- Coalition of the willing
-
For other uses, see Coalition of the willing (disambiguation).
The term coalition of the willing is a post-1990 political phrase used to collectively describe participants in military or military-humanitarian interventions for which the United Nations Security Council cannot agree to mount a full UN peacekeeping operation. It has existed in the political science/international relations literature at least since UN peacekeeping operations began to run into complications in 1993-94, and alternatives began to be considered. One early documented use of the phrase was by President Bill Clinton in June 1994 in relation to possible operations against North Korea, at the height of the 1994 stand-off with that country over nuclear weapons.[1]
It has been applied to the Australian-led INTERFET operation in East Timor, and, in its most well-known example by President George W. Bush,[1] in reference to the U.S.-led invasion of Iraq in March 2003.
Contents
Usage over Iraq
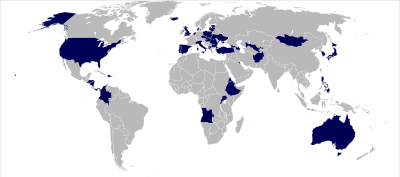
Further information: Multinational Force - IraqIn November 2002, U.S. President George W. Bush, visiting Europe for a NATO summit, declared that "should Iraqi President Saddam Hussein choose not to disarm, the United States will lead a coalition of the willing to disarm him."[2]
The Bush administration briefly used the term "Coalition of the Willing" to refer to the countries who supported, militarily or verbally, the 2003 invasion of Iraq and subsequent military presence in post-invasion Iraq. The original list released in March 2003 included 46 members.[3] In April 2003, the list was updated to include 49 countries, though it was reduced to 48 after Costa Rica objected to its inclusion. Of the 48 states on the list, three contributed troops to the invasion force (the United Kingdom, Australia and Poland). An additional 37 countries provided some number of troops to support military operations after the invasion was complete.
The list of coalition members provided by the White House included several nations that did not intend to participate in actual military operations. Some of them, such as Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Palau and Solomon Islands, do not have standing armies. However, through the Compact of Free Association, citizens of the Marshall Islands, Palau and the Federated States of Micronesia are guaranteed US national status and therefore are allowed to serve in the US military. The members of these island nations have deployed in a combined Pacific force consisting of Guamanian, Hawaiian and Samoan reserve units. They have been deployed twice to Iraq. The government of one country, the Solomon Islands, listed by the White House as a member of the coalition, was apparently unaware of any such membership and promptly denied it.[4]
In December 2008, University of Illinois Professor Scott Althaus reported that he had learned that the White House was editing and back-dating revisions to the list of countries in the coalition.[5][6] Althaus found that some versions of the list had been entirely removed from the record, and that others contradicted one another, as opposed to the procedure of archiving original documents and supplementing them with later revisions and updates.[3]
By August 2009, all non-U.S. coalition members had withdrawn from Iraq.[7] As a result, the Multinational Force - Iraq was renamed and reorganized to United States Forces - Iraq as of January 1, 2010. Thus the Coalition of the Willing came to an official end.
Criticism of use
Specific uses of the phrase in the context of disarming Iraq began appearing in mid-2001.
Iraq War critics such as John Pilger have pointed out that the vast majority of troops provided came from the U.S. and Britain and is therefore accurately described as a predominantly Anglo-American force rather than as a coalition.
Salon.com columnist Laura McClure, noting the large amounts of foreign aid being offered in exchange for supporting the Iraq War, referred to Bush's coalition as the "Coalition of the billing".[8]
In the second debate in 2004 U.S. presidential election, Democratic presidential candidate John Kerry questioned the size of the coalition participating in the initial invasion, saying, "...when we went in, there were three countries: Great Britain, Australia and the United States. That's not a grand coalition. We can do better". Bush responded by saying, "Well, actually, he forgot Poland. And now there's 30 nations involved, standing side by side with our American troops". The phrase "You forgot Poland" subsequently became a sarcastic shorthand for the perception that most members of the coalition were not contributing much to the war effort compared to the main three allies. The majority of the population in most countries involved did not, according to surveys, support the endeavour or their nation's participation.[9]
Late U.S. Senator Robert Byrd, then ranking Democrat on the Senate Appropriations Committee, referred to the coalition by the acronym COW, expressing his concern that the United States was being "milked" as a "cash cow". A Canadian Member of Parliament, Carolyn Parrish, referred to the "Coalition of the Willing" as the "Coalition of the Idiots". She was reprimanded for these comments, and was eventually removed from the Liberal Party of Canada caucus following a long-standing dispute with Prime Minister Paul Martin over policy.
References
- ^ a b Ibiblio.org (originally official White House release), Interview with the President by Sam Donaldson ABC, June 5, 1994.
- ^ "Bush: Join 'coalition of willing'". CNN. 2002-11-20. http://edition.cnn.com/2002/WORLD/europe/11/20/prague.bush.nato/. Retrieved 2010-04-30.
- ^ a b Althaus, Scott; Leetaru, Kalev (November 25, 2008). "Airbrushing History, American Style". University of Illinois Cline Center for Democracy. http://www.clinecenter.illinois.edu/research/airbrushing_history/. Retrieved 2 February 2011.
- ^ Perrott, A.: Coalition of the Willing? Not us, say Solomon islanders. The New Zealand Herald, March 27, 2003..
- ^ Kelly Gibbs (2008-12-05). "White House documents found to be altered". Daily Illini. http://media.www.dailyillini.com/media/storage/paper736/news/2008/12/05/News/White.House.Documents.Found.To.Be.Altered-3571806.shtml. Retrieved 2008-12-05. mirror
- ^ John Byrne (2008-12-05). "White House altered, deleted press releases on 'coalition of the willing'". The Raw Story. http://rawstory.com/news/2008/White_House_altered_documents_on_coalition_1205.html. Retrieved 2008-12-05.[dead link] mirror
- ^ 9010 DoD report, June 2009
- ^ "Coalition of the billing -- or unwilling?". Salon.com. 2003-12-03. http://dir.salon.com/story/news/feature/2003/03/12/foreign_aid/.
- ^ Iraq Poll 2003 Gallup International Association
External links
- Bush: Join 'Coalition of Willing (CNN)
- A Coalition of the "Willing"? Misnomer, February 11, 2003, summary of public opinion on the invasion of Iraq.
Categories:- Iraq–United States relations
- Multinational force involved in the Iraq War
- Political slogans
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.