- Cuminaldehyde
-
Cuminaldehyde[1] 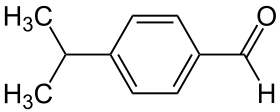 4-(1-Methylethyl)benzaldehydeOther namesCuminaldehyde
4-(1-Methylethyl)benzaldehydeOther namesCuminaldehyde
p-Isopropylbenzaldehyde
4-Isopropylbenzaldehyde
Cuminal
CumaldehydeIdentifiers CAS number 122-03-2 
ChemSpider 21106431 
UNII O0893NC35F 
KEGG C06577 
ChEMBL CHEMBL161577 
RTECS number CU7000000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(C)c1ccc(C=O)cc1
Properties Molecular formula C10H12O Molar mass 148.2 g mol−1 Appearance Colorless oil Density 0.978 g/cm3 Boiling point 235 °C, 508 K, 455 °F
Solubility in water Insoluble Hazards R-phrases R22 S-phrases S36/37 NFPA 704 Flash point 93 °C Related compounds Related compounds Benzaldehyde
Cumene
Cuminol (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cuminaldehyde, or 4-isopropylbenzaldehyde, is a natural organic compound with the molecular formula C10H12O. It is a benzaldehyde with an isopropyl group substituted in the 4-position.
Cuminaldehyde is a constituent of the essential oils of eucalyptus, myrrh, cassia, cumin and others.[1] It has a pleasant smell and contributes to the aroma of these oils. It is used commercially in perfumes and other cosmetics.
Cuminaldehyde can be prepared synthetically by the reduction of 4-isopropylbenzoyl chloride or by the formylation of cumene.
The thiosemicarbazone of cuminaldehyde has antiviral properties.
References
- ^ a b Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2623
See also
Categories:- Aldehydes
- Flavors
- Monoterpenes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

