- Peroxyacetyl nitrate
-
Peroxyacetyl nitrate 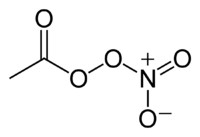
 nitroethaneperoxoateSystematic nameethanoic nitric peroxyanhydrideOther namesPAN
nitroethaneperoxoateSystematic nameethanoic nitric peroxyanhydrideOther namesPAN
peroxyacetyl nitrate
α-oxoethylperoxylnitrateIdentifiers CAS number 2278-22-0 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(OO[N+]([O-])=O)=O
- InChI=1/C2H3NO5/c1/h1H3
Properties Molecular formula C2H3NO5 Molar mass 121.05 g mol−1 Solubility in water 1.46 × 10 5 mg l−1 at 298 K log P −0.19 Vapor pressure 29.2 mmHg at 298 K kH 0.000278 m³ atm mol−1 at 298 K Atmospheric OH rate constant 10−13 cm³ molecule−1 s−1 at 298 K  nitrate (verify) (what is:
nitrate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Peroxyacetyl nitrate is a peroxyacyl nitrate. It is a secondary pollutant present in photochemical smog. It is thermally unstable and decomposes into peroxyethanoyl radical and nitrogen dioxide gas. It is a lachrymatory substance.
Peroxyacetyl nitrate, or PAN, is an oxidant more stable than ozone. Hence, it has capabilities of long-range transport greater than that of ozone. It serves as a carrier for oxides of nitrogen (NOx) into rural regions and causes ozone formation in the global troposphere.
The formation of PAN on a secondary scale becomes an issue when ethanol is used as an automotive fuel. Acetaldehyde emissions increase, which subsequently react in the atmosphere to form smog. Whereas ethanol policies solve domestic oil supply problems, they drastically exacerbate air quality conditions.[citation needed]
External links
This article about an ester is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
