- Naphthol Red
-
Not to be confused with 2-naphthol red.
Naphthol Red 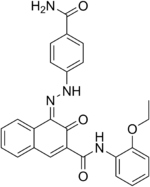 4-(2-(4-carbamoylphenyl)hydrazono)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-oxo-3,4-dihydronaphthalene-2-carboxamideOther namesC.I. 12475; C.I. Pigment Red 170
4-(2-(4-carbamoylphenyl)hydrazono)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-oxo-3,4-dihydronaphthalene-2-carboxamideOther namesC.I. 12475; C.I. Pigment Red 170Identifiers CAS number 2786-76-7 PubChem 5359812 ChemSpider 4514376 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C1C(C(NC2=CC=CC=C2OCC)=O)=CC3=CC=CC=C3/C1=N/NC4=CC=C(C(N)=O)C=C4
Properties Molecular formula C26H22N4O4 Molar mass 454.48 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Naphthol Red (Pigment red 170 or PR170) is an organic pigment extensively used in automotive coatings and painting.
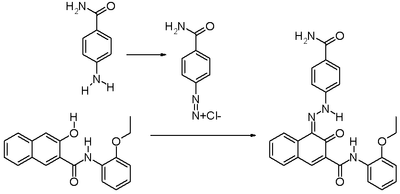
It is produced synthetically by converting p-aminobenzamide into the corresponding diazonium compound followed by diazotation with 3-hydroxy-2-naphththoic acid (2-ethoxy)anilide.
In the solid state the hydrazo tautomer forms and several crystal structures exist. In the initial α polymorph the molecules are arranged in a herringbone pattern with extensive hydrogen bonding. The φ polymorph is more dense and more stable and produced industrially by thermal treatment in water at 130°C under pressure. In this phase the molecules are planar and arranged in layers. Extensive hydrogen bonding exists within the layer but between layers the only interactions are Van der Waals forces. Dense crystal structures are preferred for pigments used in coatings because in the event of Photochemical decomposition the fragments are locked in place and are able to recombine. Research shows that by replacing the ethoxy group in this compound by a methoxy group the crystal structure is less stable and in the final application and the color fades more easily. By careful selection of substituents it is possible to optimize crystal structure and improve optical properties [1].
References
Categories:- Pigments
- Organic pigments
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.