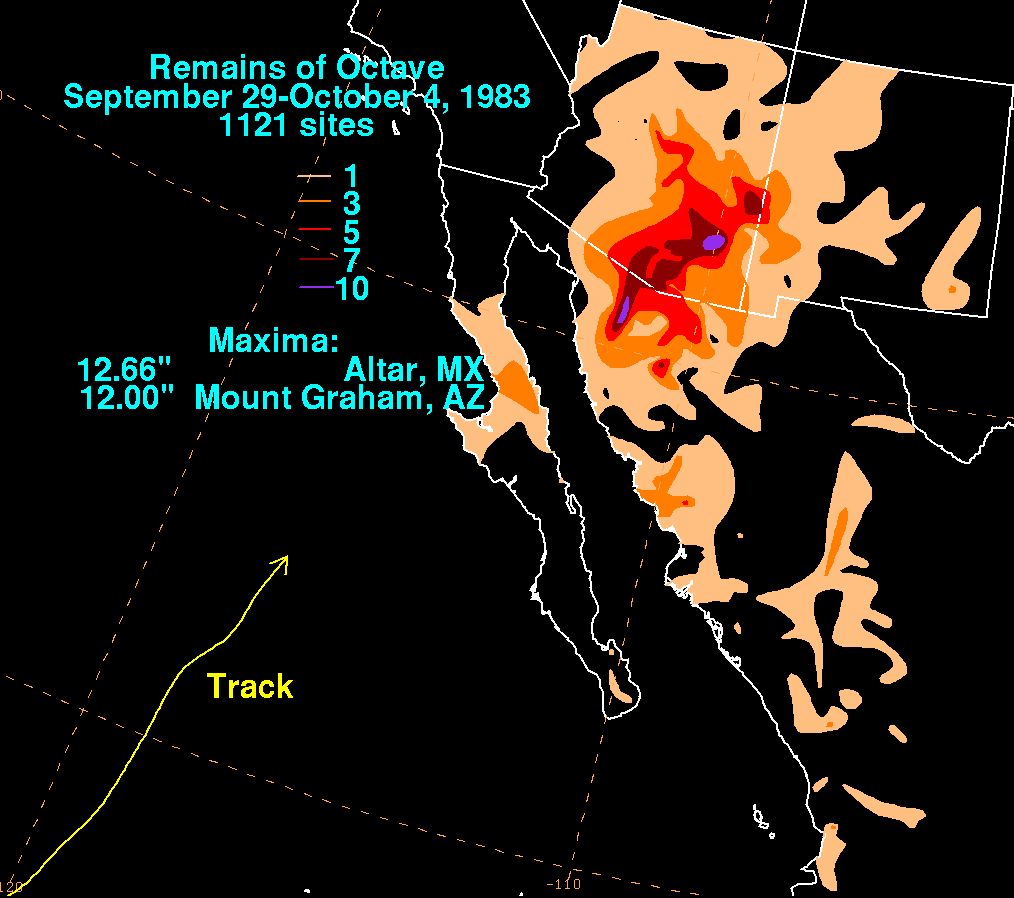
thumb|right|Rainfall_due_to_Tropical Storm Octave throughout its trackThe 1980s saw destructive tropical cyclone pass through the state, as was the case with the previous decade. A weather system, including moisture from Tropical Storm Octave, caused torrential rains over a ten-day period. The largest precipitation total occurred inMount Graham , which saw 12.00 in (305 mm) of rain overall.cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Remains of Octave - September 29-October 4, 1983 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/octave1983.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] Fourteen people drowned, 975 were injured, and roughly 10,000 people were left homeless after the flooding ended. The amount of damage from the disaster was put at 370 million (year unknown) USD. Other cities in the state also saw heavy rain, with 9.83 in (250 mm) of precipitation measured at Nogales, 6.67 in (169 mm) at Safford, 6.40 in (163 mm) at Tucson, 3.93 in (100 mm) at Flagstaff, 2.65 in (67 mm) at Phoenix, and 2.62 in (66 mm) at Prescott.In 1989,
flash flood ing produced by Hurricane Raymond caused 1.5 million (1989 USD) in damage in the state.cite web | author =National Hurricane Center | url = http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/archive/storm_wallets/epacific/ep1989-prelim/raymond/ | title = Preliminary Report: Hurricane Raymond, 25 September–5 October 1989 | publisher =National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration | date = 1989 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] Raymond passed over the state as atropical depression , and produced heavy rainfall on the southeastern portion of the state, with 4.72 in (120 mm) of rain falling in Nogales.cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Hurricane Raymond - October 4-7, 1989 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/raymond1989.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15]1990s
thumb|right|Rainfall_due_to_Hurricane Nora in theSouthwestern United States ] During the 1990s, several tropical systems have affected Arizona even after losing all tropical characteristics. The moisture from Boris in 1990 produced 3.28 in (83 mm) of rainfall on theSanta Rita Mountains .cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Hurricane Boris - June 7-11, 1990 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/boris1990.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] 1995's Ismael produced most of its damage south of the state, but light rainfall fell over Cochise County,cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Hurricane Ismael - September 12-17, 1995 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/ismael1995.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] with the highest reported rainfall being 1.44 in (37 mm).cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall for the West | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/tcwest.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] In 1998, the remnants of Hurricane Isis dropped more than two inches (50 mm) of rainfall across southernArizona , resulting in some flash flood warnings and flooding on roadways.cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Hurricane Isis - September 1-5, 1998 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/isis1998.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] cite news | author=Associated Press | date=1998-09-05 | title=Isis fizzles but makes for a wet Arizona weekend | accessdate=2007-02-08] Isis also caused up to 3 in (75 mm) across the Santa Catalina andRincon Mountains that surround Tucson. However, there was no flooding reported in the Tucson area, andTucson International Airport reported only 1.1 in (28 mm) as a result of the storm.cite web|author=Glueck|year=1998|title=September 1998 climate report for Tucson|publisher=Tucson, Arizona National Weather Service|accessdate=2007-02-08|url=http://www.wrh.noaa.gov/twc/climate/monthly/sep98.php]However, two hurricanes survived long enough to reach Arizona while still considered tropical systems. The first, Hurricane Lester, reached the state as a tropical storm, and caused over 5 in (125 mm) near Phoenix and Tucson. Much of the rest of the state reported over 1 inch (25 mm) as a result of Lester.cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Hurricane Lester - August 19-27, 1992 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/lester1992.html | publisher =
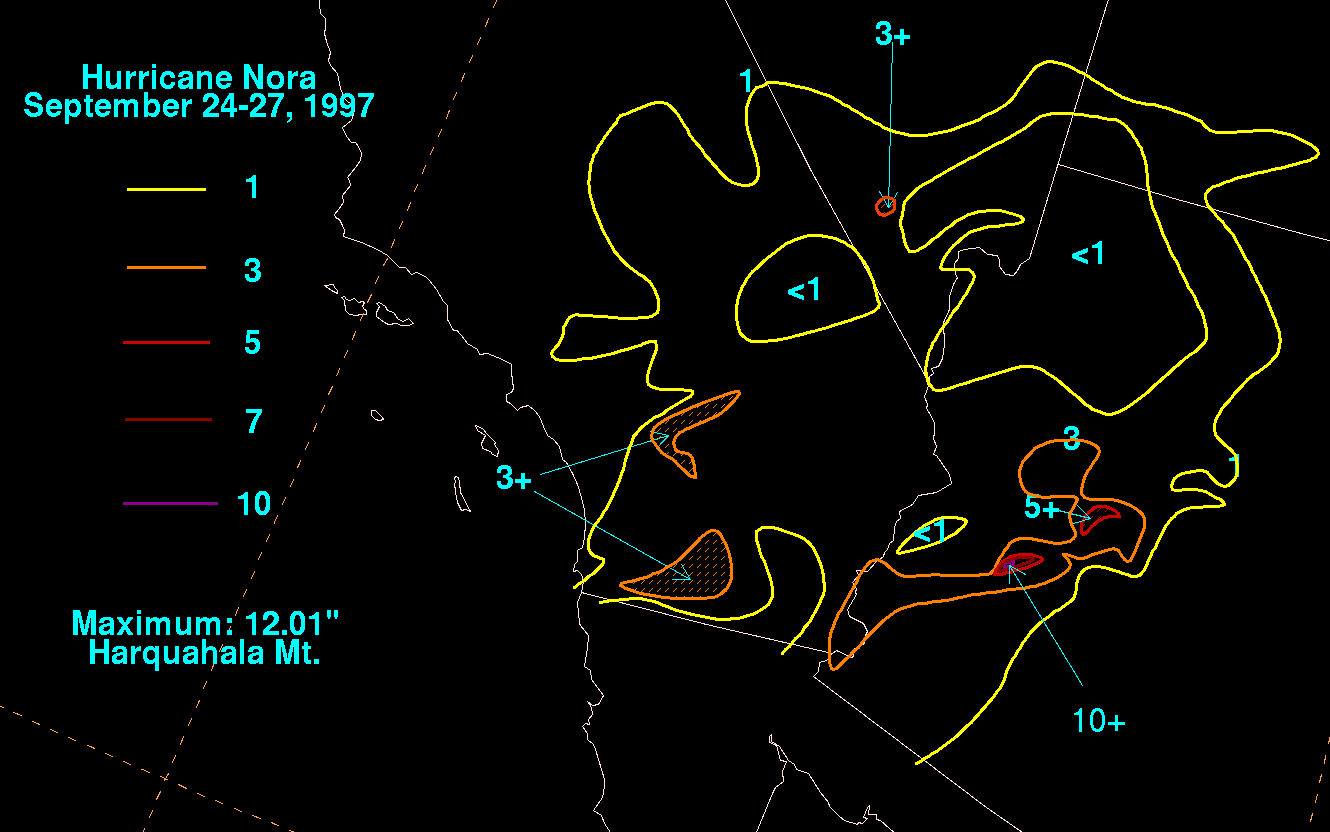
Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] The second storm, Hurricane Nora, struck the state in September 1997, and was responsible for the 24-hour rainfall record in the state. Nora produced 11.97 in (304 mm) of rainfall over theHarquahala Mountains in Western Arizona, causing some flash flooding in the area.cite web|author=Flood Control District ofMaricopa County |year=1997|title=TS Nora Storm Report|accessdate=2006-02-26|url=http://156.42.96.39/alert/nora/nora_rpt.html] Near Phoenix, rainfall from the storm caused the Narrows Dam, a smallearthen dam , to fail; localized rainfall amounts of up to 3 in (75 mm) occurred throughout the state.cite journal |author=Farfán, Luis M. and Joseph Zehnder|date = August 2001 | title=An Analysis of the Landfall of Hurricane Nora | journal =Monthly Weather Review | format=PDF | accessdate=2006-02-26 | volume = 129 | issue 8 | url=http://ams.allenpress.com/archive/1520-0493/129/8/pdf/i1520-0493-129-8-2073.pdf] Nora also caused 12,000 people to lose electric power in Yuma.cite web|author=Carter, Rebecca | year=2002 | title=Tropical Storm Impacts on Arizona and New Mexico | accessdate=2006-03-03 | publisher=Climate Assessment for the Southwest Project, Institute for the Study of Planet Earth, University of Arizona | url=http://www.ispe.arizona.edu/climas/forecasts/articles/tropical_Aug2002.pdf]2000s
The present decade has seen three tropical cyclones remnants pass over Arizona.
The first system, Hurricane Marty brought locally heavy rains to extreme southwestern Arizona in September 2003; in spite of this, there were no reports of flooding from the storm. The highest rain total was 2.83 in (72 mm) at
Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument .cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Hurricane Marty - September 21-26, 2003 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/marty2003.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] The second storm, Javier, produced heavy rain throughout the state, which helped alleviate a prolonged drought in theSouthwestern United States .cite web | url = http://usda.mannlib.cornell.edu/reports/waobr/weather/2004/summary/weth3904.txt | title = Weekly Weather and Crop Bulletin | publisher =United States Department of Agriculture | author =National Agricultural Statistics Service | date =September 21 ,2004 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] cite web | url = http://www.drought.unl.edu/dm/archive/2004/drmon0921.htm | title = U.S. Drought Monitor | author = Rippey, Brad | publisher =United States Department of Agriculture | date =September 21 ,2004 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] The heaviest rainfall occurred at Walnut Creek, which saw a total of 7.00 in (178 mm) of precipitation during the storm.cite web | author = Roth, David | title = Hurricane Javier - September 18-21, 2004 | url = http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/javier2004.html | publisher =Hydrometeorological Prediction Center | work = Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Climatology | date = 2008 | accessdate = 2008-05-15] The Tucson airport saw rainfall of 0.37 in (93 mm), while theUniversity of Arizona reported 0.89 in (26 mm) of rain.The rain and
lightning from Javier flooded several roads in the city, and forced the university to delay one of its football games.cite news | url = http://www.azstarnet.com/sn/monsoon/39628 | title = Tucson area gets welcome soaking | author = Swedlund, Eric | publisher =The Arizona Daily Star | date =September 19 ,2004 | accessdate = 2008-08-15]Thunderstorms from Tropical Storm Julio caused flooding on Interstate 17.
ee also
*
List of Pacific hurricanes
*List of Pacific hurricane seasons
*List of California hurricanes References
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.