- Diphenylalanine
-
Diphenylalanine 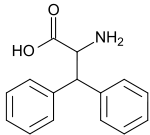 2-amino-3,3-diphenyl-propionic acid
2-amino-3,3-diphenyl-propionic acidIdentifiers CAS number 149597-92-2, (L-isomer)
149597-91-1 (D-isomer)ChemSpider 10608219 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- OC(C(N)C(C2=CC=CC=C2)C1=CC=CC=C1)=O
CC(N(c1ccccc1)c2ccccc2)C(O)=O
Properties Molecular formula C15H15NO2 Molar mass 241.11 g/mol Appearance Solid Melting point 235 °C, 508 K, 455 °F
Related compounds Related amino acids Alanine  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Diphenylalanine is an unnatural amino acid. It is similar to the two amino acids alanine and phenylalanine. It has been used for the synthesis of pseudopeptide analogues which are capable to inhibit certain enzymes.[1]
A possible synthesis starts from 3,3-diphenyl-propionic acid which is stereoselective aminated to the diphenylalanine.[2]
References
- ^ Leifeng Cheng, Christopher A. Goodwin, Michael F. Schully, Vijay V. Kakkar, and Goran Claeson (1992). "Synthesis and biological activity of ketomethylene pseudopeptide analogs as thrombin inhibitors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 35 (18): 3364–3369. doi:10.1021/jm00096a010. PMID 1527787.
- ^ Huai G. Chen, V. G. Beylin, M. Marlatt, B. Leja and O. P. Goel, (1992). "Chiral cynthesis of D- and L-3,3-diphenylalanine (DIP), unusual α-amino acids for peptides of biological interest". Tetrahedron Letters 33 (23): 3293–3296. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)92070-7.

This article about an amine is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. - OC(C(N)C(C2=CC=CC=C2)C1=CC=CC=C1)=O
